In physical geography, a fjord is a long, narrow sea inlet with steep sides or cliffs, created by a glacier. Fjords exist on the coasts of Antarctica, the Arctic, and surrounding landmasses of the northern and southern hemispheres. Norway's coastline is estimated to be 29,000 km (18,000 mi) long with its nearly 1,200 fjords, but only 2,500 km (1,600 mi) long excluding the fjords.

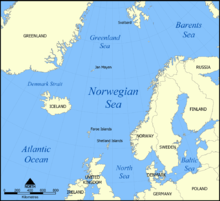
Norway is a country located in Northern Europe in the northern and western parts of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The majority of the country borders water, including the Skagerrak inlet to the south, the North Sea to the southwest, the North Atlantic Ocean to the west, and the Barents Sea to the north. It has a land border with Sweden to the east; to the northeast it has a shorter border with Finland and an even shorter border with Russia.

Nordland is one of the three northernmost counties in Norway in the Northern Norway region, bordering Troms in the north, Trøndelag in the south, Norrbotten County in Sweden to the east, Västerbotten County to the south-east, and the Atlantic Ocean to the west. The county was formerly known as Nordlandene amt. The county administration is in the town of Bodø. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen has been administered from Nordland since 1995. In the southern part of the county is Vega, listed on the UNESCO World Heritage Site list.

Troms is a county in northern Norway. It borders Finnmark county to the northeast and Nordland county in the southwest. Norrbotten Län in Sweden is located to the south and further southeast is a shorter border with Lapland Province in Finland. To the west is the Norwegian Sea. The county had a population of 169,610 in 2024.

Jæren is a traditional district in Rogaland county, Norway. The other districts in Rogaland are Dalane, Ryfylke, and Haugalandet. Jæren is one of the 15 districts that comprise Western Norway.
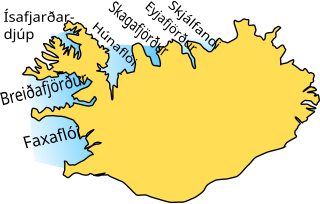
Breiðafjörður is a large shallow bay, about 50 km (31 mi) wide and 125 km (78 mi) long, to the west of Iceland. It separates the region of the Westfjords (Vestfirðir) from the Snæfellsnes peninsula to the south. Breiðafjörður is encircled by mountains, including Kirkjufell and the glacier Snæfellsjökull on the Snæfellsnes peninsula, and the Látrabjarg bird cliffs at the tip of the Westfjords. Numerous smaller fjords extend inland from Breiðafjörður, the largest being Hvammsfjörður at its southeastern corner. An interesting feature of the bay is that the land to the north was formed about 15 million years ago, whereas the land to the south was formed less than half that time ago.. Breiðafjörður therefore was formed by tectonic movements and all the islands and skerries were made by volcanic eruptions to form ridges and craters that mostly line up in a east-west position.

A skerry is a small rocky island, or islet, usually too small for human habitation. It may simply be a rocky reef. A skerry can also be called a low sea stack.
The extreme points of Norway include the coordinates that are farther north, south, east or west than any other location in Norway; and the highest and the lowest altitudes in the country. The northernmost point is Rossøya on Svalbard, the southernmost is Pysen in Lindesnes Municipality, the easternmost is Kræmerpynten on Svalbard, and the westernmost is Hoybergodden on Jan Mayen. The highest peak is Galdhøpiggen, standing at 2,469 m (8,100 ft) above mean sea level, while the lowest elevation is sea level at the coast.

The Hardangerfjord is the fifth longest fjord in the world, and the second longest fjord in Norway. It is located in Vestland county in the Hardanger region. The fjord stretches 179 kilometres (111 mi) from the Atlantic Ocean into the mountainous interior of Norway along the Hardangervidda plateau. The innermost point of the fjord reaches the town of Odda.

The Sognefjord or Sognefjorden, nicknamed the King of the Fjords, is the largest and deepest fjord in Norway. Located in Vestland county in Western Norway, it stretches 205 kilometres (127 mi) inland from the ocean to the small village of Skjolden in the municipality of Luster.

