
Molybdenum is a chemical element; it has symbol Mo and atomic number 42. The name derived from Ancient Greek Μόλυβδος molybdos, meaning lead, since its ores were confused with lead ores. Molybdenum minerals have been known throughout history, but the element was discovered in 1778 by Carl Wilhelm Scheele. The metal was first isolated in 1781 by Peter Jacob Hjelm.

Rhenium is a chemical element; it has symbol Re and atomic number 75. It is a silvery-gray, heavy, third-row transition metal in group 7 of the periodic table. With an estimated average concentration of 1 part per billion (ppb), rhenium is one of the rarest elements in the Earth's crust. It has the third-highest melting point and second-highest boiling point of any element at 5869 K. It resembles manganese and technetium chemically and is mainly obtained as a by-product of the extraction and refinement of molybdenum and copper ores. It shows in its compounds a wide variety of oxidation states ranging from −1 to +7.

Group 6, numbered by IUPAC style, is a group of elements in the periodic table. Its members are chromium (Cr), molybdenum (Mo), tungsten (W), and seaborgium (Sg). These are all transition metals and chromium, molybdenum and tungsten are refractory metals.

Chalcopyrite ( KAL-kə-PY-ryte, -koh-) is a copper iron sulfide mineral and the most abundant copper ore mineral. It has the chemical formula CuFeS2 and crystallizes in the tetragonal system. It has a brassy to golden yellow color and a hardness of 3.5 to 4 on the Mohs scale. Its streak is diagnostic as green-tinged black.

Molybdenum disulfide is an inorganic compound composed of molybdenum and sulfur. Its chemical formula is MoS2.

Bornite, also known as peacock ore, is a sulfide mineral with chemical composition Cu5FeS4 that crystallizes in the orthorhombic system (pseudo-cubic).

Group 7, numbered by IUPAC nomenclature, is a group of elements in the periodic table. It contains manganese (Mn), technetium (Tc), rhenium (Re) and bohrium (Bh). This group lies in the d-block of the periodic table, and are hence transition metals. This group is sometimes called the manganese group or manganese family after its lightest member; however, the group itself has not acquired a trivial name because it belongs to the broader grouping of the transition metals.

Powellite is a calcium molybdate mineral with formula CaMoO4. Powellite crystallizes with tetragonal – dipyramidal crystal structure as transparent adamantine blue, greenish-brown, yellow-to-grey typically anhedral forms. It exhibits distinct cleavage, and has a brittle-to-conchoidal fracture. It has a Mohs hardness of 3.5 to 4 and a specific gravity of 4.25. It forms a solid solution series with scheelite (calcium tungstate, CaWO4). It has refractive index values of nω=1.974 and nε=1.984.
Molybdenum trioxide describes a family of inorganic compounds with the formula MoO3(H2O)n where n = 0, 1, 2. The anhydrous compound is produced on the largest scale of any molybdenum compound since it is the main intermediate produced when molybdenum ores are purified. The anhydrous oxide is a precursor to molybdenum metal, an important alloying agent. It is also an important industrial catalyst. It is a yellow solid, although impure samples can appear blue or green.

A chalcogenide is a chemical compound consisting of at least one chalcogen anion and at least one more electropositive element. Although all group 16 elements of the periodic table are defined as chalcogens, the term chalcogenide is more commonly reserved for sulfides, selenides, tellurides, and polonides, rather than oxides. Many metal ores exist as chalcogenides. Photoconductive chalcogenide glasses are used in xerography. Some pigments and catalysts are also based on chalcogenides. The metal dichalcogenide MoS2 is a common solid lubricant.

Rheniite is a very rare rhenium sulfide mineral with the chemical formula. It forms metallic, silver grey platey crystals in the triclinic - pinacoidal class. It has a specific gravity of 7.5.

A native metal is any metal that is found pure in its metallic form in nature. Metals that can be found as native deposits singly or in alloys include antimony, arsenic, bismuth, cadmium, chromium, cobalt, indium, iron, manganese, molybdenum, nickel, niobium, rhenium, tantalum, tellurium, tin, titanium, tungsten, vanadium, and zinc, as well as the gold group and the platinum group. Among the alloys found in native state have been brass, bronze, pewter, German silver, osmiridium, electrum, white gold, silver-mercury amalgam, and gold-mercury amalgam.

