
The Chicago, Burlington and Quincy Railroad was a railroad that operated in the Midwestern United States. Commonly referred to as the Burlington Route, the Burlington, or as the Q, it operated extensive trackage in the states of Colorado, Illinois, Iowa, Missouri, Nebraska, Wisconsin, Wyoming, and also in Texas through subsidiaries Colorado and Southern Railway, Fort Worth and Denver Railway, and Burlington-Rock Island Railroad. Its primary connections included Chicago, Minneapolis–Saint Paul, St. Louis, Kansas City, and Denver. Because of this extensive trackage in the midwest and mountain states, the railroad used the advertising slogans "Everywhere West", "Way of the Zephyrs", and "The Way West".

The City of Denver was a streamlined passenger train operated by the Union Pacific Railroad between Chicago, Illinois, and Denver, Colorado. It operated between 1936 and 1971. From 1936–1955 the Chicago and North Western Railway handled the train east of Omaha, Nebraska; the Chicago, Milwaukee, St. Paul and Pacific Railroad handled it thereafter. The train was the fastest long-distance train in the United States when it debuted in 1936, covering 1,048 miles (1,687 km) in 16 hours. For almost its entire career its principal competitor was the Chicago, Burlington and Quincy Railroad's Denver Zephyr. When Amtrak assumed operation of most intercity trains in the United States in 1971, it discontinued the City of Denver, preferring to use the Burlington's route between Chicago and Denver.

The Missouri Pacific Railroad, commonly abbreviated as MoPac, was one of the first railroads in the United States west of the Mississippi River. MoPac was a Class I railroad growing from dozens of predecessors and mergers. In 1967, the railroad operated 9,041 miles of road and 13,318 miles of track, not including DK&S, NO&LC, T&P, and its subsidiaries C&EI and Missouri-Illinois.

A dome car is a type of railway passenger car that has a glass dome on the top of the car where passengers can ride and see in all directions around the train. It also can include features of a coach, lounge car, dining car, sleeping car or observation. Beginning in 1945, dome cars were primarily used in the United States and Canada, though a small number were constructed in Europe for Trans Europ Express service, and similar panorama cars are in service on Alpine tourist railways like the Bernina Express.

The General Pershing Zephyr was the ninth of the Chicago, Burlington & Quincy Railroad's Zephyr streamliners, and the last built as an integrated streamliner rather than a train hauled by an EMD E-unit diesel locomotive. It was constructed in 1939 with bodywork and passenger cars by Budd Company and diesel engine, electric transmission, power truck, and other locomotive equipment by General Motors Electro-Motive Corporation. Because its intended Kansas City to St Louis route passed near the birthplace and boyhood home of famous World War I General John J. Pershing, the train was named after him. The power car was named Silver Charger, after Pershing's horse Charger, while the passenger cars were named after United States Army badges of rank—Silver Leaf, Silver Eagle, and Silver Star.

The St. Louis–San Francisco Railway, commonly known as the "Frisco", was a railroad that operated in the Midwest and South Central United States from 1876 to April 17, 1980. At the end of 1970, it operated 4,547 miles (7,318 km) of road on 6,574 miles (10,580 km) of track, not including subsidiaries Quanah, Acme and Pacific Railway and the Alabama, Tennessee and Northern Railroad; that year, it reported 12,795 million ton-miles of revenue freight and no passengers. It was purchased and absorbed into the Burlington Northern Railroad in 1980. Despite its name, it never came close to San Francisco.

The Denver Zephyr was a streamlined passenger train operated by the Chicago, Burlington and Quincy Railroad between Chicago, Illinois, and Denver, Colorado. In peak years it ran to Colorado Springs. It operated from 1936 to 1973. The Denver Zephyr continued operating after the Burlington Northern Railroad merger in 1970. BN conveyed the train to Amtrak in 1971; Amtrak merged it with the Denver–Oakland City of San Francisco to form the San Francisco Zephyr and dropped the "Denver" name in 1973.

