Related Research Articles

Mac. Robertson Land is the portion of Antarctica lying southward of the coast between William Scoresby Bay and Cape Darnley. It is located at 70°00′S65°00′E. In the east, Mac. Robertson Land includes the Prince Charles Mountains. It was named by the British Australian and New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition (BANZARE) (1929–1931), under Sir Douglas Mawson, after Sir Macpherson Robertson of Melbourne, a patron of the expedition.
Cape Morse is a low, ice-covered cape which marks the east side of the entrance to Porpoise Bay and forms the division between Banzare Coast and Clarie Coast in Wilkes Land, Antarctica. It was delineated from air photos taken by U.S. Navy Operation Highjump in 1946–1947, and was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for William H. Morse, purser's steward on the brig Porpoise of the United States Exploring Expedition (1838–1842) under Charles Wilkes.
The Mawson Coast is that portion of the coast of Mac. Robertson Land, Antarctica, lying between William Scoresby Bay, at 59°34′E, and Murray Monolith, at 66°54′E. The coast was sighted during the British Australian New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition (BANZARE), 1929–30, under Sir Douglas Mawson. Further exploration and landings at Cape Bruce and Scullin Monolith were made during BANZARE, 1930–31. Mawson Coast was named by the Antarctic Names Committee of Australia after Mawson in recognition of his great contribution to Antarctic exploration.
Stefansson Bay is a bay indenting the coast for 16 kilometres (10 mi) between Law Promontory and Fold Island. Mawson of the British Australian New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition (BANZARE) applied the name to a sweep of the coast west of Cape Wilkins which he observed on about February 18, 1931. Exploration by DI personnel on the William Scoresby, 1936, and the Lars Christensen expedition 1936–37, defined this section of the coast more accurately. It was named for Vilhjalmur Stefansson, Arctic explorer.
The Tula Mountains are a group of extensive mountains lying immediately eastward of Amundsen Bay in Enderby Land, Antarctica. They were discovered on January 14, 1930, by the British Australian New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition (BANZARE) under Mawson and named "Tula Range" by him after John Biscoe's brig, the Tula, from which Biscoe discovered Enderby Land in 1831. The term "mountains" was recommended for the group following an ANARE sledge survey in 1958 by G.A. Knuckey.
The Scott Mountains are a large number of isolated peaks lying south of Amundsen Bay in Enderby Land of East Antarctica, Antarctica. Discovered on 13 January 1930 by the British Australian New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition (BANZARE) under Sir Douglas Mawson. He named the feature Scott Range after Captain Robert Falcon Scott, Royal Navy. The term mountains is considered more appropriate because of the isolation of its individual features.
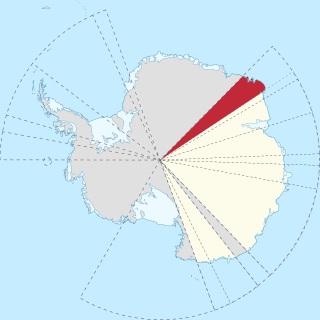
Enderby Land is a projecting landmass of Antarctica. Its shore extends from Shinnan Glacier at about 67°55′S44°38′E to William Scoresby Bay at 67°24′S59°34′E, approximately 1⁄24 of the earth's longitude. It was first documented in western and eastern literature in February 1831 by John Biscoe aboard the whaling brig Tula, and named after the Enderby Brothers of London, the ship's owners who encouraged their captains to combine exploration with sealing.

Cape Royds is a dark rock cape forming the western extremity of Ross Island, facing on McMurdo Sound, Antarctica. It was discovered by the British National Antarctic Expedition (BrNAE) (1901–1904) and named for Lieutenant Charles Royds, Royal Navy, who acted as meteorologist on the expedition. Royds subsequently rose to become an Admiral and was later Commissioner of the Metropolitan Police, London. The cape is the site of Shackleton's Hut, the expedition camp of the British Antarctic Expedition, 1907–09.
Simmers Peaks is a group of three peaks, the highest 840 m, rising above the icecap 13 miles (21 km) southeast of Cape Close and 11 miles (18 km) north of Mount Codrington. They were discovered by the British Australian New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition (BANZARE) under Mawson in 1930 and were named for R.G. Simmers, the meteorologist of the expedition.