In chemistry, a molybdate is a compound containing an oxyanion with molybdenum in its highest oxidation state of 6: O−−Mo(=O)2−O−. Molybdenum can form a very large range of such oxyanions, which can be discrete structures or polymeric extended structures, although the latter are only found in the solid state. The larger oxyanions are members of group of compounds termed polyoxometalates, and because they contain only one type of metal atom are often called isopolymetalates. The discrete molybdenum oxyanions range in size from the simplest MoO2−
4, found in potassium molybdate up to extremely large structures found in isopoly-molybdenum blues that contain for example 154 Mo atoms. The behaviour of molybdenum is different from the other elements in group 6. Chromium only forms the chromates, CrO2−
4, Cr
2O2−
7, Cr
3O2−
10 and Cr
4O2−
13 ions which are all based on tetrahedral chromium. Tungsten is similar to molybdenum and forms many tungstates containing 6 coordinate tungsten.

Ferrimolybdite is a hydrous iron molybdate mineral with formula: Fe3+2(MoO4)3·8(H2O) or Fe3+2(MoO4)3·n(H2O). It forms coatings and radial aggregates of soft yellow needles which crystallize in the orthorhombic system.

Lindgrenite is an uncommon copper molybdate mineral with formula: Cu3(MoO4)2(OH)2. It occurs as tabular to platey monoclinic green to yellow green crystals.
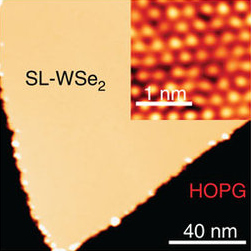
Tungsten diselenide is an inorganic compound with the formula WSe2. The compound adopts a hexagonal crystalline structure similar to molybdenum disulfide. The tungsten atoms are covalently bonded to six selenium ligands in a trigonal prismatic coordination sphere while each selenium is bonded to three tungsten atoms in a pyramidal geometry. The tungsten–selenium bond has a length of 0.2526 nm, and the distance between selenium atoms is 0.334 nm. It is a well studied example of a layered material. The layers stack together via van der Waals interactions. WSe2 is a very stable semiconductor in the group-VI transition metal dichalcogenides.

Transition-metal dichalcogenide (TMD or TMDC) monolayers are atomically thin semiconductors of the type MX2, with M a transition-metal atom (Mo, W, etc.) and X a chalcogen atom (S, Se, or Te). One layer of M atoms is sandwiched between two layers of X atoms. They are part of the large family of so-called 2D materials, named so to emphasize their extraordinary thinness. For example, a MoS2 monolayer is only 6.5 Å thick. The key feature of these materials is the interaction of large atoms in the 2D structure as compared with first-row transition-metal dichalcogenides, e.g., WTe2 exhibits anomalous giant magnetoresistance and superconductivity.
Ekplexite is a unique sulfide-hydroxide niobium-rich mineral with the formula (Nb,Mo)S2•(Mg1−xAlx)(OH)2+x. It is unique because niobium is usually found in oxide or, eventually, silicate minerals. Ekplexite is a case in which chalcophile behaviour of niobium is shown, which means niobium present in a sulfide mineral. The unique combination of elements in ekplexite has to do with its name, which comes from a Greek world on "surprise". The other example of chalcophile behaviour of niobium is edgarite, FeNb3S6, and both minerals were found in the same environment, which is a fenitic rock of Mt. Kaskasnyunchorr, Khibiny Massif, Kola Peninsula, Russia. Analysis of the same rock has revealed the presence of two analogues of ekplexite, kaskasite (molybdenum-analogue) and manganokaskasite (molybdenum- and manganese-analogue). All three minerals belong to the valleriite group, and crystallize in the trigonal system with similar possible space groups.

Tantalum diselenide is a compound made with tantalum and selenium atoms, with chemical formula TaSe2, which belongs to the family of transition metal dichalcogenides. In contrast to molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) or rhenium disulfide (ReS2), tantalum diselenide does not occur spontaneously in nature, but it can be synthesized. Depending on the growth parameters, different types of crystal structures can be stabilized.

Szenicsite is a copper hydroxy molybdate mineral, named after husband and wife Terry and Marissa Szenics, American mineral collectors who found the first specimens. When it was first discovered in Atacama, Chile, it was thought to be lindgrenite. The occurrence appeared in an isolated area, which was about one cubic meter in size. The mineral occurred in cavities of copper bearing powellite and matrix rich molybdenite. These cavities were filled with a material resembling clay. Outside of the zone the szenicsite crystals grew, copper levels seemed to decrease, and the mineralization changed to lindgrenite. Moving further from the zone, the minerals growing seemed to be lacking copper, and consisted of powellite blebs in the ore. Szenicsite was approved by the IMA in 1993.





















