
Alkaloids are a class of basic, naturally occurring organic compounds that contain at least one nitrogen atom. This group also includes some related compounds with neutral and even weakly acidic properties. Some synthetic compounds of similar structure may also be termed alkaloids. In addition to carbon, hydrogen and nitrogen, alkaloids may also contain oxygen or sulfur. More rarely still, they may contain elements such as phosphorus, chlorine, and bromine.

Cocaine is a tropane alkaloid that acts as a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant. As an extract, it is mainly used recreationally, and often illegally for its euphoric and rewarding effects. It is also used in medicine by Indigenous South Americans for various purposes and rarely, but more formally, as a local anaesthetic or diagnostic tool by medical practitioners in more developed countries. It is primarily obtained from the leaves of two Coca species native to South America: Erythroxylum coca and E. novogranatense. After extraction from the plant, and further processing into cocaine hydrochloride, the drug is administered by being either snorted, applied topically to the mouth, or dissolved and injected into a vein. It can also then be turned into free base form, in which it can be heated until sublimated and then the vapours can be inhaled.

The term narcotic originally referred medically to any psychoactive compound with numbing or paralyzing properties. In the United States, it has since become associated with opiates and opioids, commonly morphine and heroin, as well as derivatives of many of the compounds found within raw opium latex. The primary three are morphine, codeine, and thebaine.

Coca is any of the four cultivated plants in the family Erythroxylaceae, native to western South America. Coca is known worldwide for its psychoactive alkaloid, cocaine.

Methylecgonine cinnamate is a natural tropane alkaloid found within the coca plant. Its more common name, cinnamoylcocaine, reflects its close structural similarity to cocaine. It is pharmacologically inactive, but some studies funded by anti-drug agencies imply that it is active when smoked. Furthermore, the discovery of differing impurity products yielding methylecgonine cinnamate in confiscated cocaine have led enforcing agencies to postulate that illicit manufacturers have changed their oxidation procedures when refining cocaine from a crude form. Methylecgonine cinnamate can dimerize to the truxillic acid derivative truxilline. It is notable that methylecgonine cinnamate is given in patents of active cocaine analogue structures.

Mucic acid, C6H10O8 or HOOC-(CHOH)4-COOH (galactaric acid or meso-galactaric acid) is an aldaric acid obtained by nitric acid oxidation of galactose or galactose-containing compounds such as lactose, dulcite, quercite, and most varieties of gum.

Tropinone is an alkaloid, famously synthesised in 1917 by Robert Robinson as a synthetic precursor to atropine, a scarce commodity during World War I. Tropinone and the alkaloids cocaine and atropine all share the same tropane core structure. Its corresponding conjugate acid at pH 7.3 major species is known as tropiniumone.

The Misuse of Drugs Act 1973 is a statute of the Parliament of Singapore that enables authorities to prosecute offenders for crimes involving illegal drugs. The law is designed specifically to grant the Government of Singapore, through its agencies such as the Central Narcotics Bureau, enforcement powers to combat offences such as the trafficking, importation or exportation, possession, and consumption of controlled drugs.
Tropane is a nitrogenous bicyclic organic compound. It is mainly known for the other alkaloids derived from it, which include atropine and cocaine, among others. Tropane alkaloids occur in plants of the families Erythroxylaceae and Solanaceae.

(–)-2-β-Carbomethoxy-3-β-(4-fluorophenyl)tropane is a stimulant drug used in scientific research. CFT is a phenyltropane based dopamine reuptake inhibitor and is structurally derived from cocaine. It is around 3-10x more potent than cocaine and lasts around 7 times longer based on animal studies. While the naphthalenedisulfonate salt is the most commonly used form in scientific research due to its high solubility in water, the free base and hydrochloride salts are known compounds and can also be produced. The tartrate is another salt form that is reported.

Methylecgonidine is a chemical intermediate derived from ecgonine or cocaine.

Ecgonidine (anhydroecgonine) is an alkaloid related to ecgonine and cocaine. It has a structure with a cycloheptene ring, with a nitrogen bridge, and a carboxylic acid side chain.

Troparil is a stimulant drug used in scientific research. Troparil is a phenyltropane-based dopamine reuptake inhibitor (DRI) that is derived from methylecgonidine. Troparil is a few times more potent than cocaine as a dopamine reuptake inhibitor, but is less potent as a serotonin reuptake inhibitor, and has a duration spanning a few times longer, since the phenyl ring is directly connected to the tropane ring through a non-hydrolyzable carbon-carbon bond. The lack of an ester linkage removes the local anesthetic action from the drug, so troparil is a pure stimulant. This change in activity also makes troparil slightly less cardiotoxic than cocaine. The most commonly used form of troparil is the tartrate salt, but the hydrochloride and naphthalenedisulfonate salts are also available, as well as the free base.
Free base is a descriptor for the neutral form of an amine commonly used in reference to illicit drugs. The amine is often an alkaloid, such as nicotine, cocaine, morphine, and ephedrine, or derivatives thereof. Freebasing is a more efficient method of self-administering alkaloids via the smoking route.
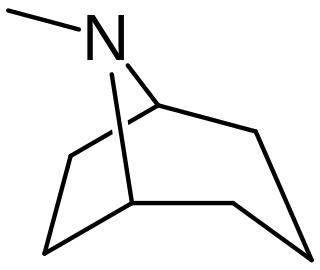
Tropane alkaloids are a class of bicyclic [3.2.1] alkaloids and secondary metabolites that contain a tropane ring in their chemical structure. Tropane alkaloids occur naturally in many members of the plant family Solanaceae. Certain tropane alkaloids such as cocaine and scopolamine are notorious for their psychoactive effects, related usage and cultural associations. Particular tropane alkaloids such as these have pharmacological properties and can act as anticholinergics or stimulants.

The biosynthesis of cocaine has long attracted the attention of biochemists and organic chemists. This interest is partly motivated by the strong physiological effects of cocaine, but a further incentive was the unusual bicyclic structure of the molecule. The biosynthesis can be viewed as occurring in two phases, one phase leading to the N-methylpyrrolinium ring, which is preserved in the final product. The second phase incorporates a C4 unit with formation of the bicyclic tropane core.
Methylecgonone reductase (EC 1.1.1.334, MecgoR (gene name)) is an enzyme with systematic name ecgonine methyl ester:NADP+ oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Coca alkaloids are the alkaloids found in the coca plant, Erythroxylum coca. They are predominantly of either the pyrrolidine or the tropane types.

Methylecgonine, also known as ecgonine methylester is a prominent tropane alkaloid found in coca leaves. It is metabolite of cocaine, and may be used as a precursor for it. It also occurs as minor alkaloid in roots of many Datura species such as Datura stramonium and Datura innoxia.















