Cladistics is an approach to biological classification in which organisms are categorized in groups ("clades") based on hypotheses of most recent common ancestry. The evidence for hypothesized relationships is typically shared derived characteristics (synapomorphies) that are not present in more distant groups and ancestors. However, from an empirical perspective, common ancestors are inferences based on a cladistic hypothesis of relationships of taxa whose character states can be observed. Theoretically, a last common ancestor and all its descendants constitute a (minimal) clade. Importantly, all descendants stay in their overarching ancestral clade. For example, if the terms worms or fishes were used within a strict cladistic framework, these terms would include humans. Many of these terms are normally used paraphyletically, outside of cladistics, e.g. as a 'grade', which are fruitless to precisely delineate, especially when including extinct species. Radiation results in the generation of new subclades by bifurcation, but in practice sexual hybridization may blur very closely related groupings.
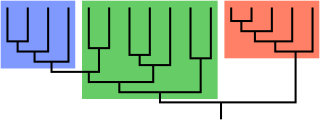
In biological phylogenetics, a clade, also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a grouping of organisms that are monophyletic – that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. In the taxonomical literature, sometimes the Latin form cladus is used rather than the English form. Clades are the fundamental unit of cladistics, a modern approach to taxonomy adopted by most biological fields.

Systematics is the study of the diversification of living forms, both past and present, and the relationships among living things through time. Relationships are visualized as evolutionary trees. Phylogenies have two components: branching order and branch length. Phylogenetic trees of species and higher taxa are used to study the evolution of traits and the distribution of organisms (biogeography). Systematics, in other words, is used to understand the evolutionary history of life on Earth.

Emil Hans Willi Hennig was a German biologist and zoologist who is considered the founder of phylogenetic systematics, otherwise known as cladistics. In 1945 as a prisoner of war, Hennig began work on his theory of cladistics, which he published in German in 1950, with a substantially revised English translation published in 1966. With his works on evolution and systematics he revolutionised the view of the natural order of beings. As a taxonomist, he specialised in dipterans.
Evolutionary taxonomy, evolutionary systematics or Darwinian classification is a branch of biological classification that seeks to classify organisms using a combination of phylogenetic relationship, progenitor-descendant relationship, and degree of evolutionary change. This type of taxonomy may consider whole taxa rather than single species, so that groups of species can be inferred as giving rise to new groups. The concept found its most well-known form in the modern evolutionary synthesis of the early 1940s.
Proceedings of the Royal Society is the main research journal of the Royal Society. The journal began in 1831 and was split into two series in 1905:
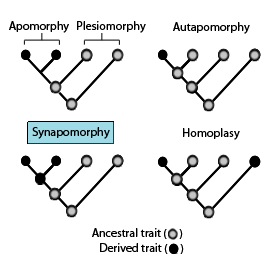
In phylogenetics, an apomorphy is a novel character or character state that has evolved from its ancestral form. A synapomorphy is an apomorphy shared by two or more taxa and is therefore hypothesized to have evolved in their most recent common ancestor. In cladistics, synapomorphy implies homology.
Phylogenetic nomenclature is a method of nomenclature for taxa in biology that uses phylogenetic definitions for taxon names as explained below. This contrasts with the traditional method, by which taxon names are defined by a type, which can be a specimen or a taxon of lower rank, and a description in words. Phylogenetic nomenclature is regulated currently by the International Code of Phylogenetic Nomenclature (PhyloCode).

Conservation Biology is a bimonthly peer-reviewed scientific journal of the Society for Conservation Biology, published by Wiley-Blackwell and established in May 1987. It covers the science and practice of conserving Earth's biological diversity, including issues concerning any of the Earth's ecosystems or regions. The editor-in-chief is Mark Burgman.

Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Computational Molecular Science is a bimonthly peer-reviewed scientific journal, published since 2011 by John Wiley & Sons. It provides a forum for review-type articles that are broadly accessible to a diverse audience of scientists and engineers. The current Editor-in-Chief is Peter R. Schreiner (Justus-Liebig-University).

