
The Challenger Deep is the deepest known point of the seabed of Earth, located in the western Pacific Ocean at the southern end of the Mariana Trench, in the ocean territory of the Federated States of Micronesia. According to the GEBCO Gazetteer of Undersea Feature Names the depression's depth is 10,920 ± 10 m (35,827 ± 33 ft) at 11°22.4′N142°35.5′E, although its exact geodetic location remains inconclusive and its depth has been measured at 10,902–10,929 m (35,768–35,856 ft) by deep-diving submersibles, remotely operated underwater vehicles, benthic landers, and sonar bathymetry. The differences in depth estimates and their geodetic positions are scientifically explainable by the difficulty of researching such deep locations.

The Mariana Trench is an oceanic trench located in the western Pacific Ocean, about 200 kilometres (124 mi) east of the Mariana Islands; it is the deepest oceanic trench on Earth. It is crescent-shaped and measures about 2,550 km (1,580 mi) in length and 69 km (43 mi) in width. The maximum known depth is 10,984 ± 25 metres at the southern end of a small slot-shaped valley in its floor known as the Challenger Deep. The deepest point of the trench is more than 2 km (1.2 mi) farther from sea level than the peak of Mount Everest.

The Challenger expedition of 1872–1876 was a scientific programme that made many discoveries to lay the foundation of oceanography. The expedition was named after the naval vessel that undertook the trip, HMS Challenger.

Xenophyophorea is a clade of foraminiferans. Xenophyophores are multinucleate unicellular organisms found on the ocean floor throughout the world's oceans, at depths of 500 to 10,600 metres. They are a kind of foraminiferan that extract minerals from their surroundings and use them to form an exoskeleton known as a test.

Foraminifera are single-celled organisms, members of a phylum or class of Rhizarian protists characterized by streaming granular ectoplasm for catching food and other uses; and commonly an external shell of diverse forms and materials. Tests of chitin are believed to be the most primitive type. Most foraminifera are marine, the majority of which live on or within the seafloor sediment, while a smaller number float in the water column at various depths, which belong to the suborder Globigerinina. Fewer are known from freshwater or brackish conditions, and some very few (nonaquatic) soil species have been identified through molecular analysis of small subunit ribosomal DNA.

The benthic zone is the ecological region at the lowest level of a body of water such as an ocean, lake, or stream, including the sediment surface and some sub-surface layers. The name comes from the Ancient Greek word βένθος (bénthos), meaning "the depths". Organisms living in this zone are called benthos and include microorganisms as well as larger invertebrates, such as crustaceans and polychaetes. Organisms here generally live in close relationship with the substrate and many are permanently attached to the bottom. The benthic boundary layer, which includes the bottom layer of water and the uppermost layer of sediment directly influenced by the overlying water, is an integral part of the benthic zone, as it greatly influences the biological activity that takes place there. Examples of contact soil layers include sand bottoms, rocky outcrops, coral, and bay mud.

An abyssal plain is an underwater plain on the deep ocean floor, usually found at depths between 3,000 and 6,000 metres. Lying generally between the foot of a continental rise and a mid-ocean ridge, abyssal plains cover more than 50% of the Earth's surface. They are among the flattest, smoothest, and least explored regions on Earth. Abyssal plains are key geologic elements of oceanic basins.

Kaikō was a remotely operated underwater vehicle (ROV) built by the Japan Agency for Marine-Earth Science and Technology (JAMSTEC) for exploration of the deep sea. Kaikō was the second of only five vessels ever to reach the bottom of the Challenger Deep, as of 2019. Between 1995 and 2003, this 10.6 ton unmanned submersible conducted more than 250 dives, collecting 350 biological species, some of which could prove to be useful in medical and industrial applications. On 29 May 2003, Kaikō was lost at sea off the coast of Shikoku Island during Typhoon Chan-Hom, when a secondary cable connecting it to its launcher at the ocean surface broke.
The abyssal zone or abyssopelagic zone is a layer of the pelagic zone of the ocean. The word abyss comes from the Greek word ἄβυσσος (ábussos), meaning "bottomless". At depths of 4,000–6,000 m (13,000–20,000 ft), this zone remains in perpetual darkness. It covers 83% of the total area of the ocean and 60% of Earth's surface. The abyssal zone has temperatures around 2–3 °C (36–37 °F) through the large majority of its mass. The water pressure can reach up to 76 MPa.
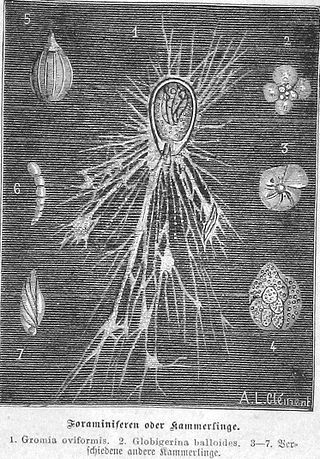
Gromia is a genus of protists, closely related to foraminifera, which inhabit marine and freshwater environments. It is the only genus of the family Gromiidae. Gromia are ameboid, producing filose pseudopodia that extend out from the cell's proteinaceous test through a gap enclosed by the cell's oral capsule. The test, a shell made up of protein that encloses the cytoplasm, is made up of several layers of membrane, which resemble honeycombs in shape – a defining character of this genus.
The hadal zone, also known as the hadopelagic zone, is the deepest region of the ocean, lying within oceanic trenches. The hadal zone ranges from around 6 to 11 km below sea level, and exists in long, narrow, topographic V-shaped depressions.