The Sunshine Special was inaugurated by the St. Louis, Iron Mountain and Southern Railway,, on December 5, 1915, to provide a premium level of passenger train service between St. Louis, Little Rock, and destinations in Texas, United States, such as El Paso, San Antonio, Laredo and Houston. An auxiliary section of the train originated in Memphis, Tennessee and linked with the train in Little Rock, Arkansas.

The Cincinnatian was a named passenger train operated by the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad (B&O). The B&O inaugurated service on January 19, 1947, with service between Baltimore, Maryland and Cincinnati, Ohio, carrying the number 75 westbound and 76 eastbound, essentially a truncated route of the National Limited which operated between Jersey City, New Jersey and St. Louis.

The City of St. Louis was a streamlined passenger train operated by the Union Pacific Railroad and the Wabash Railroad between St. Louis, Missouri and Los Angeles, California. It operated from 1946 to 1971.

The Rocky Mountain Rocket was a streamlined passenger train of the Chicago, Rock Island and Pacific Railroad. Rock Island's train numbers 7 and 8 ran between Chicago's LaSalle Street Station and Denver's Union Station and Colorado Springs, Colorado. The Rocky Mountain Rocket ran from 1939 to 1966; the train was discontinued prior to the creation of Amtrak in 1971.

The Texas Zephyr was a named passenger train operated by the Colorado & Southern Railway and the Fort Worth & Denver Railway. The train was originally designated number 1 southbound, and number 2 northbound.

The City of Kansas City was a streamlined passenger train operated by the Wabash Railroad and its successor the Norfolk and Western Railway between St. Louis and Kansas City, Missouri. It operated from 1947 to 1968. At the time of its introduction it was the only streamliner which operated entirely within the state of Missouri.

The Texas Eagle was an American streamlined passenger train operated by the Missouri Pacific Railroad and the Texas and Pacific Railway between St. Louis, Missouri, and multiple destinations in the state of Texas. It operated from 1948 to 1971. The Texas Eagle was one of many trains discontinued when Amtrak began operations in 1971, although Amtrak would revive service over the Missouri Pacific with the Inter-American in 1974. This train was renamed the Eagle in 1981 and finally the Texas Eagle in 1988.
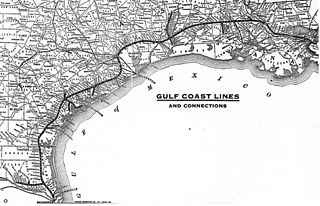
The Gulf Coast Lines was the name of a railroad system comprising three principal railroads, as well as some smaller ones, that stretched from New Orleans, Louisiana, via Baton Rouge and Houston to Brownsville, Texas. Originally chartered as subsidiaries of the Frisco Railroad, the system became independent in 1916 and was purchased by the Missouri Pacific Railroad in 1925.

The Nickel Plate Limited, later known as the City of Cleveland and City of Chicago, was a passenger night train operated by the New York, Chicago and St. Louis Railroad between Chicago and Buffalo, New York via Cleveland, Ohio, with through service to Hoboken, New Jersey via Binghamton and Scranton and the Delaware, Lackawanna and Western Railroad for the Buffalo-Hoboken segment.

The Kansas City–Florida Special was a pooled night train and the premier train of the Frisco Railroad and the Southern Railway. Operating from Kansas City, Missouri to Jacksonville, Florida, it was unique as being one of very few long distance passenger train to traverse the Mississippi River south of St. Louis, Missouri and north of New Orleans, Louisiana.

The Wabash Cannon Ball was a passenger train on the Wabash Railroad that ran from 1950 to 1971. The train was named after the song "Wabash Cannonball". It was the second train to bear the name "Cannon Ball"; the first was the fast express Cannon Ball, which ran in the late 1800s to the early 20th century.
The Valley Eagle was a named streamliner passenger train of the Missouri Pacific Railroad that began in 1948. It ran from Houston, Texas's Union Station to Brownsville, Texas at the Mexico–United States border and a second section to Corpus Christi. It first carried the numbers #11 south and #12 northbound and in later years carried the number of #321 south and #322 heading north.



















