Related Research Articles

Transport economics is a branch of economics founded in 1959 by American economist John R. Meyer that deals with the allocation of resources within the transport sector. It has strong links to civil engineering. Transport economics differs from some other branches of economics in that the assumption of a spaceless, instantaneous economy does not hold. People and goods flow over networks at certain speeds. Demands peak. Advance ticket purchase is often induced by lower fares. The networks themselves may or may not be competitive. A single trip may require the bundling of services provided by several firms, agencies and modes.
In common usage, evaluation is a systematic determination and assessment of a subject's merit, worth and significance, using criteria governed by a set of standards. It can assist an organization, program, design, project or any other intervention or initiative to assess any aim, realizable concept/proposal, or any alternative, to help in decision-making; or to generate the degree of achievement or value in regard to the aim and objectives and results of any such action that has been completed.

Ecotourism is a form of nature-oriented tourism intended to contribute to the conservation of the natural environment, generally defined as being minimally impactful, and including providing both contributions to conservation and environmental education. The definition sometimes also includes being financially beneficial to the host community or making conservation financially possible. There are a range of different definitions, and the correct definition of the term was an active subject of debate as of 2009. The term is also used more widely by many organizations offering nature tourism, which do not focus on being beneficial to the environment.

Urban geography is the subdiscipline of geography that derives from a study of cities and urban processes. Urban geographers and urbanists examine various aspects of urban life and the built environment. Scholars, activists, and the public have participated in, studied, and critiqued flows of economic and natural resources, human and non-human bodies, patterns of development and infrastructure, political and institutional activities, governance, decay and renewal, and notions of socio-spatial inclusions, exclusions, and everyday life. Urban geography includes different other fields in geography such as the physical, social, and economic aspects of urban geography. The physical geography of urban environments is essential to understand why a town is placed in a specific area, and how the conditions in the environment play an important role with regards to whether or not the city successfully develops. Social geography examines societal and cultural values, diversity, and other conditions that relate to people in the cities. Economic geography is important to examine the economic and job flow within the urban population. These various aspects involved in studying urban geography are necessary to better understand the layout and planning involved in the development of urban environments worldwide.

Urban agriculture refers to various practices of cultivating, processing, and distributing food in urban areas. The term also applies to the area activities of animal husbandry, aquaculture, beekeeping, and horticulture in an urban context. Urban agriculture is distinguished from peri-urban agriculture, which takes place in rural areas at the edge of suburbs.

Land use planning or Land-use regulation is the process of regulating the use of land by a central authority. Usually, this is done to promote more desirable social and environmental outcomes as well as a more efficient use of resources. More specifically, the goals of modern land use planning often include environmental conservation, restraint of urban sprawl, minimization of transport costs, prevention of land use conflicts, and a reduction in exposure to pollutants. In the pursuit of these goals, planners assume that regulating the use of land will change the patterns of human behavior, and that these changes are beneficial. The first assumption, that regulating land use changes the patterns of human behavior is widely accepted. However, the second assumption - that these changes are beneficial - is contested, and depends on the location and regulations being discussed.

Youth work is a community support activity aimed at older children and adolescents. Depending upon the culture and the community, different services and institutions may exist for this purpose. In general, it provides an environment where young people can engage in informal educational activities. Throughout the United Kingdom, United States, and Canada, youth work is "to facilitate personal, educational, and social development." Through participative activities and coordinated programs, it seeks to enable young people in "gaining a voice, influence, and place in society in a period of their transition from dependence to independence." By nature and design these activities would be inclusive, educative, and empowering, and based on partnership, equality of opportunity, and respecting diversity.

Community informatics (CI) is an interdisciplinary field that is concerned with using information and communication technology (ICT) to empower members of communities and support their social, cultural, and economic development. Community informatics may contribute to enhancing democracy, supporting the development of social capital, and building well connected communities; moreover, it is probable that such similar actions may let people experience new positive social change. In community informatics, there are several considerations which are the social context, shared values, distinct processes that are taken by members in a community, and social and technical systems. It is formally located as an academic discipline within a variety of academic faculties including information science, information systems, computer science, planning, development studies, and library science among others and draws on insights on community development from a range of backgrounds and disciplines. It is an interdisciplinary approach interested in using ICTs for different forms of community action, as distinct from pure academic study about ICT effects.