Propellants, Explosives, Pyrotechnics is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering all aspects of research on explosives. It was established in 1976 by Hiltmar Schubert and was intended as a successor to Explosivstoffe, a journal which had appeared between 1953 and 1975 but which had been published exclusively in German. It has been the official journal of the International Pyrotechnics Society since 1982 and is published by Wiley-VCH. The types of papers published by the journal are full papers, communications, and reviews, and a section containing news, obituaries, book reviews, and conference reports. The editors-in-chief are Randall L. Simpson, Wilhelm Eckl, and Richard Gee.
The Journal of Microscopy is the monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal of the Royal Microscopical Society which covers all aspects of microscopy including spatially resolved spectroscopy, compositional mapping, and image analysis. This includes technology and applications in physics, chemistry, material science, and the life sciences. It is published by Wiley-Blackwell on behalf of the Society. The editor-in-chief is Michelle Peckham, a Cell Biology professor at University of Leeds.
The journal publishes review articles, original research papers, short communications, and letters to the editor. It was established in 1841 as the Transactions of the Microscopical Society of London, obtaining its current name in 1869, with volume numbering restarting at 1.

The American Journal of Primatology is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal and the official journal of the American Society of Primatologists. It was established in 1981 and covers all areas of primatology, including the behavioral ecology, conservation biology, evolutionary biology, life history, demography, paleontology, physiology, endocrinology, genetics, molecular genetics, and psychobiology of non-human primates. Besides its regular issues, the journal publishes a yearly supplementary issue detailing the program of the society's annual meetings. The editor-in-chief is Karen Bales. The types of papers published are: original research papers, review articles, book reviews, commentaries, and plenary addresses.

Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica is a peer-reviewed, open access, medical journal covering gynecology, female urology, gynecologic oncology and fertility. The journal is published by Wiley-Blackwell, for the Nordic Federation of Societies of Obstetrics and Gynecology. The editor in chief is Ganesh Acharya. Articles are published fully open access since 30 July 2021.

The Journal of Zoological Systematics and Evolutionary Research is a peer-reviewed scientific journal published by Wiley-VCH in collaboration with Hindawi. It covers the systematic study of animal sciences, connected with evolutionary research. The journal was established in 1963 as the Zeitschrift für zoologische Systematik und Evolutionsforschung and published by Akademische Verlagsgesellschaft. It obtained its current title in 1994 when it was moved to Wiley-VCH.

The Journal of Traumatic Stress (JTS) is a peer-reviewed academic journal published bimonthly by Wiley-Blackwell on behalf of the International Society for Traumatic Stress Studies.
The Willi Hennig Society "was founded in 1980 with the expressed purpose of promoting the field of phylogenetic systematics." The society is represented by phylogenetic systematists managing and publishing in the peer-reviewed journal titled Cladistics. The society is named after Willi Hennig, a German systematic entomologist who developed the modern methods and philosophical approach to systematics in the 1940s and 1950s. The society is also involved in reconstructing the tree of life. The current president, Prof. Dr. Stefan Richter of Universitat Rostock, was elected in 2022, succeeding Prof. Dr. Christiane Weirauch.
Arnold G. Kluge is professor emeritus of zoology and curator emeritus of amphibians and reptiles at the University of Michigan, Museum of Zoology.
Edward Orlando Wiley III is the curator emeritus of ichthyology at the University of Kansas Biodiversity Institute and professor of systematics and evolution for the Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology at the University of Kansas. His master's adviser was Darrell Hall, of Sam Houston State University (retired), and his doctoral advisor was Donn E. Rosen, of the American Museum of Natural History (deceased). Wiley has published extensively in topics related to phylogenetic systematics, is a Past President of the Society of Systematic Biology and was involved in the founding of the Willi Hennig Society. Wiley is known for building on and establishing conceptual advances in the evolutionary species concept, first formulated by George Gaylord Simpson. Wiley defines an evolutionary species as:
Transformed cladistics, also known as pattern cladistics is an epistemological approach to the cladistic method of phylogenetic inference and classification that makes no a priori assumptions about common ancestry. It was advocated by Norman Platnick, Colin Patterson, Ronald Brady and others in the 1980s, but has few modern proponents. The book, Foundations of Systematics and Biogeography by David Williams and Malte Ebach provides a thoughtful history of the origins of this point of view.











