Related Research Articles

Velociraptor is a genus of small dromaeosaurid dinosaurs that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous epoch, about 75 million to 71 million years ago. Two species are currently recognized, although others have been assigned in the past. The type species is V. mongoliensis, named and described in 1924. Fossils of this species have been discovered in the Djadochta Formation, Mongolia. A second species, V. osmolskae, was named in 2008 for skull material from the Bayan Mandahu Formation, China.

A claw is a curved, pointed appendage found at the end of a toe or finger in most amniotes. Some invertebrates such as beetles and spiders have somewhat similar fine, hooked structures at the end of the leg or tarsus for gripping a surface as they walk. The pincers of crabs, lobsters and scorpions, more formally known as their chelae, are sometimes called claws.
The beak, bill, or rostrum is an external anatomical structure found mostly in birds, but also in turtles, non-avian dinosaurs and a few mammals. A beak is used for pecking, grasping, and holding, preening, courtship, and feeding young. The terms beak and rostrum are also used to refer to a similar mouth part in some ornithischians, pterosaurs, cetaceans, dicynodonts, rhynchosaurs, anuran tadpoles, monotremes, sirens, pufferfish, billfishes, and cephalopods.

Rattlesnakes are venomous snakes that form the genera Crotalus and Sistrurus of the subfamily Crotalinae. All rattlesnakes are vipers. Rattlesnakes are predators that live in a wide array of habitats, hunting small animals such as birds and rodents.
A cutaneous receptor is a sensory receptor found in the skin that provides information about temperature, touch, spatial orientation,pressure, and metabolic circumstances. The main four types of cutaneous receptors are tactile corpuscles, bulbous corpuscles, Pacinian corpuscles, and Merkel nerve endings, although the latter do not qualify as sensory corpuscles in the narrow sense.
A mechanoreceptor, also called mechanoceptor, is a sensory receptor that responds to mechanical pressure or distortion. Mechanoreceptors are located on sensory neurons that convert mechanical pressure into electrical signals that, in animals, are sent to the central nervous system.

Vipers are snakes in the family Viperidae, found in most parts of the world, except for Antarctica, Australia, Hawaii, Madagascar, New Zealand, Ireland, and various other isolated islands. They are venomous and have long, hinged fangs that permit deep penetration and injection of their venom. Three subfamilies are currently recognized. They are also known as viperids. The name "viper" is derived from the Latin word vipera, -ae, also meaning viper, possibly from vivus ("living") and parere, referring to the trait viviparity common in vipers like most of the species of Boidae.

Tactile corpuscles or Meissner's corpuscles are a type of mechanoreceptor discovered by anatomist Georg Meissner (1829–1905) and Rudolf Wagner. This corpuscle is a type of nerve ending in the skin that is responsible for sensitivity to pressure. In particular, they have their highest sensitivity when sensing vibrations between 10 and 50 hertz. They are rapidly adaptive receptors. They are most concentrated in thick hairless skin, especially at the finger pads.

A dorsal root ganglion is a cluster of neurons in a dorsal root of a spinal nerve. The cell bodies of sensory neurons known as first-order neurons are located in the dorsal root ganglia.

The Pacinian corpuscle is a low-threshold mechanoreceptor responsive to vibration or pressure, found in the skin and other internal organs. In the skin it is one of the four main types of cutaneous receptors.
Glabrousness is the technical term for a lack of hair, down, setae, trichomes or other such covering. A glabrous surface may be a natural characteristic of all or part of a plant or animal, or be due to loss because of a physical condition, such as alopecia universalis in humans, which causes hair to fall out or not regrow.
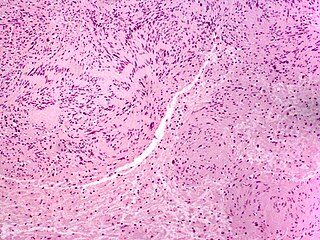
A neuroma is a growth or tumor of nerve tissue. Neuromas tend to be benign ; many nerve tumors, including those that are commonly malignant, are nowadays referred to by other terms.
Deep fascia is a fascia, a layer of dense connective tissue that can surround individual muscles and groups of muscles to separate into fascial compartments.

The tactile corpuscles of Grandry or Grandry corpuscles are mechanoreceptors found in the beak skin and oral mucosa of aquatic birds including waterfowl. They were first described in 1869 in the bill skin of ducks and geese. Their general structure includes the flattened endings of an afferent nerve fiber sandwiched between two or more somewhat flattened sensory cells called Grandry cells, all surrounded by a layer of satellite cells and a partial capsule of collagen protein. Electrophysiological studies have shown that Grandry corpuscles function as rapidly adapting velocity detectors. In birds, Grandry and Merkel corpuscles share many morphological similarities, which has led to some confusion in the literature over their classification.

The bulboid corpuscles are cutaneous receptors in humans and other animals.

Confuciusornithidae is an extinct family of pygostylian avialans known from the Early Cretaceous, found in northern China. They are commonly placed as a sister group to Ornithothoraces, a group that contains all extant birds along with their closest extinct relatives. Confuciusornithidae contains four genera, possessing both shafted and non-shafted (downy) feathers. Some specimens probably referable to this clade represents one of the earliest known fossil evidence of primary feather moulting. They are also noted for their distinctive pair of ribbon-like tail feathers of disputed function.

The ability to sense infrared thermal radiation evolved independently in three different groups of snakes, consisting of the families of Boidae (boas), Pythonidae (pythons), and the subfamily Crotalinae. What is commonly called a pit organ allows these animals to essentially "see" radiant heat at wavelengths between 5 and 30 μm. The more advanced infrared sense of pit vipers allows these animals to strike prey accurately even in the absence of light, and detect warm objects from several meters away. It was previously thought that the organs evolved primarily as prey detectors, but recent evidence suggests that it may also be used in thermoregulation and predator detection, making it a more general-purpose sensory organ than was supposed.
Pallesthesia, or vibratory sensation, is the ability to perceive vibration. This sensation, often conducted through skin and bone, is usually generated by mechanoreceptors such as Pacinian corpuscles, Merkel disk receptors, and tactile corpuscles. All of these receptors stimulate an action potential in afferent nerves found in various layers of the skin and body. The afferent neuron travels to the spinal column and then to the brain where the information is processed. Damage to the peripheral nervous system or central nervous system can result in a decline or loss of pallesthesia.

The somatosensory system, or somatic sensory system is a subset of the sensory nervous system. It has two subdivisions, one for the detection of mechanosensory information related to touch, and the other for the nociception detection of pain and temperature. The main functions of the somatosensory system are the perception of external stimuli, the perception of internal stimuli, and the regulation of body position and balance (proprioception).
A sense is a biological system used by an organism for sensation, the process of gathering information about the surroundings through the detection of stimuli. Although, in some cultures, five human senses were traditionally identified as such, many more are now recognized. Senses used by non-human organisms are even greater in variety and number. During sensation, sense organs collect various stimuli for transduction, meaning transformation into a form that can be understood by the brain. Sensation and perception are fundamental to nearly every aspect of an organism's cognition, behavior and thought.
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1061 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1061 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ↑ Edward Klein (1785). Elements of histology. Lea. p. 124 . Retrieved 13 November 2012.
- ↑ Piersma, Theunis; van Aelst, Renee; Kurk, Karin; Berkhoudt, Herman; Maas, Leo R. M. (1998). "A New Pressure Sensory Mechanism for Prey Detection in Birds: The Use of Principles of Seabed Dynamics?". Proceedings: Biological Sciences. 265 (1404): 1377–1383. doi:10.1098/rspb.1998.0445. PMC 1689215 .