Oaxaca, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Oaxaca, is one of the 32 states that compose the Federative Entities of Mexico. It is divided into 570 municipalities, of which 418 are governed by the system of usos y costumbres with recognized local forms of self-governance. Its capital city is Oaxaca de Juárez.

The Mixtecs, or Mixtecos, are indigenous Mesoamerican peoples of Mexico inhabiting the region known as La Mixteca of Oaxaca and Puebla as well as La Montaña Region and Costa Chica Regions of the state of Guerrero. The Mixtec Culture was the main Mixtec civilization, which lasted from around 1500 BC until being conquered by the Spanish in 1523.

The Oto-Manguean or Otomanguean languages are a large family comprising several subfamilies of indigenous languages of the Americas. All of the Oto-Manguean languages that are now spoken are indigenous to Mexico, but the Manguean branch of the family, which is now extinct, was spoken as far south as Nicaragua and Costa Rica. Oto-Manguean is widely viewed as a proven language family. However, this status has been recently challenged.

The Mixtec languages belong to the Mixtecan group of the Oto-Manguean language family. Mixtec is spoken in Mexico and is closely related to Trique and Cuicatec. The varieties of Mixtec are spoken by over half a million people. Identifying how many Mixtec languages there are in this complex dialect continuum poses challenges at the level of linguistic theory. Depending on the criteria for distinguishing dialects from languages, there may be as few as a dozen or as many as fifty-three Mixtec languages.
Chatino is a group of indigenous Mesoamerican languages. These languages are a branch of the Zapotecan family within the Oto-Manguean language family. They are natively spoken by 45,000 Chatino people, whose communities are located in the southern portion of the Mexican state of Oaxaca.

Tlaxiaco is a city, and its surrounding municipality of the same name, in the Mexican state of Oaxaca. It is located in the Tlaxiaco District in the south of the Mixteca Region, with a population of about 17,450.

Pinotepa Nacional is a city and seat of the municipality of the same name, in the Mexican state of Oaxaca. It is located in the Jamiltepec District in the west of the Costa Region. The name Pinotepa means "toward the crumbling hill" in Náhuatl.
San Juan Achiutla is a town and municipality in Oaxaca in south-western Mexico. The municipality covers an area of 49.76 km2. It is located in a mountain range, between the hills Negro to the East, Yucuquise to the Northwest, Cuate to the North and Totolote to the South. It is crossed by the river Los Sabinos and has a dam called Cahuayande. Its weather is temperate. It is in the Mixteca Alta, one of the three parties that make up the Mixteca region and in the Mixteca Alta is part of what was Achiutla, the significant Prehispanic place.

The Costa Region or Costa Chica lies on the Pacific coast of the state of Oaxaca, Mexico, south of the more mountainous Sierra Sur inland from the coast. It includes the districts of Jamiltepec, Juquila and Pochutla.

Nochixtlán District is located in the southeast of the Mixteca Region of the State of Oaxaca, Mexico. The main city is Asunción Nochixtlán.

The Indigenous people of Oaxaca are descendants of the inhabitants of what is now the state of Oaxaca, Mexico who were present before the Spanish invasion. Several cultures flourished in the ancient region of Oaxaca from as far back as 2000 BC, of whom the Zapotecs and Mixtecs were perhaps the most advanced, with complex social organization and sophisticated arts.
Mixteca Alta Formative Project (2003–present) is an archaeological project directed by Andrew Balkansky that focuses on the Mixtec of Oaxaca, Mexico. The project, which is funded by the National Science Foundation, the National Geographic Society, and the H. John Heinz III Fund, seeks to understand Mixtec origins and their transition to urbanism. Excavations are currently taking place at the ancient site of Tayata.

Huamelulpan is an archaeological site of the Mixtec culture, located in the town of San Martín Huamelulpan at an elevation of 2,218 metres (7,277 ft), about 96 kilometres (60 mi) north-west of the city of Oaxaca, the capital of Oaxaca state.

The Amuzgos are an indigenous people of Mexico. They primarily live in a region along the Guerrero/Oaxaca border, chiefly in and around four municipalities: Xochistlahuaca, Tlacoachistlahuaca and Ometepec in Guerrero, and San Pedro Amuzgos in Oaxaca. Their languages are similar to those of the Mixtec, and their territories overlap. They once dominated a larger area, from La Montaña down to the Costa Chica of Guerrero and Oaxaca, but Mixtec expansion, rule and later Spanish colonization has pushed them into the more inaccessible mountain regions and away from the coast. The Amuzgos maintain much of their language and dress and are known for their textiles, handwoven on backstrap looms with very intricate two-dimensional designs. The Amuzgo area is very poor with an economy mostly dependent on subsistence agriculture and handcraft production.
Silacayoapan is one of the more extensive Mixtec languages. It is spoken by 150,000 people in Puebla and across the border in Guerrero, as well as by emigrants to the United States.
Atatláhuca–San Miguel Mixtec is a diverse Mixtec language of Oaxaca.
Mixtepec Mixtec is a Mixtec language that is spoken in the lower Mixteca region. Mixtec language is largely spoken in the area of San Juan Mixtepec, district of Juxtlahuaca, state of Oaxaca. However, the language is also spoken in other areas including Tlaxiaco, San Quintín Baja California, Santa María California, and Oregon. In 2004, it was reported that approximately 12,000 people spoke the Mixtepec Mixtec language. While most speakers of the language refer to it as 'sa'an ntavi' meaning 'language of the poor' or 'poor people's language,' others refer to it as 'sa'an save' which means 'rain language.' It is not closely related to other varieties of Mixtec.
Santiago, Oaxaca may refer to:

Regional communications in ancient Mesoamerica are believed to have been extensive. There were various trade routes attested since prehistoric times. In this article, especially the routes starting in the Mexico Central Plateau, and going down to the Pacific coast will be considered. These contacts then went on as far as Central America.
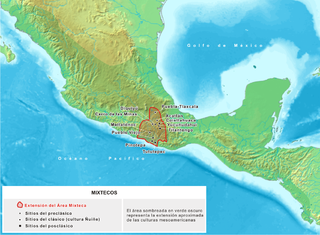
The Mixtec culture was a pre-hispanic archaeological culture, corresponding to the ancestors of the Mixtec people; they called themselves ñuu Savi, which means "people or nation of the rain". It had its first manifestations in the Mesoamerican Middle Preclassic period and ended with the Spanish conquest in the first decades of the 16th century. The historical territory of this people is the area known as La Mixteca, a mountainous region located between the current Mexican states of Puebla, Oaxaca, and Guerrero.














