Related Research Articles
Lumen can refer to:
The Pentium Pro is a sixth-generation x86 microprocessor developed and manufactured by Intel and introduced on November 1, 1995. It introduced the P6 microarchitecture and was originally intended to replace the original Pentium in a full range of applications. While the Pentium and Pentium MMX had 3.1 and 4.5 million transistors, respectively, the Pentium Pro contained 5.5 million transistors. Later, it was reduced to a more narrow role as a server and high-end desktop processor and was used in supercomputers like ASCI Red, the first computer to reach the teraFLOPS performance mark. The Pentium Pro was capable of both dual- and quad-processor configurations. It only came in one form factor, the relatively large rectangular Socket 8. The Pentium Pro was succeeded by the Pentium II Xeon in 1998.

The red-breasted swallow , also known as the rufous-chested swallow, is a member of the family Hirundinidae, found in Sub-Saharan Africa. It is confined to the tropical rainforest during the wet season.

Dentin or dentine is a calcified tissue of the body and, along with enamel, cementum, and pulp, is one of the four major components of teeth. It is usually covered by enamel on the crown and cementum on the root and surrounds the entire pulp. By volume, 45% of dentin consists of the mineral hydroxyapatite, 33% is organic material, and 22% is water. Yellow in appearance, it greatly affects the color of a tooth due to the translucency of enamel. Dentin, which is less mineralized and less brittle than enamel, is necessary for the support of enamel. Dentin rates approximately 3 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness. There are two main characteristics which distinguish dentin from enamel: firstly, dentin forms throughout life; secondly, dentin is sensitive.
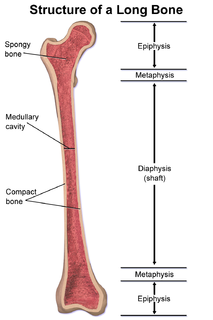
The diaphysis is the main or midsection (shaft) of a long bone. It is made up of cortical bone and usually contains bone marrow and adipose tissue (fat).

A gyrotron is a class of high-power linear-beam vacuum tubes which generates millimeter-wave electromagnetic waves by the cyclotron resonance of electrons in a strong magnetic field. Output frequencies range from about 20 to 527 GHz, covering wavelengths from microwave to the edge of the terahertz gap. Typical output powers range from tens of kilowatts to 1–2 megawatts. Gyrotrons can be designed for pulsed or continuous operation. The gyrotron was invented by soviet scientists at NIRFI, based in Nizhny Novgorod, Russia.

The mantle is a significant part of the anatomy of molluscs: it is the dorsal body wall which covers the visceral mass and usually protrudes in the form of flaps well beyond the visceral mass itself.

Tsintaosaurus is a genus of hadrosaurid dinosaur from China. It was about 8.3 metres (27 ft) long and weighed 2.5 tonnes. The type species is Tsintaosaurus spinorhinus, first described by Chinese paleontologist C. C. Young in 1958.

The tube-eye or thread-tail, Stylephorus chordatus, is a deep-sea fish, the only fish in the genus Stylephorus and family Stylephoridae.

Lateral plate mesoderm is a type of mesoderm that is found at the periphery of the embryo.

Octocorallia is a subclass of Anthozoa comprising around 3,000 species of water-based organisms formed of colonial polyps with 8-fold symmetry. It includes the blue coral, soft corals, sea pens, and gorgonians within three orders: Alcyonacea, Helioporacea, and Pennatulacea. These organisms have an internal skeleton secreted by mesoglea and polyps with eight tentacles and eight mesentaries. As with all Cnidarians these organisms have a complex life cycle including a motile phase when they are considered plankton and later characteristic sessile phase.

"Far Above the Clouds" is a single by musician Mike Oldfield, released on 12 April 1999. The single is the final track from the album Tubular Bells III. "Far Above the Clouds" similarly features tubular bells in fashion with the part-one-finales of Oldfield's previous works, Tubular Bells and Tubular Bells II. The sound of the bells has a slightly more dramatic tone than in its previous appearances, and it is a combination of actual tubular bells and sampled sounds from various keyboards, most prominently a Korg M1.

The siphonal canal is an anatomical feature of the shells of certain groups of sea snails within the clade Neogastropoda. Some sea marine gastropods have a soft tubular anterior extension of the mantle called a siphon through which water is drawn into the mantle cavity and over the gill and which serves as a chemoreceptor to locate food. In certain groups of carnivorous snails, where the siphon is particularly long, the structure of the shell has been modified in order to house and protect the soft structure of the siphon. Thus the siphonal canal is a semi-tubular extension of the aperture of the shell through which the siphon is extended when the animal is active.

A siphonal notch is a feature of the shell anatomy in some sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks.
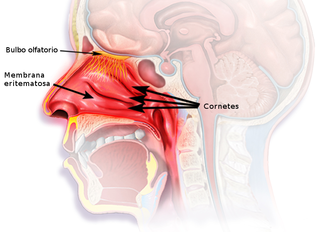
The nasal mucosa lines the nasal cavity. It is part of the respiratory mucosa, the mucous membrane lining the respiratory tract. The nasal mucosa is intimately adherent to the periosteum or perichondrium of the nasal conchae. It is continuous with the skin through the nostrils, and with the mucous membrane of the nasal part of the pharynx through the choanae. From the nasal cavity its continuity with the conjunctiva may be traced, through the nasolacrimal and lacrimal ducts; and with the frontal, ethmoidal, sphenoidal, and maxillary sinuses, through the several openings in the nasal meatuses. The mucous membrane is thickest, and most vascular, over the nasal conchae. It is also thick over the nasal septum where increased numbers of goblet cells produce a greater amount of nasal mucus. It is very thin in the meatuses on the floor of the nasal cavities, and in the various sinuses. It is one of the most commonly infected tissues in adults and children. Inflammation of this tissue may cause significant impairment of daily activities, with symptoms such as stuffy nose, headache, mouth breathing, etc.
Well studied Periodontal pathogens are bacteria that have been shown to significantly contribute to periodontitis.
The Archigregarinorida are an order of parasitic alveolates in the phylum Apicomplexa. Species in this order infect marine invertebrates — usually annelids, ascidians, hemichordates and sipunculids.
The Textulariacea is a superfamily of Middle Jurassic to Holocene agglutinated benthic textulariid Foraminifera. Tests are trochospiral, triserial, or biserial in early stages; later may be biserial or uniserial. Walls are agglutinated, made of gathered material cemented together and are canaliculate - contain micro-tubular cavities extending between the inner and outer surfaces.
The Pseudogaudryinidae is a family of Late Cretaceous to recent benthic aggultinated Foraminifera included in the Textulariida. Tests are elongate with an early triserial stage, later reduced to biserial or uniserial. Walls are of agglutinated material and are canaliculate, that is have micro-tubular cavities. Apertures, an interiomarginal arch. The Pseudogaudryinidae differs from the Verneuilinidae in the canaliculate wall and from the Valvulinidae in having a simple aperture with-out a tooth.

Clavulinopsis fusiformis, commonly known as golden spindles, spindle-shaped yellow coral, or spindle-shaped fairy club, is a species of coral fungus in the family Clavariaceae.