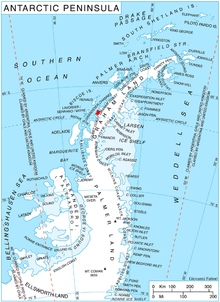
Palmer Land is the portion of the Antarctic Peninsula, Antarctica that lies south of a line joining Cape Jeremy and Cape Agassiz. This application of Palmer Land is consistent with the 1964 agreement between US-ACAN and UK-APC, in which the name Antarctic Peninsula was approved for the major peninsula of Antarctica, and the names Graham Land and Palmer Land for the northern and southern portions, respectively. The line dividing them is roughly 69 degrees south.

The Scaife Mountains is a group of mountains rising west of Prehn Peninsula and between the Ketchum and Ueda glaciers, in Palmer Land, at the base of Antarctic Peninsula.
Zephyr Glacier 1 is a glacier, about 8 miles long, flowing westward from the southwest side of Mount Edgell into George VI Sound to the south of Cape Jeremy. The feature was surveyed by Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS), 1948, and British Antarctic Survey (BAS), 1971-72; photographed from the air by U.S. Navy, 1966. Named by United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) in 1977 after Zephyrus, the west wind. One of several features in this area named after winds.
Atom Rock is an insular rock 0.5 miles (0.8 km) northeast of Rambler Island in the Bragg Islands, lying in Crystal Sound off the west coast of Graham Land. It was mapped from surveys by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (1958–59), and named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in association with Bragg Islands.
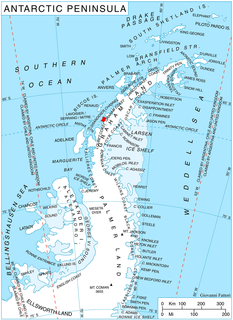
Wooden Peak is a peak 2 nautical miles (3.7 km) southeast of Black Head on Stresher Peninsula on the west coast of Graham Land. Charted by the British Graham Land Expedition (BGLE) under Rymill, 1934-37. Named by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) in 1959 for Frederick E. Wooden, Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) surveyor at Danco Island in 1956 and at Prospect Point in 1957. Wooden was also attached to the British Naval Hydrographic Survey Unit which worked in the area in 1957-58.
Bedford Island is an island about 1 nautical mile (2 km) long, lying at the south end of the Barcroft Islands in the Biscoe Islands. It was mapped from air photos taken by the Falkland Islands and Dependencies Aerial Survey Expedition (1956–57), and named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee for Thomas Bedford, an English physicist who specialized in the measurement of the physical environment of man.

The Boker Rocks are a rocky exposure located 5 nautical miles (9 km) northeast of Von der Wall Point on the south coast of Thurston Island. The feature was mapped by the United States Geological Survey from surveys and from U.S. Navy air photos, 1960–66, and named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Helmut C. Boker, a meteorologist at Byrd Station, 1964–65.
The Bragg Islands are a small group of islands in Crystal Sound, about 7 nautical miles (13 km) north of Cape Rey, Graham Land. They were mapped from surveys by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (1958–59) and from air photos obtained by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition (1947–48). The group was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee for Sir William H. Bragg, an English physicist who interpreted X-ray measurements to give the location of oxygen atoms in the structure of ice.
Triad Islands is a group of three small islands lying 1.5 nautical miles (2.8 km) east of Chavez Island, off the west coast of Graham Land. First charted by the British Graham Land Expedition (BGLE) under Rymill, 1934-37. The name given by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) in 1959 is descriptive.

Dragon Beach is a broad gravel and bounder strewn area flanking Dragon Cove, and extending up to about 10 metres (33 ft) above sea level on Varna Peninsula, Livingston Island in Antarctica. To the north it ascends to the Williams Point platform, to the south it is bounded by an ice ramp, and rises to the west onto the flank of Gargoyle Bastion. The feature is a major source of petrified wood, which is abundantly strewn over this area and has been exposed by weathering from an underlying, poorly exposed volcanic ignimbrite deposit. It was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1998 in association with Dragon Cove.

Mondor Glacier is a glacier 3.5 nautical miles (6 km) long flowing southwest from the head of Depot Glacier into Duse Bay, Trinity Peninsula, Antarctica. This glacier and Depot Glacier together fill the depression between Hope Bay and Duse Bay which marks the northern limit of Tabarin Peninsula. The glacier was mapped in 1946 and 1956 by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS), who named the feature in association with Tabarin Peninsula. "Operation Tabarin" was derived from the "Bal Tabarin" in Paris. In Recueil General des Oeuvres et Fantaisies de Tabarin, Tabarin was the buffoon who attracted the crowd to the booth where Mondor sold his quack medicines.
Gibbs Glacier is a glacier, 15 nautical miles (28 km) long, flowing southeast into the northern part of Mercator Ice Piedmont on the east side of the Antarctic Peninsula. This feature together with Neny Glacier, which flows northwest, occupy a transverse depression between Mercator Ice Piedmont and Neny Fjord on the west side of the Antarctic Peninsula. Gibbs Glacier was photographed from the air and first mapped by the United States Antarctic Service, 1939–41, and the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition, 1947–48. It was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee for Peter M. Gibbs of the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey, a surveyor at Horseshoe Island, 1957, and leader at Stonington Island, 1958, who was responsible for the first ground survey of the glacier.
Morton Cliff is a prominent sub-vertical rock cliff rising to about 35 metres (115 ft) above sea level, forming the western escarpment of Williams Point, Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands off Antarctica. It was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1998 after British Antarctic Survey field assistant Ashley Morton.

Melville Glacier is a glacier, 12 nautical miles (22 km) long, between Mapple Glacier and Pequod Glacier on the east coast of Graham Land, Antarctica. It flows eastwards between Stevrek Ridge and Parlichev Ridge in the Aristotle Mountains, to enter Domlyan Bay in the Weddell Sea. It was surveyed by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey in 1947 and 1955, and was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee after Herman Melville, the author of Moby-Dick. Several other features in the area are named after characters in the story.
Salmon Island is the westernmost of the Fish Islands, lying off the west coast of Graham Land. Charted by the British Graham Land Expedition (BGLE) under Rymill, 1934-37. So named by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) in 1959 because it is one of the Fish Islands.

Slumkey Island is the largest island of the group lying east of Tupman Island, Pitt Islands, in the Biscoe Islands, Antarctica. It is separated from neighbouring Kereka Island to the east-northeast by an 80 m wide passage.

Thompson Peninsula is a peninsula 3 nautical miles (6 km) long on the northeast coast of Anvers Island in the Palmer Archipelago, Antarctica. It is bounded by Patagonia Bay on the northwest and Fournier Bay on the southeast, and ends in Dralfa Point on the northeast.
Rambler Island is the largest of the Bragg Islands, lying in Crystal Sound about 7.5 nautical miles (14 km) north of Cape Rey, Graham Land. Mapped from surveys by Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) (1958–59). The name derives from association with Rambler Harbor which lies on the north side of the island.