Related Research Articles
The Silurian is a geologic period and system spanning 24.6 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at 443.8 million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, 419.2 Mya. The Silurian is the shortest period of the Paleozoic Era. As with other geologic periods, the rock beds that define the period's start and end are well identified, but the exact dates are uncertain by a few million years. The base of the Silurian is set at a series of major Ordovician–Silurian extinction events when up to 60% of marine genera were wiped out.

Chitons are marine molluscs of varying size in the class Polyplacophora, formerly known as Amphineura. About 940 extant and 430 fossil species are recognized.
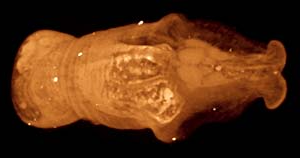
Aplacophora is a possibly paraphyletic taxon. This is a class of small, deep-water, exclusively benthic, marine molluscs found in all oceans of the world.

The halkieriids are a group of fossil organisms from the Lower to Middle Cambrian. Their eponymous genus is Halkieria, which has been found on almost every continent in Lower to Mid Cambrian deposits, forming a large component of the small shelly fossil assemblages. The best known species is Halkieria evangelista, from the North Greenland Sirius Passet Lagerstätte, in which complete specimens were collected on an expedition in 1989. The fossils were described by Simon Conway Morris and John Peel in a short paper in 1990 in the journal Nature. Later a more thorough description was undertaken in 1995 in the journal Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London and wider evolutionary implications were posed.

In the geologic timescale, the Homerian is an age of the Wenlock Epoch of the Silurian Period of the Paleozoic Era of the Phanerozoic Eon that is comprehended between 430.5 ± 0.7 Ma and 427.4 ± 0.5 Ma, approximately. The Homerian Age succeeds the Sheinwoodian Age and precedes the Gorstian Age.

In the geologic timescale, the Telychian is the third and final age of the Llandovery Epoch of the Silurian Period of the Paleozoic Era of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Telychian Age was between 438.5 ± 1.2 million years ago (Ma) and 433.4 ± 0.8 Ma. The Telychian Age succeeds the Aeronian Age and precedes the Sheinwoodian Age. The name of the interval is derived from the Pen-lan-Telych Farm near Llandovery, Powys, Wales.

The Burgsvik Beds are a sequence of shallow marine limestones and sandstones found near the locality of Burgsvik in the southern part of Gotland, Sweden. The beds were deposited in the Upper Silurian period, around 420 million years ago, in warm, equatorial waters frequently ravaged by storms, in front of an advancing shoreline. The Burgsvik Formation comprises two members, the Burgsvik Sandstone and the Burgsvik Oolite.
The Lau event was the last of three relatively minor mass extinctions during the Silurian period. It had a major effect on the conodont fauna, but barely scathed the graptolites, though they suffered an extinction very shortly thereafter termed the Kozlowskii event that some authors have suggested was coeval with the Lau event and only appears asynchronous due to taphonomic reasons. It coincided with a global low point in sea level caused by glacioeustasy and is closely followed by an excursion in geochemical isotopes in the ensuing late Ludfordian faunal stage and a change in depositional regime.

Halwaxiida or halwaxiids is a proposed clade equivalent to the older orders Sachitida He 1980 and Thambetolepidea Jell 1981, loosely uniting scale-bearing Cambrian animals, which may lie in the stem group to molluscs or lophotrochozoa. Some palaeontologists question the validity of the Halwaxiida clade.
Graticula, formerly incorrectly named Craticula, is a genus of Palaeozoic coralline alga. They form the framework of reef rocks in the Silurian of Gotland, from the Högklint, Slite and Halla groups.

The origin of the brachiopods is uncertain; they either arose from reduction of a multi-plated tubular organism, or from the folding of a slug-like organism with a protective shell on either end. Since their Cambrian origin, the phylum rose to a Palaeozoic dominance, but dwindled during the Mesozoic.

Pilina unguis is an extinct species of Paleozoic Silurian monoplacophoran. It was first named as Tryblidium unguis and described by Gustaf Lindström in Latin from the Silurian deposits of Gotland in Sweden, in 1880.

Pilina solarium is an extinct species of a paleozoic Silurian monoplacophoran. It was first named as Palaeacmaea solarium and described by Gustaf Lindström from Silurian of Gotland in Sweden in 1884.

Plumulites is an extinct genus of machaeridians, extinct annelid group.
Rothpletzella is a genus of calcimicrobe known from the Silurian of Gotland, the Devonian of France, as well as the Ordovician of China. It has been hypothesised to be a cyanobacterium, and shares morphological similarities with extant cyanobacteria. The genus is named in honor of August Rothpletz.
The Heloplacidae are a group of plated aplacophora known from Silurian deposits. Their best understood representative, Acaenoplax, can be taken as representative of the family; it is the only genus for which soft part anatomy is known.
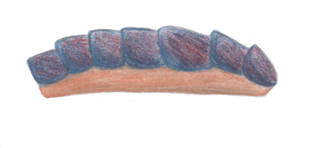
Kulindroplax perissokomos is a Silurian mollusk, known from a single fossil from the Coalbrookdale Formation fauna of England. It lived during the Homerian Age. It is considered a basal aplacophoran. Unlike all modern aplacophorans, which are shell-less, Kulindroplax has a chiton-like shell, and it is considered a transitional fossil in the evolution of molluscs.
Trimeroceras is a genus of straight oncocerid from the Silurian of Europe, China, and North America. Originally classified as a part of Gomphoceras, it is now type for the Trimeroceratidae.

Strophomenata is an extinct class of brachiopods in the subphylum Rhynchonelliformea.

Holophragma calceoloides is an extinct species of rugose coral known from Silurian layers mainly on, but not limited to, the northwestern coast of Gotland, where it is very common. The species was recognised in 1866 by Gustaf Lindström. It was small and benthic, and always solitary.
References
- 1 2 3 Cherns, L. (2004). "Early Palaeozoic diversification of chitons (Polyplacophora, Mollusca) based on new data from the Silurian of Gotland, Sweden". Lethaia. 37 (4): 445–456. Bibcode:2004Letha..37..445C. doi:10.1080/00241160410002180.
- ↑ Bischoff, G. C. O. 1981. Cobcrephora n. g., representative of a new Polyplacophoran order phosphatoloricata, with calciumphosphatic shells. Senckenbergiana Lethaea, 61:173-215