Related Research Articles
Azotemia, also spelled azotaemia, is a medical condition characterized by abnormally high levels of nitrogen-containing compounds in the blood. It is largely related to insufficient or dysfunctional filtering of blood by the kidneys. It can lead to uremia and acute kidney injury if not controlled.
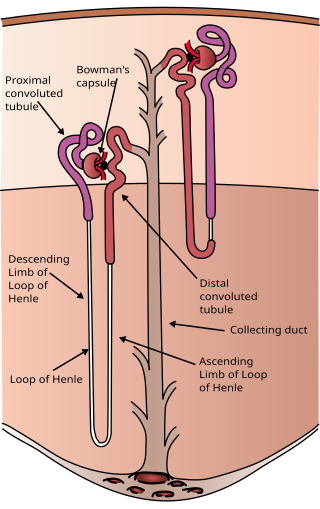
The nephron is the minute or microscopic structural and functional unit of the kidney. It is composed of a renal corpuscle and a renal tubule. The renal corpuscle consists of a tuft of capillaries called a glomerulus and a cup-shaped structure called Bowman's capsule. The renal tubule extends from the capsule. The capsule and tubule are connected and are composed of epithelial cells with a lumen. A healthy adult has 1 to 1.5 million nephrons in each kidney. Blood is filtered as it passes through three layers: the endothelial cells of the capillary wall, its basement membrane, and between the podocyte foot processes of the lining of the capsule. The tubule has adjacent peritubular capillaries that run between the descending and ascending portions of the tubule. As the fluid from the capsule flows down into the tubule, it is processed by the epithelial cells lining the tubule: water is reabsorbed and substances are exchanged ; first with the interstitial fluid outside the tubules, and then into the plasma in the adjacent peritubular capillaries through the endothelial cells lining that capillary. This process regulates the volume of body fluid as well as levels of many body substances. At the end of the tubule, the remaining fluid—urine—exits: it is composed of water, metabolic waste, and toxins.

The renin-angiotensin system (RAS), or renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), is a hormone system that regulates blood pressure, fluid, and electrolyte balance, and systemic vascular resistance.
Diuresis is the excretion of urine, especially when excessive (polyuria). The term collectively denotes the physiologic processes underpinning increased urine production by the kidneys during maintenance of fluid balance.

The collecting duct system of the kidney consists of a series of tubules and ducts that physically connect nephrons to a minor calyx or directly to the renal pelvis. The collecting duct participates in electrolyte and fluid balance through reabsorption and excretion, processes regulated by the hormones aldosterone and vasopressin.

Renal physiology is the study of the physiology of the kidney. This encompasses all functions of the kidney, including maintenance of acid-base balance; regulation of fluid balance; regulation of sodium, potassium, and other electrolytes; clearance of toxins; absorption of glucose, amino acids, and other small molecules; regulation of blood pressure; production of various hormones, such as erythropoietin; and activation of vitamin D.

Loop diuretics are pharmacological agents that primarily inhibit the Na-K-Cl cotransporter located on the luminal membrane of cells along the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle. They are often used for the treatment of hypertension and edema secondary to congestive heart failure, liver cirrhosis, or chronic kidney disease. While thiazide diuretics are more effective in patients with normal kidney function, loop diuretics are more effective in patients with impaired kidney function.

Metabolic acidosis is a serious electrolyte disorder characterized by an imbalance in the body's acid-base balance. Metabolic acidosis has three main root causes: increased acid production, loss of bicarbonate, and a reduced ability of the kidneys to excrete excess acids. Metabolic acidosis can lead to acidemia, which is defined as arterial blood pH that is lower than 7.35. Acidemia and acidosis are not mutually exclusive – pH and hydrogen ion concentrations also depend on the coexistence of other acid-base disorders; therefore, pH levels in people with metabolic acidosis can range from low to high.

Respiratory acidosis is a state in which decreased ventilation (hypoventilation) increases the concentration of carbon dioxide in the blood and decreases the blood's pH.
The anion gap is a value calculated from the results of multiple individual medical lab tests. It may be reported with the results of an electrolyte panel, which is often performed as part of a comprehensive metabolic panel.

