This article needs additional citations for verification .(July 2013) |
Coca alkaloids are the alkaloids found in the coca plant, Erythroxylum coca . [1] They are predominantly of either the pyrrolidine or the tropane types.
This article needs additional citations for verification .(July 2013) |
Coca alkaloids are the alkaloids found in the coca plant, Erythroxylum coca . [1] They are predominantly of either the pyrrolidine or the tropane types.

Cocaine is a tropane alkaloid that acts as a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant. As an extract, it is mainly used recreationally, and often illegally for its euphoric and rewarding effects. It is also used in medicine by Indigenous South Americans for various purposes and rarely, but more formally, as a local anaesthetic by medical practitioners in more developed countries. It is primarily obtained from the leaves of two Coca species native to South America: Erythroxylum coca and E. novogranatense. After extraction from the plant, and further processing into cocaine hydrochloride, the drug is administered by being either snorted, applied topically to the mouth, or dissolved and injected into a vein. It can also then be turned into free base form, in which it can be heated until sublimated and then the vapours can be inhaled.

Coca is any of the four cultivated plants in the family Erythroxylaceae, native to western South America. Coca is known worldwide for its psychoactive alkaloid, cocaine.

Pemberton's French Wine Coca was a coca wine created by the druggist John Pemberton, the inventor of Coca-Cola. It was an alcoholic beverage, mixed with coca, kola nut, and damiana. The original recipe contained the ingredient cocaethylene, which was removed, just like the alcohol had before it, in 1899 because of a social stigma surrounding the rampant use of cocaine at the time.

Coca wine is an alcoholic beverage combining wine with cocaine. One popular brand was Vin Mariani, developed in 1863 by French-Corsican chemist and entrepreneur Angelo Mariani.

Methylecgonine cinnamate is a natural tropane alkaloid found within the coca plant. Its more common name, cinnamoylcocaine, reflects its close structural similarity to cocaine. It is pharmacologically inactive, but some studies funded by anti-drug agencies imply that it is active when smoked. Furthermore, the discovery of differing impurity products yielding methylecgonine cinnamate in confiscated cocaine have led enforcing agencies to postulate that illicit manufacturers have changed their oxidation procedures when refining cocaine from a crude form. Methylecgonine cinnamate can dimerize to the truxillic acid derivative truxilline. It is notable that methylecgonine cinnamate is given in patents of active cocaine analogue structures.

Erythroxylum coca is one of two species of cultivated coca.

Hydroxytropacocaine is a tropane alkaloid found in Erythroxylum coca.

Erythroxylum (Erythroxylon) is a genus of tropical flowering plants in the family Erythroxylaceae. Many of the approximately 200 species contain the tropane alkaloid cocaine, and two of the species within this genus, Erythroxylum coca and Erythroxylum novogranatense, both native to South America, are the main commercial source of cocaine and of the mild stimulant coca tea. Another species, Erythroxylum vaccinifolium is used as an aphrodisiac in Brazilian drinks and herbal medicine.

Coca tea, also called mate de coca, is an herbal tea (infusion) made using the raw or dried leaves of the coca plant, which is native to South America. It is made either by submerging the coca leaf or dipping a tea bag in hot water. The tea is most commonly consumed in the Andes mountain range, particularly Argentina, Bolivia, Colombia, Ecuador and especially in Peru, where it is consumed all around the country. It is greenish yellow in color and has a mild bitter flavor similar to green tea with a more organic sweetness.

Ypadú or ypadu is an unrefined, unconcentrated powder made from toasted coca leaves and the ash of various other plants. It is traditionally prepared and consumed by indigenous tribes in the Northwest Amazon. Like coca teas consumed in Peru to adapt to sickness induced by high elevation, it has a long ethnobotanical history and cultural associations.
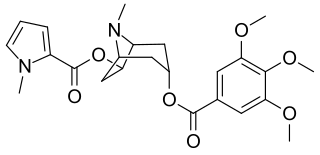
Catuabines are a group of tropane alkaloids, isolated from Erythroxylum vaccinifolium, which are used in the preparation of the drug Catuaba. While catuabine A, B and C were isolated and characterized by Graf and Lude, catuabine D was recently isolated by Zanolari et al. The catuabines are not known to have any physiological effects, this is in contrast to cocaine, which is an active constituent of another species, Erythroxylum coca.
Free base is a descriptor for the neutral form of an amine commonly used in reference to illicit drugs. The amine is often an alkaloid, such as nicotine, cocaine, morphine, and ephedrine, or derivatives thereof. Freebasing is a more efficient method of self-administering alkaloids via the smoking route.
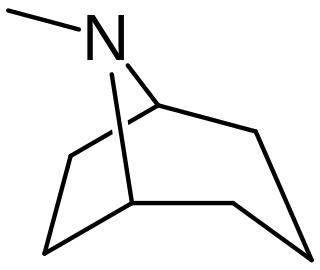
Tropane alkaloids are a class of bicyclic [3.2.1] alkaloids and secondary metabolites that contain a tropane ring in their chemical structure. Tropane alkaloids occur naturally in many members of the plant family Solanaceae. Certain tropane alkaloids such as cocaine and scopolamine are notorious for their psychoactive effects, related usage and cultural associations. Particular tropane alkaloids such as these have pharmacological properties and can act as anticholinergics or stimulants.
Albert Friedrich Emil Niemann was a German chemist. In 1859 - about the same time as Paolo Mantegazza - he isolated cocaine, and he published his finding in 1860.

Agwa de Bolivia, often shortened to AGWA, is a herbal liqueur made with Bolivian coca leaves and 37 other natural herbs and botanicals including green tea, ginseng, and guarana, distilled and produced in Amsterdam by BABCO Europe Limited. The coca leaf content of the drink, like that in Coca-Cola, has the cocaine alkaloids removed during production, and does not contain the drug.

Erythroxylum novogranatense is a neotropical species of Erythroxylum (Erythroxylaceae). Cocaine is produced from the leaves.
Coca flour is made from whole ground dried coca leaves harvested from the coca plant, Erythroxylum coca or Erythroxylum novogranatense. Coca flour is commercially produced and sold in stores in Argentina, Bolivia, Colombia and Peru.
Methylecgonone reductase (EC 1.1.1.334, MecgoR (gene name)) is an enzyme with systematic name ecgonine methyl ester:NADP+ oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Meteloidine is an alkaloid found in some Brugmansia and Datura species. Its also found in Erythroxylum australe and is said to be cocaine-like alkaloid.

Methylecgonine is a prominent tropane alkaloid found in coca leaves. It is metabolite of cocaine, and may be used as a precursor for it. It also occurs as minor alkaloid in roots of many Datura species such as Datura stramonium and Datura innoxia.