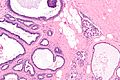
The parotid gland is a major salivary gland in many animals. In humans, the two parotid glands are present on either side of the mouth and in front of both ears. They are the largest of the salivary glands. Each parotid is wrapped around the mandibular ramus, and secretes serous saliva through the parotid duct into the mouth, to facilitate mastication and swallowing and to begin the digestion of starches. There are also two other types of salivary glands; they are submandibular and sublingual glands. Sometimes accessory parotid glands are found close to the main parotid glands.

Apocrine is a term used to classify the mode of secretion of exocrine glands. In apocrine secretion, secretory cells accumulate material at their apical ends, and this material then buds off from the cells, forming extracellular vesicles. The secretory cells therefore lose part of their cytoplasm in the process of secretion.

Nipple discharge is fluid from the nipple, with or without squeezing the breast. The discharge can be milky, clear, green, purulent, bloody, or faintly yellow. The consistency can be thick, thin, sticky, or watery.

Fibroadenomas are benign breast tumours characterized by an admixture of stromal and epithelial tissue. Breasts are made of lobules and ducts. These are surrounded by glandular, fibrous and fatty tissues. Fibroadenomas develop from the lobules. The glandular tissue and ducts grow over the lobule to form a solid lump.

Invasive carcinoma of no special type, invasive breast carcinoma of no special type (IBC-NST), invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC), infiltrating ductal carcinoma (IDC) or invasive ductal carcinoma, not otherwise specified (NOS) is a disease. For international audiences this article will use "invasive carcinoma NST" because it is the preferred term of the World Health Organization (WHO).

Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), also known as intraductal carcinoma, is a pre-cancerous or non-invasive cancerous lesion of the breast. DCIS is classified as Stage 0. It rarely produces symptoms or a breast lump one can feel, typically being detected through screening mammography. It has been diagnosed in a significant percentage of men.

Granular cell tumor is a tumor that can develop on any skin or mucosal surface, but occurs on the tongue 40% of the time.

Lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS) is an incidental microscopic finding with characteristic cellular morphology and multifocal tissue patterns. The condition is a laboratory diagnosis and refers to unusual cells in the lobules of the breast. The lobules and acini of the terminal duct-lobular unit (TDLU), the basic functional unit of the breast, may become distorted and undergo expansion due to the abnormal proliferation of cells comprising the structure. These changes represent a spectrum of atypical epithelial lesions that are broadly referred to as lobular neoplasia (LN).

High-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (HGPIN) is an abnormality of prostatic glands and believed to precede the development of prostate adenocarcinoma.

Male breast cancer (MBC) is a cancer in males that originates in their breasts. Males account for less than 1% of new breast cancers with about 20,000 new cases being diagnosed worldwide every year. Its incidence rates in males vs. females are, respectively, 0.4 and 66.7 per 100,000 person-years. The worldwide incidences of male as well as female breast cancers have been increasing over the last few decades. Currently, one of every 800 men are estimated to develop this cancer during their lifetimes.

Atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH) is the term used for a benign lesion of the breast that indicates an increased risk of breast cancer.

Poromas are rare, benign, cutaneous adnexal tumors. Cutaneous adnexal tumors are a group of skin tumors consisting of tissues that have differentiated towards one or more of the four primary adnexal structures found in normal skin: hair follicles, sebaceous sweat glands, apocrine sweat glands, and eccrine sweat glands. Poromas are eccrine or apocrine sweat gland tumors derived from the cells in the terminal portion of these glands' ducts. This part of the sweat gland duct is termed the acrosyringium and had led to grouping poromas in the acrospiroma class of skin tumors. Here, poromas are regarded as distinct sweat gland tumors that differ from other sweat gland tumors by their characteristic clinical presentations, microscopic histopathology, and the genetic mutations that their neoplastic cells have recently been found to carry.

Sclerosing polycystic adenosis is a rare salivary gland tumor first described in 1996 by Dr. Brion Smith. The major salivary glands, specifically the parotid gland and the submandibular gland, are affected most commonly. Patients usually come to clinical attention with a mass or swelling in their salivary glands in the 5th decade of life, with females affected much more commonly than males. Nearly all of the cases reported so far have a benign behavior, although there is a single case that has had an associated malignant transformation.
Papillomatosis of the breast (PB) is a rare, benign, epitheliosis-like lesion, i.e. an overgrowth of the cells lining the ducts of glands that resembles a papilla or nipple-like nodule/tumor. PB tumors develop in the apocrine glands of the breast. PB is also termed juvenile papillomatosis because of its frequent occurrence in younger women and Swiss cheese disease because of its microscopic appearance. Rarely, PB has also been diagnosed in very young, adolescent, and adult males.
A histopathologic diagnosis of prostate cancer is the discernment of whether there is a cancer in the prostate, as well as specifying any subdiagnosis of prostate cancer if possible. The histopathologic subdiagnosis of prostate cancer has implications for the possibility and methodology of any subsequent Gleason scoring. The most common histopathological subdiagnosis of prostate cancer is acinar adenocarcinoma, constituting 93% of prostate cancers. The most common form of acinar adenocarcinoma, in turn, is "adenocarcinoma, not otherwise specified", also termed conventional, or usual acinar adenocarcinoma.
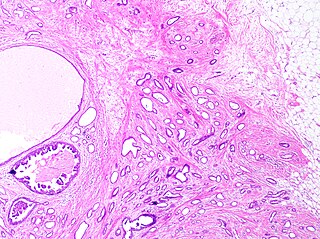
Tubular carcinoma is a subtype of invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast. More rarely, tubular carcinomas may arise in the pancreas or kidney. Most tubular carcinomas begin in the milk duct of the breast and spread to healthy tissue around it.
Papillary carcinomas of the breast (PCB), also termed malignant papillary carcinomas of the breast, are rare forms of the breast cancers. The World Health Organization (2019) classified papillary neoplasms of the breast into 5 types: intraductal papilloma, papillary ductal carcinoma in situ (PDCIS), encapsulated papillary carcinoma (EPC), solid-papillary carcinoma (SPC), and invasive papillary carcinoma (IPC). The latter four carcinomas are considered here; intraductal papilloma is a benign neoplasm. The World Health Organization regarded solid papillary carcinoma as having two subtypes: in situ and invasive SPC.

Invasive cribriform carcinoma of the breast (ICCB), also termed invasive cribriform carcinoma, is a rare type of breast cancer that accounts for 0.3% to 0.6% of all carcinomas in the breast. It originates in a lactiferous duct as opposed to the lobules that form the alveoli in the breasts' mammary glands. ICCB was first described by Dixon and colleagues in 1983 as a tumor that on microscopic histopathological inspection had a cribriform pattern, i.e. a tissue pattern consisting of numerous "Swiss cheese"-like open spaces and/or sieve-like small holes. The latest edition (2019) of the World Health Organization (2019) termed these lesions invasive cribriform carcinomas indicating that by definition they must have a component that invades out of their ducts of origin into adjacent tissues. In situ ductal cancers that have a cribriform histopathology are regarded as belonging to the group of ductal carcinoma in situ tumors.
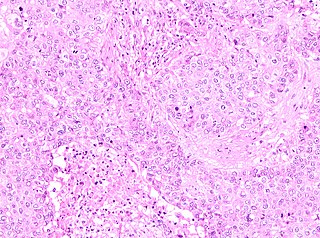
Pure apocrine carcinoma of the breast (PACB) is a rare carcinoma derived from the epithelial cells in the lactiferous ducts of the mammary gland. The mammary gland is an apocrine gland. Its lactiferous ducts have two layers of epithelial cells, a luminal layer which faces the duct's lumen and a basal layer which lies beneath the luminal layer. There are at least 4 subtypes of epithelial cells in these ducts: luminal progenitor cells and luminal mature cells which reside in the luminal layer and mammary stem cells and basal cells which reside in the basal layer. Examination of the genes expressed in PACB cancer cells indicate that most of these tumors consist of cells derived from luminal cells but a minority of these tumors consist of cells derived from basal cells.