Posadowsky Glacier is a glacier about 9 nautical miles long, flowing north to Posadowsky Bay immediately east of Gaussberg. Posadowsky Bay is an open embayment, located just east of the West Ice Shelf and fronting on the Davis Sea in Kaiser Wilhelm II Land. Kaiser Wilhelm II Land is the part of East Antarctica lying between Cape Penck, at 87°43'E, and Cape Filchner, at 91°54'E, and is claimed by Australia as part of the Australian Antarctic Territory. Other notable geographic features in this area include Drygalski Island, located 45 mi NNE of Cape Filchner in the Davis Sea, and Mirny Station, a Russian scientific research station.
Fold Island, also known as Foldøya is an offshore island north of Ives Tongue, 11 kilometres (6 nmi) long and 6 kilometres (3 nmi) wide, which, with smaller islands south, separate Stefansson Bay to the west from William Scoresby Bay to the east. This feature was seen by Discovery Investigations (DI) personnel on the RSS William Scoresby in February 1936, who mapped it as part of the mainland. It was determined to be an island and named Foldøya by Norwegian cartographers who charted this area from aerial photographs taken by the Lars Christensen Expedition (LCE) in January–February 1937.
Borradaile Island is one of the Balleny Islands. It was the site of the first landing south of the Antarctic Circle, and features the "remarkable pinnacle" called Beale Pinnacle, near Cape Beale on its south-eastern coast, and Cape Scoresby on its north-western coast.
Nilsen Bay is a small bay just west of Strahan Glacier, and 18 nautical miles (33 km) east-southeast of Cape Daly. Discovered in February 1931 by the British Australian New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition (BANZARE) under Mawson, who named it after the master of the Norwegian whaler Sir James Clark Ross which transported coal to Antarctic waters for the Discovery. On the map published in the Cape Daly and the Strahan Glacier is called Nielsen Bay. Recent examination of Mawson's notes shows that the bay was placed too far west and the name misspelled.
Cape Davis is a rounded ice-covered cape along the north coast of Edward VIII Plateau, 17 kilometres (9 nmi) east of Magnet Bay. It was discovered on 12 January 1930 by the British Australian and New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition (BANZARE) under Mawson, who named it for Captain John King Davis, Director of Navigation under the Commonwealth Government and ship's captain and second in command of BANZARE.

Jubilee Peak is a peak rising to about 500 metres (1,600 ft) at the north end of Clarence Island, west of Cape Lloyd, in the South Shetland Islands. Following the ascent of the peak by a JSEEIG party, February 2, 1977, it was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in honor of the Silver Jubilee year of Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II.
Cape Pepin is an ice-covered cape between Ravin Bay and Barre Glacier in Antarctica. Discovered in 1840 by the French expedition under Captain Jules Dumont d'Urville and named by him for his wife Adele Pepin. The area was charted by the Australasian Antarctic Expedition in 1912–13, and again by the British Australian New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition (BANZARE) in 1931, both under Mawson. The cape was more recently delineated from aerial photographs taken by U.S. Navy Operation Highjump, 1946–47.

Ferguslie Peninsula is a peninsula 2.4 km (1.5 mi) long, lying between Browns Bay and Macdougal Bay on the north coast of Laurie Island, in the South Orkney Islands of Antarctica. The peninsula was charted in 1903 by the Scottish National Antarctic Expedition under William Speirs Bruce, who named it for Ferguslie, the residence of James Coats, chief patron of the expedition.
Mount Hawkes is, at 1,975 metres (6,480 ft), the highest mountain along the Washington Escarpment, standing at the east side of Jones Valley in the Neptune Range of the Pensacola Mountains, Antarctica.
Mount Marr is a rock peak which rises above the surrounding ice surface 8 nautical miles (15 km) south of Johnston Peak and 8 nautical miles (15 km) west of Douglas Peak, in Enderby Land, Antarctica. It was discovered in January 1930 by the British Australian New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition (BANZARE) under Douglas Mawson and was named after James W.S. Marr, a zoologist on the expedition, whose services were lent to BANZARE by the British Discovery Investigations Committee.
Mount Selwood is a mountain 5 nautical miles (9 km) northeast of Pythagoras Peak, in the Tula Mountains in Enderby Land. It was plotted from air photos taken from ANARE aircraft in 1956 and was named by the Antarctic Names Committee of Australia (ANCA) for C.H.V. Selwood, a member of the crew of the Discovery during the British Australian New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition (BANZARE) of 1929–31.
References
- ↑ "Conradi Peak". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior . Retrieved 2011-11-21.
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from "Conradi Peak". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey.
This article incorporates public domain material from "Conradi Peak". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey.