
Diabetes insipidus (DI), alternately called arginine vasopressin deficiency (AVP-D) or arginine vasopressin resistance (AVP-R), is a condition characterized by large amounts of dilute urine and increased thirst. The amount of urine produced can be nearly 20 liters per day. Reduction of fluid has little effect on the concentration of the urine. Complications may include dehydration or seizures.
The molar gas constant is denoted by the symbol R or R. It is the molar equivalent to the Boltzmann constant, expressed in units of energy per temperature increment per amount of substance, rather than energy per temperature increment per particle. The constant is also a combination of the constants from Boyle's law, Charles's law, Avogadro's law, and Gay-Lussac's law. It is a physical constant that is featured in many fundamental equations in the physical sciences, such as the ideal gas law, the Arrhenius equation, and the Nernst equation.

In physiology, dehydration is a lack of total body water, with an accompanying disruption of metabolic processes. It occurs when free water loss exceeds free water intake, usually due to exercise, disease, or high environmental temperature. Mild dehydration can also be caused by immersion diuresis, which may increase risk of decompression sickness in divers.
In physiology, body water is the water content of an animal body that is contained in the tissues, the blood, the bones and elsewhere. The percentages of body water contained in various fluid compartments add up to total body water (TBW). This water makes up a significant fraction of the human body, both by weight and by volume. Ensuring the right amount of body water is part of fluid balance, an aspect of homeostasis.
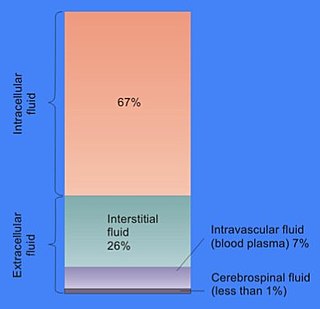
In cell biology, extracellular fluid (ECF) denotes all body fluid outside the cells of any multicellular organism. Total body water in healthy adults is about 50–60% of total body weight; women and the obese typically have a lower percentage than lean men. Extracellular fluid makes up about one-third of body fluid, the remaining two-thirds is intracellular fluid within cells. The main component of the extracellular fluid is the interstitial fluid that surrounds cells.

Hypovolemia, also known as volume depletion or volume contraction, is a state of abnormally low extracellular fluid in the body. This may be due to either a loss of both salt and water or a decrease in blood volume. Hypovolemia refers to the loss of extracellular fluid and should not be confused with dehydration.

In the kidney, the loop of Henle is the portion of a nephron that leads from the proximal convoluted tubule to the distal convoluted tubule. Named after its discoverer, the German anatomist Friedrich Gustav Jakob Henle, the loop of Henle's main function is to create a concentration gradient in the medulla of the kidney.
In environmental chemistry, the chemical oxygen demand (COD) is an indicative measure of the amount of oxygen that can be consumed by reactions in a measured solution. It is commonly expressed in mass of oxygen consumed over volume of solution which in SI units is milligrams per litre (mg/L). A COD test can be used to easily quantify the amount of organics in water. The most common application of COD is in quantifying the amount of oxidizable pollutants found in surface water or wastewater. COD is useful in terms of water quality by providing a metric to determine the effect an effluent will have on the receiving body, much like biochemical oxygen demand (BOD).
The Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH), also known as the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuresis (SIAD), is characterized by a physiologically inappropriate release of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) either from the posterior pituitary gland, or an abnormal non-pituitary source. Unsuppressed ADH causes a physiologically inappropriate increase in solute-free water being reabsorbed by the tubules of the kidney to the venous circulation leading to hypotonic hyponatremia.

Saline is a mixture of sodium chloride (salt) and water. It has a number of uses in medicine including cleaning wounds, removal and storage of contact lenses, and help with dry eyes. By injection into a vein, it is used to treat dehydration such as that from gastroenteritis and diabetic ketoacidosis. Large amounts may result in fluid overload, swelling, acidosis, and high blood sodium. In those with long-standing low blood sodium, excessive use may result in osmotic demyelination syndrome.

