Bioleaching is the extraction or liberation of metals from their ores through the use of living organisms. Bioleaching is one of several applications within biohydrometallurgy and several methods are used to treat ores or concentrates containing copper, zinc, lead, arsenic, antimony, nickel, molybdenum, gold, silver, and cobalt.

Smelting is a process of applying heat and a chemical reducing agent to an ore to extract a desired base metal product. It is a form of extractive metallurgy that is used to obtain many metals such as iron, copper, silver, tin, lead and zinc. Smelting uses heat and a chemical reducing agent to decompose the ore, driving off other elements as gases or slag and leaving the metal behind. The reducing agent is commonly a fossil-fuel source of carbon, such as carbon monoxide from incomplete combustion of coke—or, in earlier times, of charcoal. The oxygen in the ore binds to carbon at high temperatures, as the chemical potential energy of the bonds in carbon dioxide is lower than that of the bonds in the ore.

Limonite is an iron ore consisting of a mixture of hydrated iron(III) oxide-hydroxides in varying composition. The generic formula is frequently written as FeO(OH)·nH2O, although this is not entirely accurate as the ratio of oxide to hydroxide can vary quite widely. Limonite is one of the three principal iron ores, the others being hematite and magnetite, and has been mined for the production of iron since at least 400 BC.
Extractive metallurgy is a branch of metallurgical engineering wherein process and methods of extraction of metals from their natural mineral deposits are studied. The field is a materials science, covering all aspects of the types of ore, washing, concentration, separation, chemical processes and extraction of pure metal and their alloying to suit various applications, sometimes for direct use as a finished product, but more often in a form that requires further working to achieve the given properties to suit the applications.

Chalcopyrite ( KAL-kə-PY-ryte, -koh-) is a copper iron sulfide mineral and the most abundant copper ore mineral. It has the chemical formula CuFeS2 and crystallizes in the tetragonal system. It has a brassy to golden yellow color and a hardness of 3.5 to 4 on the Mohs scale. Its streak is diagnostic as green-tinged black.

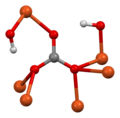
Basic copper carbonate is a chemical compound, more properly called copper(II) carbonate hydroxide. It can be classified as a coordination polymer or a salt. It consists of copper(II) bonded to carbonate and hydroxide with formula Cu2(CO3)(OH)2. It is a green solid that occurs in nature as the mineral malachite. It has been used since antiquity as a pigment, and it is still used as such in artist paints, sometimes called verditer, green bice, or mountain green.

Galena, also called lead glance, is the natural mineral form of lead(II) sulfide (PbS). It is the most important ore of lead and an important source of silver.

Azurite or Azure spar is a soft, deep-blue copper mineral produced by weathering of copper ore deposits. During the early 19th century, it was also known as chessylite, after the type locality at Chessy-les-Mines near Lyon, France. The mineral, a basic carbonate with the chemical formula Cu3(CO3)2(OH)2, has been known since ancient times, and was mentioned in Pliny the Elder's Natural History under the Greek name kuanos (κυανός: "deep blue," root of English cyan) and the Latin name caeruleum. Copper (Cu2+) gives it its blue color.

Nickeline or niccolite is the mineral form of nickel arsenide. The naturally-occurring mineral contains roughly 43.9% nickel and 56.1% arsenic by mass, but composition of the mineral may vary slightly.

Copper extraction refers to the methods used to obtain copper from its ores. The conversion of copper ores consists of a series of physical, chemical, and electrochemical processes. Methods have evolved and vary with country depending on the ore source, local environmental regulations, and other factors.

Dioptase is an intense emerald-green to bluish-green mineral that is cyclosilicate of copper. It is transparent to translucent. Its luster is vitreous to sub-adamantine. Its formula is Cu6Si6O18·6H2O, also reported as CuSiO2(OH)2. It has a Mohs hardness of 5, the same as tooth enamel. Its specific gravity is 3.28–3.35, and it has two perfect and one very good cleavage directions. Additionally, dioptase is very fragile, and specimens must be handled with great care. It is a trigonal mineral, forming six-sided crystals that are terminated by rhombohedra.
Hydrometallurgy is a technique within the field of extractive metallurgy, the obtaining of metals from their ores. Hydrometallurgy involve the use of aqueous solutions for the recovery of metals from ores, concentrates, and recycled or residual materials. Processing techniques that complement hydrometallurgy are pyrometallurgy, vapour metallurgy, and molten salt electrometallurgy. Hydrometallurgy is typically divided into three general areas:

Copper(II) hydroxide is the hydroxide of copper with the chemical formula of Cu(OH)2. It is a pale greenish blue or bluish green solid. Some forms of copper(II) hydroxide are sold as "stabilized" copper(II) hydroxide, although they likely consist of a mixture of copper(II) carbonate and hydroxide. Cupric hydroxide is a strong base, although its low solubility in water makes this hard to observe directly.

Heap leaching is an industrial mining process used to extract precious metals, copper, uranium, and other compounds from ore using a series of chemical reactions that absorb specific minerals and re-separate them after their division from other earth materials. Similar to in situ mining, heap leach mining differs in that it places ore on a liner, then adds the chemicals via drip systems to the ore, whereas in situ mining lacks these liners and pulls pregnant solution up to obtain the minerals. Heap leaching is widely used in modern large-scale mining operations as it produces the desired concentrates at a lower cost compared to conventional processing methods such as flotation, agitation, and vat leaching.
In ore deposit geology, supergene processes or enrichment are those that occur relatively near the surface as opposed to deep hypogene processes. Supergene processes include the predominance of meteoric water circulation (i.e. water derived from precipitation) with concomitant oxidation and chemical weathering. The descending meteoric waters oxidize the primary (hypogene) sulfide ore minerals and redistribute the metallic ore elements. Supergene enrichment occurs at the base of the oxidized portion of an ore deposit. Metals that have been leached from the oxidized ore are carried downward by percolating groundwater, and react with hypogene sulfides at the supergene-hypogene boundary. The reaction produces secondary sulfides with metal contents higher than those of the primary ore. This is particularly noted in copper ore deposits where the copper sulfide minerals chalcocite (Cu2S), covellite (CuS), digenite (Cu18S10), and djurleite (Cu31S16) are deposited by the descending surface waters.

In-situ leaching (ISL), also called in-situ recovery (ISR) or solution mining, is a mining process used to recover minerals such as copper and uranium through boreholes drilled into a deposit, in situ. In-situ leach works by artificially dissolving minerals occurring naturally in the solid state.
The Whim Creek Copper Mine is a copper oxide mine, located in the City of Karratha in the Pilbara region of Western Australia.

Pseudomalachite is a phosphate of copper with hydroxyl, named from the Greek for "false" and "malachite", because of its similarity in appearance to the carbonate mineral malachite, Cu2(CO3)(OH)2. Both are green coloured secondary minerals found in oxidised zones of copper deposits, often associated with each other. Pseudomalachite is polymorphous with reichenbachite and ludjibaite. It was discovered in 1813. Prior to 1950 it was thought that dihydrite, lunnite, ehlite, tagilite and prasin were separate mineral species, but Berry analysed specimens labelled with these names from several museums, and found that they were in fact pseudomalachite. The old names are no longer recognised by the IMA.

Cobalt extraction refers to the techniques used to extract cobalt from its ores and other compound ores. Several methods exist for the separation of cobalt from copper and nickel. They depend on the concentration of cobalt and the exact composition of the ore used.

Azurite is an inorganic pigment derived from the mineral of the same name. It was likely used by artists as early as the Fourth Dynasty in Egypt, but it was less frequently employed than synthetically produced copper pigments such as Egyptian Blue. In the Middle Ages and Renaissance, it was the most prevalent blue pigment in European paintings, appearing more commonly than the more expensive ultramarine. Azurite's derivation from copper mines tends to give it a greenish hue, in contrast with the more violet tone of ultramarine. Azurite is also less stable than ultramarine, and notable paintings such as Michelangelo's The Entombment have seen their azure blues turn to olive green in time. Azurite pigment typically includes traces of malachite and cuprite; both minerals are found alongside azurite in nature, and they may account for some of the green discoloration of the pigment. The particle size of azurite pigment has been shown to have a significant effect on its chromatic intensity, and the manner of grinding and preparing the pigment therefore has a major impact on its appearance.