| Sphaeropleales | |
|---|---|
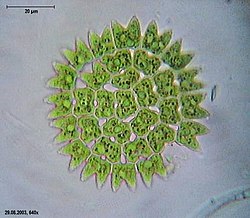 | |
| Pediastrum duplex , an algae within the order Sphaeropleales | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Chlorophyta |
| Class: | Chlorophyceae |
| Order: | Sphaeropleales Luerssen |
| Families [1] | |
| |
Sphaeropleales is an order of green algae that used to be called Chlorococcales. [2] The order includes some of the most common freshwater planktonic algae such as Scenedesmus and Pediastrum . [3] The Sphaeropleales includes vegetatively non-motile unicellular, colonial , or filamentous taxa. They have biflagellate zoospores with flagella that are directly opposed in direction (the DO arrangement): Sphaeroplea , Atractomorpha , Neochloris , Hydrodictyon , and Pediastrum . All of these taxa have basal body core connections. [2] Motile cells generally lack cell walls or have only a very fine layer surrounding the cell membrane. [4] Other common characteristics include a robust vegetative cell wall, cup-shaped chloroplasts with large pyrenoids, and relatively large nuclei. [5]
With an increase in the number of taxa for which sequence data are available, there is evidence of an expanded DO clade that includes additional zoosporic ( Bracteacoccus , Schroederia ) and some strictly autosporic genera such as Ankistrodesmus , Scenedesmus , Selenastrum , and Monoraphidium . The filamentous Microspora has been allied with the coccoid genus Bracteacoccus based on molecular data.
Monophyly of the DO clade is supported by phylogenetic analysis of multi-gene data. [3] [4]