
Pentlandite is an iron–nickel sulfide with the chemical formula (Fe,Ni)9S8. Pentlandite has a narrow variation range in nickel to iron ratios (Ni:Fe), but it is usually described as 1:1. In some cases, this ratio is skewed by the presence of pyrrhotite inclusions. It also contains minor cobalt, usually at low levels as a fraction of weight.

Chalcopyrite ( KAL-kə-PY-ryte, -koh-) is a copper iron sulfide mineral and the most abundant copper ore mineral. It has the chemical formula CuFeS2 and crystallizes in the tetragonal system. It has a brassy to golden yellow color and a hardness of 3.5 to 4 on the Mohs scale. Its streak is diagnostic as green-tinged black.

Nickeline or niccolite is the mineral form of nickel arsenide. The naturally-occurring mineral contains roughly 43.9% nickel and 56.1% arsenic by mass, but composition of the mineral may vary slightly.

Volcanogenic massive sulfide ore deposits, also known as VMS ore deposits, are a type of metal sulfide ore deposit, mainly copper-zinc which are associated with and produced by volcanic-associated hydrothermal events in submarine environments.

Temagami, formerly spelled Timagami, is a municipality in northeastern Ontario, Canada, in the Nipissing District with Lake Temagami at its heart.

The Kanichee Mine, also less commonly known as the Ajax Mine, is an abandoned base metal and precious metal mine, located in the Temagami region of northeastern Ontario, Canada. It is near the small unincorporated community of Temagami North, accessed by the Kanichee Mine Road from Highway 11. The Kanichee Mine zone has been explored and mined discontinuously from as early as 1910. During the 20th century, it operated and closed down at least three times, with the most recent being from 1973 to 1976. To date, the discontinuous operation of Kanichee Mine has produced 4.2 million pounds of metal.
Temagami Island, formerly spelt as Timagami Island, is an island in Lake Temagami in Northeastern Ontario, Canada. It is the largest island within the lake, with Bear Island coming second. The island has many hiking trails that lead into the old-growth forest that is a mix of large white and red pine trees. Temagami Mine, later known as Copperfields Mine, was a copper mine that opened on Temagami Island in 1954. It was considered to be the largest deposit of nearly pure chalcopyrite ever discovered in Canada. The mine closed in 1972.
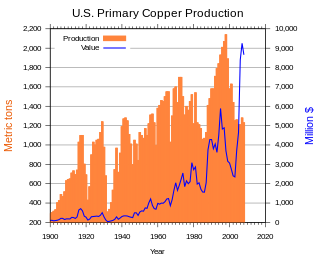
In the United States, copper mining has been a major industry since the rise of the northern Michigan copper district in the 1840s. In 2017, the US produced 1.27 million metric tonnes of copper, worth $8 billion, making it the world's fourth largest copper producer, after Chile, China, and Peru. Copper was produced from 23 mines in the US. Top copper producing states in 2014 were Arizona, Utah, New Mexico, Nevada, and Montana. Minor production also came from Idaho and Missouri. As of 2014, the US had 45 million tonnes of known remaining reserves of copper, the fifth largest known copper reserves in the world, after Chile, Australia, Peru, and Mexico.

The Temagami Greenstone Belt (TGB) is a small 2.7 billion year old greenstone belt in the Temagami region of Northeastern Ontario, Canada. It represents a feature of the Superior craton, an ancient and stable part of the Earth's lithosphere that forms the core of the North American continent and Canadian Shield. The belt is composed of metamorphosed volcanic rocks that range in composition from basalt to rhyolite. These form the east-northeast trend of the belt and are overlain by metamorphosed sedimentary rocks. They were created during several volcanic episodes involving a variety of eruptive styles ranging from passive lava eruptions to viscous explosive eruptions.
The Lac des Îles igneous complex of northwestern Ontario, Canada is a layered gabbroic intrusion which is the host for the largest palladium orebody in Canada. The orebody is currently being mined as a combined open pit and underground operation by North American Palladium.

Beanland Mine, also known as Clenor Mine, is an abandoned surface and underground mine in Northeastern Ontario, Canada. It is located about 1 km (0.62 mi) west of Arsenic Lake and 4 km (2.5 mi) northwest of the town of Temagami in central Strathy Township. It is named after Sydney Beanland, who first claimed the mine site in the 1920s and was a director for the mine from 1937 to 1938.

The Northland Pyrite Mine, also known as James Lake Mine, Rib Lake Mine, Harris Mine or simply Northland Mine, is an abandoned underground mine in Northeastern Ontario, Canada, located on the southwestern shore of James Lake in Best Township of Temagami. It was operated by the Northland Mining Company during the early 1900s with the construction of a 91 m (299 ft) shaft and many open-cuts north of the shaft. Minerals present at the mine include chalcopyrite, pyrite and pyrrhotite, deposited in Precambrian volcanic rock of the Canadian Shield.
Barton Mine, also known as Net Lake Mine, is an abandoned surface and underground mine in Northeastern Ontario, Canada. It is located about 0.50 km (0.31 mi) north of the Temagami Arena in Temagami North and just east of the Ontario Northland Railway in northwestern Strathy Township. Dating back to the early 1900s, it is one of the oldest mines in Temagami. Barton was the site of a fire in the early 1900s, after which it never had active mining again.
The Kanichee layered intrusive complex, also called the Kanichee intrusion and Ajax intrusion, is a layered intrusion in Northeastern Ontario, Canada, located in the central portion of Strathy Township about 6.5 km (4.0 mi) northwest of the town of Temagami. It consists of mafic-ultramafic rocks and is the largest of many mafic-ultramafic intrusions associated with felsic and mafic metavolcanic rocks in the northern Archean Temagami Greenstone Belt.

Big Dan Mine is an abandoned underground mine in Northeastern Ontario, Canada. It is located about 1 km (0.62 mi) southwest of Net Lake and just west of the Ontario Northland Railway in east-central Strathy Township. It is named after Dan O'Connor, who first claimed the site in the 1890s.
O'Connor Mine, also known as Milestone Mine, is an abandoned surface mine in Northeastern Ontario, Canada. It is located about 1 km (0.62 mi) southwest of the town of Temagami near the Northeast Arm of Lake Temagami in northern Strathcona Township. It is named after John O'Connor who first developed the mine site.
Temagami-Lorrain Mine is an abandoned surface and underground mine in Northeastern Ontario, Canada. It is located about 10 km (6.2 mi) northeast of the town of Temagami near Sauvé Lake in central Cassels Township. It is named after the Temagami-Lorrain Mining Company, which carried out work on the property in the early 1900s.
Priest Mine is an abandoned surface and underground mine in Northeastern Ontario, Canada. It is located about 19 km (12 mi) northwest of the hamlet of Marten River on an island in north-central Cross Lake. Dating back to the early 1900s, it is one of the oldest mines in the municipality of Temagami.
The Danlou Occurrence, also known as the Danlou Gold Occurrence and the Mortimer Occurrence, is a mineralized zone in Northeastern Ontario, Canada. Gold is the occurrence's primary commodity, while copper and silver are secondary commodities. It occurs in a quartz vein within a diabase-porphyry shear zone. Pyrite and chalcopyrite are present in small amounts.