Metabolic alkalosis is an acid-base disorder in which the pH of tissue is elevated beyond the normal range (7.35–7.45). This is the result of decreased hydrogen ion concentration, leading to increased bicarbonate, or alternatively a direct result of increased bicarbonate concentrations. The condition typically cannot last long if the kidneys are functioning properly.
Hyperaldosteronism is a medical condition wherein too much aldosterone is produced. High aldosterone levels can lead to lowered levels of potassium in the blood (hypokalemia) and increased hydrogen ion excretion (alkalosis). Aldosterone is normally produced in the adrenal glands.
Hyperchloremic acidosis is a form of metabolic acidosis associated with a normal anion gap, a decrease in plasma bicarbonate concentration, and an increase in plasma chloride concentration. Although plasma anion gap is normal, this condition is often associated with an increased urine anion gap, due to the kidney's inability to secrete ammonia.

Renal tubular acidosis (RTA) is a medical condition that involves an accumulation of acid in the body due to a failure of the kidneys to appropriately acidify the urine. In renal physiology, when blood is filtered by the kidney, the filtrate passes through the tubules of the nephron, allowing for exchange of salts, acid equivalents, and other solutes before it drains into the bladder as urine. The metabolic acidosis that results from RTA may be caused either by insufficient secretion of hydrogen ions into the latter portions of the nephron or by failure to reabsorb sufficient bicarbonate ions from the filtrate in the early portion of the nephron. Although a metabolic acidosis also occurs in those with chronic kidney disease, the term RTA is reserved for individuals with poor urinary acidification in otherwise well-functioning kidneys. Several different types of RTA exist, which all have different syndromes and different causes. RTA is usually an incidental finding based on routine blood draws that show abnormal results. Clinically, patients may present with vague symptoms such as dehydration, mental status changes, or delayed growth in adolescents.

Bartter syndrome (BS) is a rare inherited disease characterised by a defect in the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle, which results in low potassium levels (hypokalemia), increased blood pH (alkalosis), and normal to low blood pressure. There are two types of Bartter syndrome: neonatal and classic. A closely associated disorder, Gitelman syndrome, is milder than both subtypes of Bartter syndrome.

Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors are a class of pharmaceuticals that suppress the activity of carbonic anhydrase. Their clinical use has been established as anti-glaucoma agents, diuretics, antiepileptics, in the management of mountain sickness, gastric and duodenal ulcers, idiopathic intracranial hypertension, neurological disorders, or osteoporosis.
Acid–base homeostasis is the homeostatic regulation of the pH of the body's extracellular fluid (ECF). The proper balance between the acids and bases in the ECF is crucial for the normal physiology of the body—and for cellular metabolism. The pH of the intracellular fluid and the extracellular fluid need to be maintained at a constant level.
Acid–base imbalance is an abnormality of the human body's normal balance of acids and bases that causes the plasma pH to deviate out of the normal range. In the fetus, the normal range differs based on which umbilical vessel is sampled. It can exist in varying levels of severity, some life-threatening.

Distal renal tubular acidosis (dRTA) is the classical form of RTA, being the first described. Distal RTA is characterized by a failure of acid secretion by the alpha intercalated cells of the distal tubule and cortical collecting duct of the distal nephron. This failure of acid secretion may be due to a number of causes. It leads to relatively alkaline urine, due to the kidney's inability to acidify the urine to a pH of less than 5.3.

A diuretic is any substance that promotes diuresis, the increased production of urine. This includes forced diuresis. A diuretic tablet is sometimes colloquially called a water tablet. There are several categories of diuretics. All diuretics increase the excretion of water from the body, through the kidneys. There exist several classes of diuretic, and each works in a distinct way. Alternatively, an antidiuretic, such as vasopressin, is an agent or drug which reduces the excretion of water in urine.
References
- ↑ "Acid-Base Tutorial - Metabolic Acidosis and Alkalosis". Acid-base.com. 2004-11-18. Retrieved 2012-02-15.
- ↑ Garella, Serafino; Chang, Bruce S.; Kahn, Sewell I. (1975). "Dilution acidosis and contraction alkalosis: Review of a concept". Kidney International. 8 (5): 279–283. doi: 10.1038/ki.1975.114 .
- ↑ Luke, R. G.; Galla, J. H. (2012). "It is Chloride Depletion Alkalosis, Not Contraction Alkalosis". Journal of the American Society of Nephrology. 23 (2): 204–207. doi:10.1681/ASN.2011070720. PMC 3269186 . PMID 22223876.