
Herbicides, also commonly known as weed killers, are substances used to control undesired plants, also known as weeds. Selective herbicides control specific weed species while leaving the desired crop relatively unharmed, while non-selective herbicides can be used to clear waste ground, industrial and construction sites, railways and railway embankments as they kill all plant material with which they come into contact. Apart from selective/non-selective, other important distinctions include persistence, means of uptake, and mechanism of action. Historically, products such as common salt and other metal salts were used as herbicides, however, these have gradually fallen out of favor, and in some countries, a number of these are banned due to their persistence in soil, and toxicity and groundwater contamination concerns. Herbicides have also been used in warfare and conflict.
Roundup is the brand name of a systemic, broad-spectrum glyphosate-based herbicide originally produced by Monsanto, which Bayer acquired in 2018. Glyphosate is the most widely used herbicide in the United States. As of 2009, sales of Roundup herbicides still represented about 10 percent of Monsanto's revenue despite competition from Chinese producers of other glyphosate-based herbicides. The overall Roundup line of products, which includes genetically modified seeds, represented about half of Monsanto's yearly revenue. The product is marketed to consumers by Scotts Miracle-Gro Company.

Pesticide resistance describes the decreased susceptibility of a pest population to a pesticide that was previously effective at controlling the pest. Pest species evolve pesticide resistance via natural selection: the most resistant specimens survive and pass on their acquired heritable changes traits to their offspring. If a pest has resistance then that will reduce the pesticide's efficacy – efficacy and resistance are inversely related.
Chlordane, or chlordan, is an organochlorine compound that was used as a pesticide. It is a white solid. In the United States, chlordane was used for termite-treatment of approximately 30 million homes until it was banned in 1988. Chlordane was banned 10 years earlier for food crops like corn and citrus, and on lawns and domestic gardens.

Glyphosate is a broad-spectrum systemic herbicide and crop desiccant. It is an organophosphorus compound, specifically a phosphonate, which acts by inhibiting the plant enzyme 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase (EPSP). It is used to kill weeds, especially annual broadleaf weeds and grasses that compete with crops. Its herbicidal effectiveness was discovered by Monsanto chemist John E. Franz in 1970. Monsanto brought it to market for agricultural use in 1974 under the trade name Roundup. Monsanto's last commercially relevant United States patent expired in 2000.

Lindane, also known as gamma-hexachlorocyclohexane (γ-HCH), gammaxene, Gammallin and benzene hexachloride (BHC), is an organochlorine chemical and an isomer of hexachlorocyclohexane that has been used both as an agricultural insecticide and as a pharmaceutical treatment for lice and scabies.
Silviculture is the practice of controlling the growth, composition/structure, as well as quality of forests to meet values and needs, specifically timber production.

Paraquat (trivial name; ), or N,N′-dimethyl-4,4′-bipyridinium dichloride (systematic name), also known as methyl viologen, is an organic compound with the chemical formula [(C6H7N)2]Cl2. It is classified as a viologen, a family of redox-active heterocycles of similar structure. This salt is one of the most widely used herbicides. It is quick-acting and non-selective, killing green plant tissue on contact. It is also toxic (lethal) to human beings and animals due to its redox activity, which produces superoxide anions. It has been linked to the development of Parkinson's disease and is banned in dozens of countries.
A biopesticide is a biological substance or organism that damages, kills, or repels organisms seen as pests. Biological pest management intervention involves predatory, parasitic, or chemical relationships.
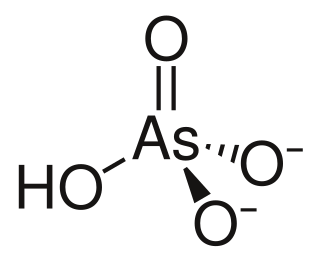
Lead hydrogen arsenate, also called lead arsenate, acid lead arsenate or LA, chemical formula PbHAsO4, is an inorganic insecticide used primarily against the potato beetle. Lead arsenate was the most extensively used arsenical insecticide. Two principal formulations of lead arsenate were marketed: basic lead arsenate (Pb5OH(AsO4)3, CASN: 1327-31-7) and acid lead arsenate (PbHAsO4).

