
The Court of Cassation is the supreme court for civil and criminal cases in France. It is one of the country's four apex courts, along with the Council of State, the Constitutional Council and the Jurisdictional Disputes Tribunal.

The Palais de Justice, is a judicial center and courthouse in Paris, located on the Île de la Cité. It contains the Court of Appeal of Paris, the busiest appellate court in France, and France's highest court for ordinary cases, the Court of Cassation. It formerly housed the Tribunal de grande instance de Paris which was relocated in 2018 to a new high-rise building in Paris's Batignolles neighborhood. The Palais de Justice occupies a large part of the medieval Palais de la Cité, the former royal palace of the kings of France, which also includes Sainte Chapelle, the royal chapel, and the Conciergerie, a notorious former prison, which operated from 1380 to 1914. It is located in close proximity to the Tribunal of Commerce, the Prefecture of Police of Paris, and the offices of the Paris Bar Association.

A court of cassation is a high-instance court that exists in some judicial systems. Courts of cassation do not re-examine the facts of a case; they only interpret the relevant law. In this, they are appellate courts of the highest instance. In this way, they differ from systems that have a supreme court that can rule on both the facts of a case and the relevant law. The term derives from the Latin cassare, "to reverse or overturn".

France's independent court system enjoys special statutory protection from the executive branch. Procedures for the appointment, promotion, and removal of judges vary depending on whether it is for the ordinary or the administrative stream. Judicial appointments in the judicial stream must be approved by a special panel, the High Council of the Judiciary. Once appointed, career judges serve for life and cannot be removed without specific disciplinary proceedings conducted before the council with due process.

The judiciary of Romania is organized as a hierarchical system of courts, with a civil law system. Provisions regarding its structure and organization are found in the Constitution and Law no. 304/2004 on judicial organization.
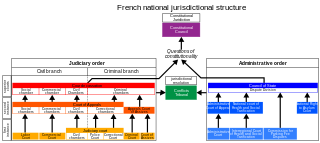
French law has a dual jurisdictional system comprising private law, also known as judicial law, and public law.

The Supreme Court of Cassation is the highest court of appeal or court of last resort in Italy. It has its seat in the Palace of Justice, Rome.

The judicial system of Egypt is an independent branch of the Egyptian government which includes both secular and religious courts.

The Court of Cassation of Belgium is the supreme court of the Belgian judiciary. The court is composed of thirty judges with life tenure who are nominated by the High Council of Justice of Belgium and appointed by the Belgian federal government. The court handles cases in the two main languages of Belgium, Dutch and French, and provides certain facilities for cases in German. The court is assisted in its work by a public prosecutor's office and a bar association, which both function separately from other structures. The duty of the public prosecutor's office is to provide advisory opinions to the court on how the law ought to be interpreted and applied. The attorneys of the court's bar association assist litigants in proceedings before the court; in certain cases, their assistance is mandatory.

In most legal jurisdictions, a supreme court, also known as a court of last resort, apex court, and highcourt of appeal, and court of final appeal, is the highest court within the hierarchy of courts. Broadly speaking, the decisions of a supreme court are binding on all other courts in a nation and are not subject to further review by any other court. Supreme courts typically function primarily as appellate courts, hearing appeals from decisions of lower trial courts, or from intermediate-level appellate courts. A supreme court can also, in certain circumstances, act as a court of original jurisdiction.

The Court of Cassation is the main court of last resort in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It has its seat in the Kinshasa Palace of Justice.

The courts of appeal are the main appellate courts in the judicial system of Belgium, which hear appeals against judgements of the tribunals of first instance, the enterprise tribunals and the presidents of those tribunals in their judicial area. There are five courts of appeal for each of the five judicial areas, which are the largest geographical subdivisions of Belgium for judicial purposes. The division of the Belgian territory into the five judicial areas is laid down in article 156 of the Belgian Constitution. A judicial area covers multiple judicial arrondissements ("districts"), except for the judicial area of Mons. Each arrondissement has a tribunal of first instance. Further below, an overview is provided of the five courts of appeal and the judicial arrondissements their judicial area covers. The courts of appeal do not hear appeals against judgements of the labour tribunals; these are heard by the courts of labour.

The court of labour is the appellate court in the judicial system of Belgium which hears appeals against judgements of the labour tribunals and the presidents of those tribunals in their respective judicial area. There are five courts of labour for each of the five judicial areas, which are the largest geographical subdivisions of Belgium for judicial purposes. Some of the courts of labour hear cases in multiple seats. Further below, an overview is provided of the five courts of labour and their seats. Whilst their territorial organisation is the same, the courts of labour are separate from the courts of appeal, which are the main appellate courts in Belgium.

The Supreme Court is the highest civil and criminal court in Burundi. It has nine members, including the Court President, who are nominated by the Judicial Service Commission and appointed by the President of the Republic after the approval of the Senate. The court's president is referred to as the Chief Justice.

The Supreme Court of Haiti is the highest court in the Haitian legal system. The Supreme Court building is located in Port-au-Prince.

The judiciary of Belgium is similar to the French judiciary. Belgium evolved from a unitary to a federal state, but its judicial system has not been adapted to a federal system.
The judiciary of Luxembourg comprises a number of courts.

The Tunisian Constitution of 2014 was adopted on 26 January 2014 by the Constituent Assembly elected on 23 October 2011 in the wake of Tunisia's Jasmine Revolution that overthrew President Zine El Abidine Ben Ali. It was passed on 10 February 2014, replacing the constitutional law of 16 December 2011 that temporarily formed the basis of government after the suspension of the Constitution of 1959.

The Supreme Court of the Republic of Latvia or the Senate of Latvia is the highest level court in the three-tiered court system of Latvia. It deals with criminal, civil and administrative matters. Its oversight is determined in the Constitution, the structure and competence of the court are established by the Act On Judicial Power. The Court consists of the Civil Cases Court, three departments, administration and two divisions, located in the Palace of Justice on Brīvības bulvāris, Central Riga.
The Court of Revision is the highest judicial court in the Principality of Monaco. The Court rules on all matters concerning violation of the law, and on appeals against any last resort decision or final judgment of the court. The jurisdiction of the Court of Revision is regulated by Article 25 of the Law no 783 July 15, 1965 from 15 July 1965 on judicial organization. By statute, the Court of Revision consists of seven judges: a President, a Vice-President and five advisors. The Court of Revision is a member of the Francophone Association of High Courts of Cassation (AHJUCAF). As of 2021 the president of the Court of Revision is Cécile Chatel Petit, Honorary First Advocate General at the First Civil Chamber of the French Court of Cassation, former member of the Superior Council of the French Magistracy.















