
The Bahamas, officially the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is a country in the Atlantic Ocean. It is an island country within the Lucayan Archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean. It contains 97% of the Lucayan Archipelago's land area and 88% of its population. The archipelagic country consists of more than 3,000 islands, cays, and islets in the Atlantic Ocean, and is located north of Cuba and northwest of the island of Hispaniola and the Turks and Caicos Islands, southeast of the U.S. state of Florida, and east of the Florida Keys. The capital is Nassau on the island of New Providence. The Royal Bahamas Defence Force describes The Bahamas' territory as encompassing 470,000 km2 (180,000 sq mi) of ocean space.

The Bahamas are a group of about 700 islands and cays in the western Atlantic Ocean, of which only between 30 and 40 are inhabited. The largest of the islands is Andros Island, located north of Cuba and 200 kilometres southeast of Florida. The Bimini islands are to its northwest. To the North is the island of Grand Bahama, home to the second-largest city in the country, Freeport. The island of Great Abaco is to its east. In the far south is the island of Great Inagua, the second-largest island in the country. Other notable islands include Eleuthera, Cat Island, San Salvador Island, Acklins, Crooked Island, and Mayaguana. Nassau is the capital and largest city, located on New Providence. The islands have a tropical savannah climate, moderated by the Gulf Stream. The total size is 13,878 km2 (5,358 sq mi). Due to the many widespread islands it has the 41st largest Exclusive Economic Zone of 654,715 km2 (252,787 sq mi).
This article talks about transportation in the Bahamas, a North American archipelagic state in the Atlantic Ocean.

Durham is a town in Greene County, New York, United States. The population was 2,627 at the 2020 census. The town was named after Durham, Connecticut, and is in the northwestern corner of Greene County.
The Lucayan people were the original residents of The Bahamas and the Turks and Caicos Islands before the European colonisation of the Americas. They were a branch of the Taínos who inhabited most of the Caribbean islands at the time. The Lucayans were the first Indigenous Americans encountered by Christopher Columbus. Shortly after contact, the Spanish kidnapped and enslaved Lucayans, with the displacement culminating in the complete eradication of the Lucayan people from the Bahamas by 1520.
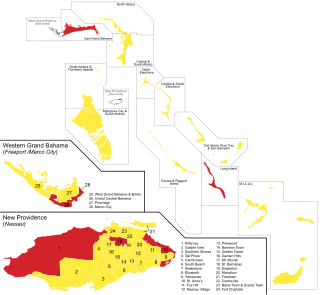
New Providence is the most populous island in the Bahamas, containing more than 70% of the total population. On the eastern side of the island is the national capital city of Nassau; it had a population of 246,329 at the 2010 Census; the latest estimate (2016) is 274,400.

Local government in The Bahamas exists at two levels: 32 districts and 41 towns. The boundaries of districts are defined by the First Schedule of The Bahamas Local Government Act 1996, defined with reference to parliamentary constituency boundaries. The Second Schedule lists 13 districts which are divided into town areas. Towns are governed by directly elected town committees. Second Schedule districts are governed by nine-person district councils composed of the chairs of the town committees, and if numerically required, additional people elected by the town committees. The 19 Third Schedule districts are unitary authorities which cannot be divided into towns. They are governed by nine-person district councils which are directly elected by voters. The powers of Second Schedule and Third Schedule councils are slightly different, and the Third Schedule district known as the City of Freeport has a slightly different list of enumerated powers.

Eleuthera refers both to a single island in the archipelagic state of the Commonwealth of the Bahamas and to its associated group of smaller islands. Eleuthera forms a part of the Great Bahama Bank. The island of Eleuthera incorporates the smaller Harbour Island. "Eleuthera" derives from the feminine form of the Greek adjective ἐλεύθερος (eleútheros), meaning "free". Known in the 17th century as Cigateo, it lies 80 km east of Nassau. It is long and thin—180 km long and in places little more than 1.6 km wide. At its narrowest point, the Glass Window Bridge, which has been called the narrowest place on earth, Eleuthera stands 30 feet wide. Its eastern side faces the Atlantic Ocean and its western side faces the Great Bahama Bank. The topography of the island varies from wide rolling pink sand beaches to large outcrops of ancient coral reefs and the highest elevation point is 200 feet. The population is approximately 11,000 and the principal economy of the island is tourism.

Cat Island is located in central Bahamas, and is one of its districts. Cat Island also has the nation's highest point, Mount Alvernia. It rises to 63 metres (207 ft) and is topped by a monastery called The Hermitage. This assembly of buildings was erected by the Franciscan "Brother Jerome".
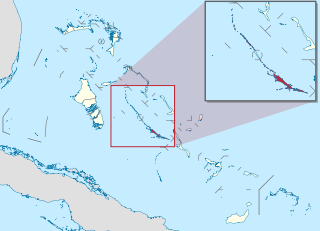
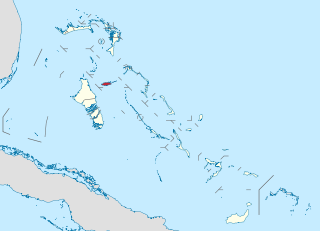
Exuma is a district of The Bahamas, consisting of over 365 islands and cays.

Inagua is the southernmost district of the Bahamas, comprising the islands of Great Inagua and Little Inagua. The headquarters for the district council are in Matthew Town.

Acklins and Crooked Islands was a district of the Bahamas until 1996, and as Acklins, Crooked Island and Long Cay until 1999.

Acklins is an island and district of the Bahamas.

The Cuban amazon, also known as the Cuban parrot and the rose-throated parrot, is a medium-sized mainly green parrot found in woodlands and dry forests of Cuba, the Bahamas and Cayman Islands in the Caribbean. Although they have been observed in the wild in Puerto Rico, they are probably the result of escaped pets, and no reproduction has been recorded.
Colonel Hill is a town in the Bahamas, located on Crooked Island. As of 2010 it has a population of 51.
Long Cay is an 8-square-mile island in the Bahamas in an atoll that includes Acklins Island and Crooked Island. Since 1999, it has also been one of the Third Schedule districts of The Bahamas. As of 2010, its population was 29. Coordinates = 2235 North and 7422 West.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to The Bahamas:
The following is an alphabetical list of topics related to the Commonwealth of The Bahamas.
Spring Point is a town in Acklins, Bahamas and serves as its capital. As of 2010, it had a population of 36.
Mayaguana, Inagua, Crooked Island, Acklins and Long Cay, abbreviated as MICAL, is a parliamentary constituency represented in the House of Assembly of the Bahamas.