Oral rehydration therapy (ORT) is a type of fluid replacement used to prevent and treat dehydration, especially due to diarrhea. It involves drinking water with modest amounts of sugar and salts, specifically sodium and potassium. Oral rehydration therapy can also be given by a nasogastric tube. Therapy should routinely include the use of zinc supplements. Use of oral rehydration therapy has been estimated to decrease the risk of death from diarrhea by up to 93%.
Fluid balance is an aspect of the homeostasis of organisms in which the amount of water in the organism needs to be controlled, via osmoregulation and behavior, such that the concentrations of electrolytes in the various body fluids are kept within healthy ranges. The core principle of fluid balance is that the amount of water lost from the body must equal the amount of water taken in; for example, in humans, the output must equal the input. Euvolemia is the state of normal body fluid volume, including blood volume, interstitial fluid volume, and intracellular fluid volume; hypovolemia and hypervolemia are imbalances. Water is necessary for all life on Earth. Humans can survive for 4 to 6 weeks without food but only for a few days without water.
The trans-tubular potassium gradient (TTKG) is an index reflecting the conservation of potassium in the cortical collecting ducts (CCD) of the kidneys. It is useful in diagnosing the causes of hyperkalemia or hypokalemia. The TTKG estimates the ratio of potassium in the lumen of the CCD to that in the peritubular capillaries.

Osmotic concentration, formerly known as osmolarity, is the measure of solute concentration, defined as the number of osmoles (Osm) of solute per litre (L) of solution. The osmolarity of a solution is usually expressed as Osm/L, in the same way that the molarity of a solution is expressed as "M". Whereas molarity measures the number of moles of solute per unit volume of solution, osmolarity measures the number of osmoles of solute particles per unit volume of solution. This value allows the measurement of the osmotic pressure of a solution and the determination of how the solvent will diffuse across a semipermeable membrane (osmosis) separating two solutions of different osmotic concentration.
Plasma osmolality measures the body's electrolyte–water balance. There are several methods for arriving at this quantity through measurement or calculation.
In the physiology of the kidney, free water clearance (CH2O) is the volume of blood plasma that is cleared of solute-free water per unit time. An example of its use is in the determination of an individual's state of hydration. Conceptually, free water clearance should be thought of relative to the production of isoosmotic urine, which would be equal to the osmolarity of the plasma. If an individual is producing urine more dilute than the plasma, there is a positive value for free water clearance, meaning pure water is lost in the urine in addition to a theoretical isoosmotic filtrate. If the urine is more concentrated than the plasma, then free water is being extracted from the urine, giving a negative value for free water clearance. A negative value is typical for free water clearance, as the kidney usually produces concentrated urine except in the cases of volume overload by the individual.
A volume expander is a type of intravenous therapy that has the function of providing volume for the circulatory system. It may be used for fluid replacement or during surgery to prevent nausea and vomiting after surgery.

In thermodynamics, the volume of a system is an important extensive parameter for describing its thermodynamic state. The specific volume, an intensive property, is the system's volume per unit mass. Volume is a function of state and is interdependent with other thermodynamic properties such as pressure and temperature. For example, volume is related to the pressure and temperature of an ideal gas by the ideal gas law. The physical region covered by a system may or may not coincide with a control volume used to analyze the system.
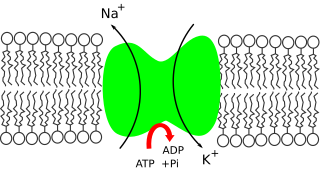
Sodium ions are necessary in small amounts for some types of plants, but sodium as a nutrient is more generally needed in larger amounts by animals, due to their use of it for generation of nerve impulses and for maintenance of electrolyte balance and fluid balance. In animals, sodium ions are necessary for the aforementioned functions and for heart activity and certain metabolic functions. The health effects of salt reflect what happens when the body has too much or too little sodium. Characteristic concentrations of sodium in model organisms are: 10 mM in E. coli, 30 mM in budding yeast, 10 mM in mammalian cell and 100 mM in blood plasma.

A diuretic is any substance that promotes diuresis, the increased production of urine. This includes forced diuresis. A diuretic tablet is sometimes colloquially called a water tablet. There are several categories of diuretics. All diuretics increase the excretion of water from the body, through the kidneys. There exist several classes of diuretic, and each works in a distinct way. Alternatively, an antidiuretic, such as vasopressin, is an agent or drug which reduces the excretion of water in urine.

