Nordfjord is a traditional district of Norway.

The Varangerfjord is the easternmost fjord in Norway, north of Finland. The fjord is located in Finnmark county between the Varanger Peninsula and the mainland of Norway. The fjord flows through the municipalities of Vardø, Vadsø, Nesseby, and Sør-Varanger. The fjord is approximately 100 kilometres (62 mi) long, emptying into the Barents Sea. In a strict sense, it is a false fjord, since it does not have the hallmarks of a fjord carved by glaciers.

Boknafjord or Boknafjorden is a fjord located in Rogaland county, Norway. The huge fjord lies between the cities of Stavanger and Haugesund and dominates the central part of the county. The main part of the fjord is shared between the municipalities of Kvitsøy, Stavanger, Tysvær, Bokn, and Karmøy. There are dozens of smaller fjords that branch off the main part of the fjord, reaching most municipalities in the county. At its longest, the Boknafjord reaches about 96 kilometres (60 mi) into the mainland at the innermost point of the Hylsfjorden. Other notable branches include the Saudafjorden, Sandsfjorden, Vindafjorden, Hervikfjorden, Førresfjorden, Erfjorden, Jøsenfjorden, Årdalsfjorden, Idsefjorden, Høgsfjorden, Lysefjorden, and Gandsfjorden.

The Porsangerfjorden is a fjord in Finnmark county, Norway.

Appat Island is an uninhabited island in the Avannaata municipality in northwestern Greenland. At 211 km2 (81.5 sq mi), it is one of the larger islands in the Uummannaq Fjord system, located in its north-central part. It is the site of the former settlements of Ritenbenck and Qaqortuatsiaq.
Sugar Loaf Bay is a bay in the Upernavik Archipelago in the Avannaata municipality in northwestern Greenland. It is an indentation of northeastern Baffin Bay. The name of the bay derives from the name of an island of the same name in the bay, Sugar Loaf Island.

Bjørnafjorden is a fjord in Vestland county, Norway. It runs through the municipalities of Austevoll, Bjørnafjorden, and Tysnes. The large island of Tysnesøya lie along the south side of the Bjørnafjorden and the Bergen Peninsula and the mainland lie along the north and east sides of the fjord. The Fusafjorden split off from the main fjord on the north side by the village of Osøyro. The 30-kilometre (19 mi) fjord is about 10 kilometres (6.2 mi) wide and its maximum depth is 583 metres (1,913 ft) below sea level.

Strandflat is a landform typical of the Norwegian coast consisting of a flattish erosion surface on the coast and near-coast seabed. In Norway, strandflats provide room for settlements and agriculture, constituting important cultural landscapes. The shallow and protected waters of strandflats are valued fishing grounds that provide sustenance to traditional fishing settlements. Outside Norway proper, strandflats can be found in other high-latitude areas, such as Antarctica, Alaska, the Canadian Arctic, the Russian Far North, Greenland, Svalbard, Sweden, and Scotland.

The coastline of Djursland in Denmark is 260 kilometers long as measured from the ferry berth in Voer in the middle of Randers Fjord ending at Avlsgård in Aarhus Bay to the south. There are 18 sandy beaches for swimming along the coastline according to the folder, Kystkort Djursland published by the peninsula's two municipalities, Norddjurs and Syddjurs. These beaches cover 15 – 20%. of the total coastline. The remaining 200 plus kilometres are mostly unspoiled coastal nature.

Søndeledfjorden is a fjord in Risør municipality in Agder county, Norway. The 15-kilometre (9.3 mi) long fjord begins at the village of Søndeled and flows east into the Skaggerak. The large island of Barmen sits in the middle of the fjord, effectively separating it into two fjords known as the Nordfjorden in the north and the Sørfjorden in the south. At the western end of Barmen, the Nordfjorden and Sørfjorden reconnect in an area known as the Rødsfjorden. There are many islands at the mouth of the fjord as well as in the fjord itself.