
Algae are any of a large and diverse group of photosynthetic, eukaryotic organisms. The name is an informal term for a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular microalgae, such as Chlorella, Prototheca and the diatoms, to multicellular forms, such as the giant kelp, a large brown alga which may grow up to 50 metres (160 ft) in length. Most are aquatic and lack many of the distinct cell and tissue types, such as stomata, xylem and phloem that are found in land plants. The largest and most complex marine algae are called seaweeds. In contrast, the most complex freshwater forms are the Charophyta, a division of green algae which includes, for example, Spirogyra and stoneworts. Algae that are carried by water are plankton, specifically phytoplankton.

The green algae are a group of chlorophyll-containing autotrophic eukaryotes consisting of the phylum Prasinodermophyta and its unnamed sister group that contains the Chlorophyta and Charophyta/Streptophyta. The land plants (Embryophytes) have emerged deep in the Charophyte alga as a sister of the Zygnematophyceae. Since the realization that the Embryophytes emerged within the green algae, some authors are starting to include them. The completed clade that includes both green algae and embryophytes is monophyletic and is referred to as the clade Viridiplantae and as the kingdom Plantae. The green algae include unicellular and colonial flagellates, most with two flagella per cell, as well as various colonial, coccoid (spherical), and filamentous forms, and macroscopic, multicellular seaweeds. There are about 22,000 species of green algae, many of which live most of their lives as single cells, while other species form coenobia (colonies), long filaments, or highly differentiated macroscopic seaweeds.

Ocythoe tuberculata, also known as the tuberculate pelagic octopus or football octopus, is a pelagic octopus. It is the only known species in the family Ocythoidae.

The red-rimmed melania, also known as Malayan livebearing snails or Malayan/Malaysian trumpet snails by aquarists, is a species of freshwater snail with an operculum, a parthenogenetic, aquatic gastropod mollusk in the family Thiaridae.

Cotylorhiza tuberculata is a species of jellyfish of the phylum Cnidaria, also known as the Mediterranean jellyfish, Mediterranean jelly, or fried egg jellyfish. It is commonly found in the Mediterranean Sea, Aegean Sea, and Adriatic Sea.

Majidae is a family of crabs, comprising around 200 marine species inside 52 genera, with a carapace that is longer than it is broad, and which forms a point at the front. The legs can be very long in some species, leading to the name "spider crab". The exoskeleton is covered with bristles to which the crab attaches algae and other items to act as camouflage.

AlgaeBase is a global species database of information on all groups of algae, both marine and freshwater, as well as sea-grass.

Colpomenia is a genus of brown macroalgae in the family Scytosiphonaceae.

Jellyella is a genus of bryozoans in the family Membraniporidae.

Collinsiella is a genus of green algae in the order Ulotrichales.
Pedinomonas is a genus of green algae in the family Pedinomonadaceae.
Hypnomonas is a genus of green algae, in the family Hypnomonadaceae. Its sole species is Hypnomonas tuberculata.

The green ormer is a northeast Atlantic and Mediterranean species of sea snail, a coastal marine gastropod mollusc in the family Haliotidae, the abalones or ormer snails.

Red algae, or Rhodophyta, make up one of the oldest groups of eukaryotic algae. The Rhodophyta comprises one of the largest phyla of algae, containing over 7,000 recognized species within over 900 genera amidst ongoing taxonomic revisions. The majority of species (6,793) are Florideophyceae, and mostly consist of multicellular, marine algae, including many notable seaweeds. Red algae are abundant in marine habitats. Approximately 5% of red algae species occur in freshwater environments, with greater concentrations in warmer areas. Except for two coastal cave dwelling species in the asexual class Cyanidiophyceae, no terrestrial species exist, which may be due to an evolutionary bottleneck in which the last common ancestor lost about 25% of its core genes and much of its evolutionary plasticity.
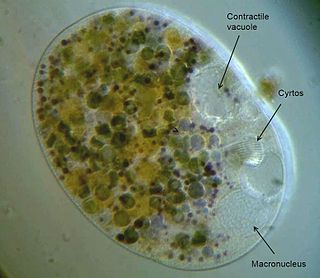
Nassula is a genus of unicellular ciliates, belonging to the class Nassophorea. Like other members of the class, Nassula possesses a basket-like feeding apparatus made up of cytopharyngeal rods (nematodesmata), which are themselves composed of closely packed microtubules. Nassula use this structure to ingest filamentous cyanobacteria, drawing individual strands of blue-green algae through the cytopharynx and into the body of the cell, where they are digested. As the algae are broken down, they can take on a variety of bright colours, which give Nassula a distinctive, variegated appearance under the microscope.
A mixotroph is an organism that uses a mix of different sources of energy and carbon, instead of having a single trophic mode, on the continuum from complete autotrophy to complete heterotrophy. It is estimated that mixotrophs comprise more than half of all microscopic plankton. There are two types of eukaryotic mixotrophs. There are those with their own chloroplasts - including those with endosymbionts providing the chloroplasts. And there are those that acquire them through kleptoplasty, or through symbiotic associations with prey, or through 'enslavement' of the prey's organelles.
Mesoclemmys tuberculata is a species of turtle. It is found in northeastern Brazil.

Acanthocardia is a genus of saltwater clams, marine bivalve molluscs in the family Cardiidae. They are infaunal suspension feeders.

Frank Shipley Collins (1848–1920) was an American botanist and algologist specializing in the study of marine algae. He was a pioneer in the study of the distribution of algae on the Atlantic seaboard and Bermudas and was the leading American algologist of his time. He wrote The Green Algae of North America and Working Key to the Genera of North American Algae. Several species bear his name in his honor, including Collinsiella tuberculata, and Phaeosaccion collinsii.

Ochromonas is a genus of algae belonging to the family Ochromonadaceae.
















