
Cobalt(II) chloride is an inorganic compound of cobalt and chlorine, with the formula CoCl
2. It is a sky blue crystalline solid.
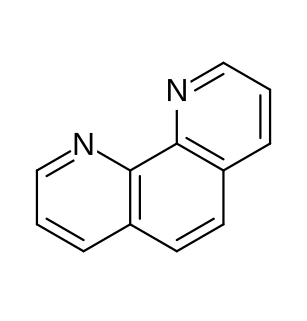
Phenanthroline (phen) is a heterocyclic organic compound. It is a white solid that is soluble in organic solvents. It is used as a ligand in coordination chemistry, forming strong complexes with most metal ions. It is often sold as the monohydrate.

Ferric acetate is the acetate salt of the coordination complex [Fe3O(OAc)6(H2O)3]+ (OAc− is CH3CO2−). Commonly the salt is known as "basic iron acetate". The formation of the red-brown complex was once used as a test for ferric ions.

Organoactinide chemistry is the science exploring the properties, structure and reactivity of organoactinide compounds, which are organometallic compounds containing a carbon to actinide chemical bond.

A dithiocarbamate is a functional group in organic chemistry. It is the analog of a carbamate in which both oxygen atoms are replaced by sulfur atoms.
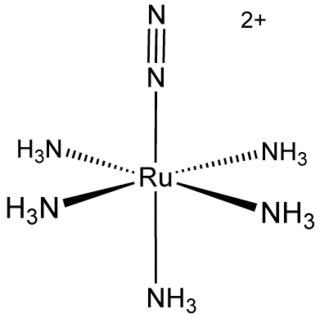
Transition metal dinitrogen complexes are coordination compounds that contain transition metals as ion centers the dinitrogen molecules (N2) as ligands.
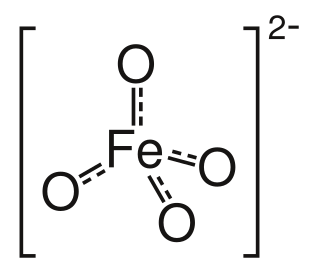
High-valent iron commonly denotes compounds and intermediates in which iron is found in a formal oxidation state > 3 that show a number of bonds > 6 with a coordination number ≤ 6. The term is rather uncommon for hepta-coordinate compounds of iron. It has to be distinguished from the terms hypervalent and hypercoordinate, as high-valent iron compounds neither necessarily violate the 18-electron rule nor necessarily show coordination numbers > 6. The ferrate(VI) ion [FeO4]2− was the first structure in this class synthesized. The synthetic compounds discussed below contain highly oxidized iron in general, as the concepts are closely related.

Metal bis(trimethylsilyl)amides are coordination complexes composed of a cationic metal with anionic bis(trimethylsilyl)amide ligands and are part of a broader category of metal amides.

Bromopentaamminecobalt(III) bromide is the dibromide salt of the cobalt coordination compound with the formula [Co(NH3)5Br]2+. It is a purple, water-soluble solid. The analogous chloropentaamminecobalt(III) chloride is also well known.
Cobalt(III) nitrate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Co(NO3)3.

Iron tris(dimethyldithiocarbamate) is the coordination complex of iron with dimethyldithiocarbamate with the formula Fe(S2CNMe2)3 (Me = methyl). It is marketed as a fungicide.

Transition metal nitrile complexes are coordination compounds containing nitrile ligands. Because nitriles are weakly basic, the nitrile ligands in these complexes are often labile.

Water oxidation catalysis (WOC) is the acceleration (catalysis) of the conversion of water into oxygen and protons:

Transition metal pyridine complexes encompass many coordination complexess that contain pyridine as a ligand. Most examples are mixed-ligand complexes. Many variants of pyridine are also known to coordinate to metal ions, such as the methylpyridines, quinolines, and more complex rings.

Transition metal isocyanide complexes are coordination compounds containing isocyanide ligands. Because isocyanide are relatively basic, but also good pi-acceptors, a wide range of complexes are known. Some isocyanide complexes are used in medical imaging.

In chemistry, a transition metal chloride complex is a coordination complex that consists of a transition metal coordinated to one or more chloride ligand. The class of complexes is extensive.

Transition metal carboxylate complexes are coordination complexes with carboxylate (RCO2−) ligands. Reflecting the diversity of carboxylic acids, the inventory of metal carboxylates is large. Many are useful commercially, and many have attracted intense scholarly scrutiny. Carboxylates exhibit a variety of coordination modes, most common are κ1- (O-monodentate), κ2 (O,O-bidentate), and bridging.

Iron tris(diethyldithiocarbamate) is the coordination complex of iron with diethyldithiocarbamate with the formula Fe(S2CNEt2)3 (Et = ethyl). It is a black solid that is soluble in organic solvents.

Transition metal dithiocarbamate complexes are coordination complexes containing one or more dithiocarbamate ligand, which are typically abbreviated R2dtc-. Many complexes are known. Several homoleptic derivatives have the formula M(R2dtc)n where n = 2 and 3.

Marinella Mazzanti is an Italian inorganic chemist specialized in coordination chemistry. She is a professor at EPFL and the head of the group of Coordination Chemistry at EPFL's School of Basic Sciences.


