The Allogromiida is an order of single-chambered, mostly organic-walled foraminiferans, including some that produce agglutinated tests (Lagynacea). Genetic studies indicate that some foraminiferans with agglutinated tests, previously included in the Textulariida or as their own order Astrorhizida, may also belong here. Allogromiids produce relatively simple tests, usually with a single chamber, similar to those of other protists such as Gromia. They are found as both marine and freshwater forms, and are the oldest forms known from the fossil record.
The Komokiacea are a small group of amoeboid protozoa, considered to be foraminifera, though there have been suggestions that they are a separate group, closely related to foraminifera. Komokiacea are rather large organisms, often exceeding 300 micrometers in maximum dimensions. Along with Xenophyophores they dominate the macro- and megabenthic fauna in the deep sea and are commonly referred to as "giants protists".

The deep sea is broadly defined as the ocean depth where light begins to fade, at an approximate depth of 200 m (660 ft) or the point of transition from continental shelves to continental slopes. Conditions within the deep sea are a combination of low temperatures, darkness, and high pressure. The deep sea is considered the least explored Earth biome as the extreme conditions make the environment difficult to access and explore.

The Porcupine Abyssal Plain (PAP) is located in international waters, adjacent to the Irish continental margin. The PAP lies beyond the Porcupine Bank's deepest point and is southwest of it. It has a muddy seabed, with scattered abyssal hills that covers an area approximately half the size of Europe's landmass. Its depth ranges from 4,000 metres (13,000 ft) to 4,850 m (15,910 ft).

A deep-sea community is any community of organisms associated by a shared habitat in the deep sea. Deep sea communities remain largely unexplored, due to the technological and logistical challenges and expense involved in visiting this remote biome. Because of the unique challenges, it was long believed that little life existed in this hostile environment. Since the 19th century however, research has demonstrated that significant biodiversity exists in the deep sea.

The North Pacific Subtropical Gyre (NPSG) is the largest contiguous ecosystem on earth. In oceanography, a subtropical gyre is a ring-like system of ocean currents rotating clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and counterclockwise in the Southern Hemisphere caused by the Coriolis Effect. They generally form in large open ocean areas that lie between land masses.
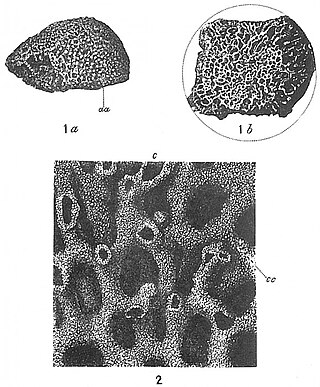
Syringammina is a xenophyophore found off the coast of Scotland, near Rockall. It is one of the largest single-celled organisms known, at up to 20 centimetres (8 in) across. It was first described in 1882 by the oceanographer John Murray, after being discovered on an expedition in the ship Triton which dredged the deep ocean bed off the west coast of Scotland in an effort to find organisms new to science. It was the first xenophyophore to be described and at first its relationship with other organisms was a mystery, but it is now considered to be a member of the Foraminifera.
Stercomata are extracellular pellets of waste material produced by some groups of foraminiferans, including xenophyophoreans and komokiaceans, Gromia, and testate amoebae. The pellets are ovoid (egg-shaped), brownish in color, and on average measure from 10-20 μm in length. Stercomata are composed of small mineral grains and undigested waste products held together by strands of glycosaminoglycans.













