Tick-borne diseases, which afflict humans and other animals, are caused by infectious agents transmitted by tick bites. They are caused by infection with a variety of pathogens, including rickettsia and other types of bacteria, viruses, and protozoa. The economic impact of tick-borne diseases is considered to be substantial in humans, and tick-borne diseases are estimated to affect ~80 % of cattle worldwide.

Dermacentor variabilis, also known as the American dog tick or wood tick, is a species of tick that is known to carry bacteria responsible for several diseases in humans, including Rocky Mountain spotted fever and tularemia. It is one of the best-known hard ticks. Diseases are spread when it sucks blood from the host. It may take several days for the host to experience symptoms.

Pseudophilautus variabilis, also known as the variable bush frog or variable bubble-nest frog, is a species of frog in the family Rhacophoridae. This now extinct species was endemic to Sri Lanka. Despite extensive searches in recent times, it is only known from collections prior to 1858. The reasons for its disappearance are unknown but probably involve habitat loss.

Ghatixalus variabilis is a species of frog in the family Rhacophoridae. It is endemic to the Western Ghats of southern India. It has a number of common names, including green tree frog, though it is terrestrial rather than arboreal in its life style.

Stegastes variabilis is a damselfish in the family Pomacentridae, found on coral and rocky reefs in the Caribbean Sea and neighboring areas of the Atlantic Ocean and Gulf of Mexico. They are often solitary fish.
Notodytes is a genus of parasitic flies in the family Tachinidae. There are at least three described species in Notodytes.

Dermacentor is a genus of ticks in the family Ixodidae, the hard ticks. The genus has a cosmopolitan distribution, with native species on all continents except Australia. Most occur in the Nearctic realm.
Tillandsia variabilis, the leatherleaf airplant, is a species of bromeliad in the genus Tillandsia. This species is native to Bolivia, Costa Rica, Mexico, Venezuela, Colombia, the West Indies and southern Florida.

Tricolia is a genus of sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the family Phasianellidae.
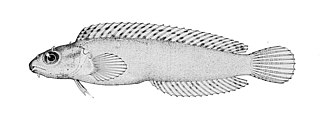
Petroscirtes variabilis, the variable sabretooth blenny, variable fangblenny, or the variable blenny, is a species of combtooth blenny found in the western Pacific and Indian ocean. This species reaches a length of 15 centimetres (5.9 in) TL.

Zimmermann's poison frog, also referred to as the variable poison frog, is a small species of poison dart frog known from the upper Huallaga River drainage of San Martín Region, Peru. It also occurs in western Brazil (Amazonas), Colombia, Ecuador. It is semi-arboreal, living in the forest understory and canopy. Like other poison frogs, it contains alkaloid poisons. The mimic poison frog is a Müllerian mimic of this species.

Carl Benjamin Klunzinger was a German physician and zoologist.

Apophysomyces variabilis is an emerging fungal pathogen that can cause serious and sometimes fatal infection in humans. This fungus is a soil-dwelling saprobe with tropical to subtropical distribution. It is a zygomycete that causes mucormycosis, an infection in humans brought about by fungi in the order Mucorales. Infectious cases have been reported globally in locations including the Americas, Southeast Asia, India, and Australia. Apophysomyces variabilis infections are not transmissible from person to person.
Cladiella krempfi is a species of soft coral in the family Alcyoniidae. It is found in the western Indo-Pacific and was first described by the British zoologist Sydney John Hickson in 1919.

Cladiella is a genus of soft corals native to the Indo-Pacific region. These corals are commonly known as colt corals or finger leather corals and are often kept in reef aquaria. They grow fast, have short rounded or conical lobes and are sticky to the touch owing to the production of much mucus. They are creamy or pale grey in colour. The polyps are fully retractable and give the colony a fluffy look when extended. They may be a contrasting green or brown hue.

Cladiella australis is a species of soft coral in the family Alcyoniidae. It is found in the western Indo-Pacific. It is commonly known as the finger blanching soft coral because with the polyps extended it appears brown but when poked with a finger, the polyps retract into the leathery base tissue and the coral appears white.

Solenosmilia variabilis is a species of colonial coral in the family Caryophylliidae. It is a deep water, azooxanthellate coral with a semi-cosmopolitan distribution.
Cladiella elegantissima is a species of soft corals in the genus Cladiella from New Caledonia.

Canis mosbachensis, sometimes known as the Mosbach wolf, is an extinct small wolf that once inhabited Eurasia from the Middle Pleistocene era to the Late Pleistocene. It is widely accepted as the ancestor of Canis lupus, the grey wolf.

Sebastes ciliatus, the dusky rockfish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the subfamily Sebastinae, the rockfishes, part of the family Scorpaenidae. It is typically found in the North Pacific Ocean, specifically in the Bering Sea near British Columbia, in the Gulf of Alaska, and in the depths of the Aleutian Islands.
