A charitable organization or charity is an organization whose primary objectives are philanthropy and social well-being.
A social enterprise is an organization that applies commercial strategies to maximize improvements in financial, social and environmental well-being. This may include maximizing social impact alongside profits for co-owners.

In mathematics, a manifold is a topological space that locally resembles Euclidean space near each point. More precisely, an -dimensional manifold, or -manifold for short, is a topological space with the property that each point has a neighborhood that is homeomorphic to an open subset of -dimensional Euclidean space.

Community organization or community based organization refers to organization aimed at making desired improvements to a community's social health, well-being, and overall functioning. Community organization occurs in geographically, psychosocially, culturally, spiritually, and digitally bounded communities.

Urban horticulture is the science and study of the growing plants in an urban environment. It focuses on the functional use of horticulture so as to maintain and improve the surrounding urban area. Urban horticulture has seen an increase in attention with the global trend of urbanization and works to study the harvest, aesthetic, architectural, recreational and psychological purposes and effects of plants in urban environments.

Comprehensive planning is an ordered process that determines community goals and aspirations in terms of community development. The end product is called a comprehensive plan, also known as a general plan, or master plan. This resulting document expresses and regulates public policies on transportation, utilities, land use, recreation, and housing. Comprehensive plans typically encompass large geographical areas, a broad range of topics, and cover a long-term time horizon. The term comprehensive plan is most often used by urban planners in the United States.
A settlement hierarchy is a way of arranging settlements into a hierarchy based upon their size. The term is used by landscape historians and in the National Curriculum for England. The term is also used in the planning system for the UK and for some other countries such as Ireland, India, and Switzerland. The term was used without comment by the geographer Brian Roberts in 1972.
Intelligence cycle management refers to the overall activity of guiding the intelligence cycle, which is a set of processes used to provide decision-useful information (intelligence) to leaders. The cycle consists of several processes, including planning and direction, collection, processing and exploitation, analysis and production, and dissemination and integration. The related field of counterintelligence is tasked with impeding the intelligence efforts of others. Intelligence organizations are not infallible but, when properly managed and tasked, can be among the most valuable tools of management and government.
Sustainability metrics and indices are measures of sustainability, using numbers to quantify environmental, social and economic aspects of the world. There are multiple perspectives on how to measure sustainability as there is no universal standard. Intead, different disciplines and international organizations have offered measures or indicators of how to measure the concept.
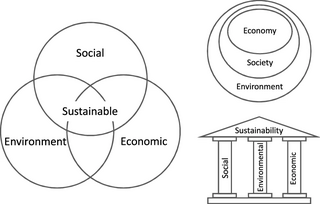
Sustainability is a social goal for people to co-exist on Earth over a long period of time. Definitions of this term are disputed and have varied with literature, context, and time. Sustainability usually has three dimensions : environmental, economic, and social. Many definitions emphasize the environmental dimension. This can include addressing key environmental problems, including climate change and biodiversity loss. The idea of sustainability can guide decisions at the global, national, organizational, and individual levels. A related concept is that of sustainable development, and the terms are often used to mean the same thing. UNESCO distinguishes the two like this: "Sustainability is often thought of as a long-term goal, while sustainable development refers to the many processes and pathways to achieve it."
Community-based monitoring (CBM) is a form of public oversight, ideally driven by local information needs and community values, to increase the accountability and quality of social services such as health, development aid, or to contribute to the management of natural resources. Within the CBM framework, members of a community affected by a social program or environmental change track this change and its local impacts, and generate demands, suggestions, critiques and data that they then act on, including by feeding back to the organization implementing the program or managing the environmental change. For a Toolkit on Community-Based Monitoring methodology with a focus on community oversight of infrastructure projects, see www.communitymonitoring.org. For a library of resources relating to community-based monitoring of tropical forests, see forestcompass.org/how/resources.

Land recycling is the reuse of abandoned, vacant, or underused properties for redevelopment or repurposing.