Glufosinate is a naturally occurring broad-spectrum herbicide produced by several species of Streptomyces soil bacteria. Glufosinate is a non-selective, contact herbicide, with some systemic action. Plants may also metabolize bialaphos and phosalacine, other naturally occurring herbicides, directly into glufosinate. The compound irreversibly inhibits glutamine synthetase, an enzyme necessary for the production of glutamine and for ammonia detoxification, giving it antibacterial, antifungal and herbicidal properties. Application of glufosinate to plants leads to reduced glutamine and elevated ammonia levels in tissues, halting photosynthesis and resulting in plant death.
Polyethoxylated tallow amine refers to a range of non-ionic surfactants derived from animal fats (tallow). They are a class of polyethoxylated amines (POEAs). The abbreviation 'POEA' is often erroneously used to refer to POE-tallowamine. They are used primarily as emulsifiers and wetting agents for agrochemical formulations, such as pesticides and herbicides.
Neonicotinoids are a class of neurotoxic insecticides chemically similar to nicotine, developed by scientists at Shell and Bayer in the 1980s. Neonicotinoids became among the widest-used insecticides in crop protection because of their efficacy against a broad spectrum of sucking and chewing pests, together with their high specificity to insects, relatively low risk for nontarget organisms and the environment, and versatility of application. They are also widely employed for veterinary purposes including tick and flea control.
A seed treatment is a treatment of the seed with either biological or chemical agents or by physical methods. Usually done to provide protection to the seed and improve the establishment of healthy crops. Not to be confused with a seed coating.

Christmas tree cultivation is an agricultural, forestry, and horticultural occupation which involves growing pine, spruce, and fir trees specifically for use as Christmas trees.

Pesticide application refers to the practical way in which pesticides are delivered to their biological targets. Public concern about the use of pesticides has highlighted the need to make this process as efficient as possible, in order to minimise their release into the environment and human exposure. The practice of pest management by the rational application of pesticides is supremely multi-disciplinary, combining many aspects of biology and chemistry with: agronomy, engineering, meteorology, socio-economics and public health, together with newer disciplines such as biotechnology and information science.

Torilis japonica, the erect hedgeparsley, upright hedge-parsley or Japanese hedge parsley, is a herbaceous flowering plant species in the celery family Apiaceae. Japanese hedge parsley is considered both an annual and biennial plant depending on the biogeographical location. This means Japanese hedge parsley can complete its life cycle in either one or two growing seasons depending on habitat. Japanese hedge parsley is typically found in areas with disturbed soils, pastures, margins, open woodland, near waste sites, or right-of-way habitats. It can withstand a variety of habitats, thriving in partial and full shaded areas, but also withstanding habitats with full sunlight penetration. It is considered an aggressive invasive species in North America; invading a wide range of habitats due to its environmental tolerance and tendency to outcompete native vegetation. This species is considered a threat in several areas that causes problems relating to overall environmental health and stability. Aside from its environmental implications, T. japonica has potential to fight several cancers through a terpene it produces called Torilin, extracted from its fruits.

2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid is an organic compound with the chemical formula C8H6Cl2O3 which is usually referred to by its ISO common name 2,4-D. It is a systemic herbicide which kills most broadleaf weeds by causing uncontrolled growth in them but most grasses such as cereals, lawn turf, and grassland are relatively unaffected.

Animocarb (Matacil) is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C11H16N2O2. It has a colorless or white crystal-like appearance and is most commonly used as an insecticide.
Glyphosate-based herbicides are usually made of a glyphosate salt that is combined with other ingredients that are needed to stabilize the herbicide formula and allow penetration into plants. The glyphosate-based herbicide Roundup was first developed by Monsanto in the 1970s. It is used most heavily on corn, soy, and cotton crops that have been genetically modified to be resistant to the herbicide. Some products include two active ingredients, such as Enlist Duo which includes 2,4-D as well as glyphosate. As of 2010, more than 750 glyphosate products were on the market. The names of inert ingredients used in glyphosate formulations are usually not listed on the product labels.











