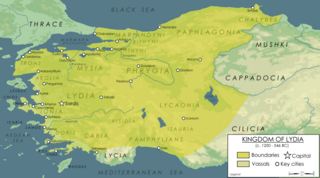
Lydia was an Iron Age kingdom situated in the west of Asia Minor, in modern-day Turkey. The ethnic group inhabiting this kingdom are known as the Lydians, and their language as Lydian and their capital was Sardis.

Croesus was the king of Lydia, who reigned from 585 BC until his defeat by the Persian king Cyrus the Great in 547 or 546 BC. According to Herodotus, he reigned 14 years. Croesus was renowned for his wealth; Herodotus and Pausanias noted that his gifts were preserved at Delphi. The fall of Croesus had a profound effect on the Greeks, providing a fixed point in their calendar. "By the fifth century at least", J. A. S. Evans has remarked, "Croesus had become a figure of myth, who stood outside the conventional restraints of chronology."
Gordias was the name of at least two members of the royal house of Phrygia.

The Battle of Thymbra was the decisive battle in the war between Croesus of the Lydian Kingdom and Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid Empire. Cyrus, after he had pursued Croesus into Lydia after the drawn Battle of Pteria, met the remains of Croesus' partially-disbanded army in battle on the plain north of Sardis in December 547 BC. Croesus' army was about twice as large and had been reinforced with many new men, but Cyrus still utterly defeated it. That proved to be decisive, and after the 14-day Siege of Sardis, the city and possibly its king fell, and Lydia was conquered by the Persians.

The Histories of Herodotus is considered the founding work of history in Western literature. Although not a fully impartial record, it remains one of the West's most important sources regarding these affairs. Moreover, it established the genre and study of history in the Western world.

Cyrus II of Persia, commonly known as Cyrus the Great, was the founder of the Achaemenid Persian Empire. Hailing from Persis, he brought the Achaemenid dynasty to power by defeating the Median Empire and embracing all of the previous civilized states of the ancient Near East, expanding vastly and eventually conquering most of West Asia and much of Central Asia to create what would soon become the largest polity in human history at the time. Widely considered the world's first superpower, the Achaemenid Empire's largest territorial extent was achieved under Darius the Great, whose rule stretched from the Balkans and the rest of Southeast Europe in the west to the Indus Valley in the east.

Astyages was the last king of the Median kingdom, reigning from 585 to 550 BCE. The son of Cyaxares, he was dethroned by the Persian king Cyrus the Great. He was a follower of the Vedic religion as per Iranian customs.
Harpagus, also known as Harpagos or Hypargus, was a Median general during the 6th century BC, credited by Herodotus as having put Cyrus the Great on the throne through his defection during the Battle of Pasargadae.
Tellus was an Athenian statesman featured in Herodotus's Histories, in which the wise man Solon describes him as the happiest man ever.

This is a list of works by Russian writer Leo Tolstoy (1828–1910), including his novels, novellas, short stories, fables and parables, plays, and nonfiction.

"The Three Questions" is a 1903 short story by Russian author Leo Tolstoy as part of the collection What Men Live By, and Other Tales. The story takes the form of a parable, and it concerns a king who wants to find the answers to what he considers the three most important questions in life.
Promoting a Devil is a short story by Russian author Leo Tolstoy first published in 1886.. It is a cautionary tale story about a man who fell into a sinful life when he was given more than he needed.
"Repentance" is a short story by Russian author Leo Tolstoy first published in 1886. The story details the difficulties of a repentant sinner's attempts to enter Heaven.
"The Grain" or "A Grain As Big As A Hen's Egg" is an 1886 short story by Leo Tolstoy about a king seeking to understand the properties of a grain he acquires.

Der hochmütige, gestürzte und wieder erhabene Croesus is a three-act opera composed by Reinhard Keiser. The German language libretto by Lucas von Bostel was based on Nicolò Minato's 1678 dramma per musica Creso, the music for which was composed by the Emperor Leopold I.

The siege of Sardis was the last decisive conflict after the Battle of Thymbra, which was fought between the forces of Croesus of Lydia and Cyrus the Great, when Cyrus followed Croesus to his city, laid siege to it for 14 days and captured it.

Count Lev Nikolayevich Tolstoy, usually referred to in English as Leo Tolstoy, was a Russian writer. He is regarded as one of the greatest and most influential authors of all time. He received nominations for the Nobel Prize in Literature every year from 1902 to 1906 and for the Nobel Peace Prize in 1901, 1902, and 1909.

Kleobis (Cleobis) and Biton are two Archaic Greek Kouros brothers from Argos, whose stories date back to about 580 BCE. Two statues, discovered in Delphi, represent them.












