Genus is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses, in biology. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus.

In taxonomy, binomial nomenclature, also called binominal nomenclature or binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, both of which use Latin grammatical forms, although they can be based on words from other languages. Such a name is called a binomial name, a binomen, binominal name or a scientific name; more informally it is also called a Latin name.

The lagomorphs are the members of the taxonomic order Lagomorpha, of which there are two living families: the Leporidae and the Ochotonidae (pikas). The name of the order is derived from the Ancient Greek lagos + morphē. There are 102 extant species of lagomorph, including 37 species of pika, 33 species of rabbit and cottontail, and 32 species of hare.

The glaucophytes, also known as glaucocystophytes or glaucocystids, are a small group of freshwater unicellular algae, less common today than they were during the Proterozoic. Only 15 species have been described, but more species are likely to exist. Together with the red algae (Rhodophyta) and the green algae plus land plants, they form the Archaeplastida. However, the relationships among the red algae, green algae and glaucophytes are unclear, in large part due to limited study of the glaucophytes.

Starlings are small to medium-sized passerine birds in the family Sturnidae. The name "Sturnidae" comes from the Latin word for starling, sturnus. Many Asian species, particularly the larger ones, are called mynas, and many African species are known as glossy starlings because of their iridescent plumage. Starlings are native to Europe, Asia and Africa, as well as northern Australia and the islands of the tropical Pacific. Several European and Asian species have been introduced to these areas as well as North America, Hawaii and New Zealand, where they generally compete for habitats with native birds and are considered to be invasive species. The starling species familiar to most people in Europe and North America is the common starling, and throughout much of Asia and the Pacific, the common myna is indeed common.
In biology, a monotypic taxon is a taxonomic group (taxon) that contains only one immediately subordinate taxon.

In zoological nomenclature, a type species is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological type specimen(s). A similar concept is used for suprageneric groups and called a type genus.

Acacia, commonly known as the wattles or acacias, is a large genus of shrubs and trees in the subfamily Mimosoideae of the pea family Fabaceae. Initially, it comprised a group of plant species native to Africa and Australasia, but it has now been limited to contain only the Australasian species. The genus name is New Latin, borrowed from the Greek ἀκακία, a term used by Dioscorides for a preparation extracted from the leaves and fruit pods of Vachellia nilotica, the original type of the genus. In his Pinax (1623), Gaspard Bauhin mentioned the Greek ἀκακία from Dioscorides as the origin of the Latin name.
The Conservatoire Serge Rachmaninoff de Paris is a professional music school in Paris, which conducts its courses in both French and Russian.
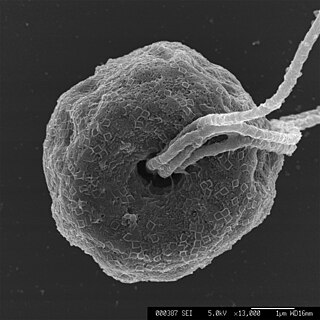
Pyramimonadales are an order of green algae in the Chlorophyta.
In taxonomy, Mychonastes is a genus of green algae, specifically of the Chlorophyceae.
Scourfieldia is a genus of green algae in the family Scourfieldiaceae. Cardiomona Korshikov is an invalid synonym.

In biological classification, taxonomic rank is the relative level of a group of organisms in a taxonomic hierarchy. Examples of taxonomic ranks are species, genus, family, order, class, phylum, kingdom, domain, etc.

Corallimorpharia is an order of marine cnidarians closely related to stony or reef building corals (Scleractinia). They occur in both temperate and tropical climates, although they are mostly tropical. Temperate forms tend to be very robust, with wide and long columns, whereas tropical forms tend to have very short columns with a wide oral disc and very short tentacles. The tentacles are usually arranged in rows radiating from the mouth. Many species occur together in large groups, although there are recorded instances of individuals. In many respects, they resemble the stony corals, except for the absence of a stony skeleton. Morphological and molecular evidence suggests that they are very closely related to stony corals.
Aleksandr Ivanovich Timoshinin is a Russian rower, born in Moscow, who competed for the Soviet Union in the 1968 Summer Olympics and in the 1972 Summer Olympics.
Gennadi Egorovich Korshikov is a Russian rower who competed for the Soviet Union in the 1972 Summer Olympics and in the 1976 Summer Olympics.
Chlorolobion is a genus of algae belonging to the family Selenastraceae.
Eutetramorus is a genus of algae belonging to the family Radiococcaceae.
Hyaloraphidium is a genus of fungi belonging to the class Chytridiomycetes, unknown order and family.








