Related Research Articles

SR proteins are a conserved family of proteins involved in RNA splicing. SR proteins are named because they contain a protein domain with long repeats of serine and arginine amino acid residues, whose standard abbreviations are "S" and "R" respectively. SR proteins are ~200-600 amino acids in length and composed of two domains, the RNA recognition motif (RRM) region and the RS domain. SR proteins are more commonly found in the nucleus than the cytoplasm, but several SR proteins are known to shuttle between the nucleus and the cytoplasm.
RNA-binding proteins are proteins that bind to the double or single stranded RNA in cells and participate in forming ribonucleoprotein complexes. RBPs contain various structural motifs, such as RNA recognition motif (RRM), dsRNA binding domain, zinc finger and others. They are cytoplasmic and nuclear proteins. However, since most mature RNA is exported from the nucleus relatively quickly, most RBPs in the nucleus exist as complexes of protein and pre-mRNA called heterogeneous ribonucleoprotein particles (hnRNPs). RBPs have crucial roles in various cellular processes such as: cellular function, transport and localization. They especially play a major role in post-transcriptional control of RNAs, such as: splicing, polyadenylation, mRNA stabilization, mRNA localization and translation. Eukaryotic cells express diverse RBPs with unique RNA-binding activity and protein–protein interaction. According to the Eukaryotic RBP Database (EuRBPDB), there are 2961 genes encoding RBPs in humans. During evolution, the diversity of RBPs greatly increased with the increase in the number of introns. Diversity enabled eukaryotic cells to utilize RNA exons in various arrangements, giving rise to a unique RNP (ribonucleoprotein) for each RNA. Although RBPs have a crucial role in post-transcriptional regulation in gene expression, relatively few RBPs have been studied systematically.It has now become clear that RNA–RBP interactions play important roles in many biological processes among organisms.

The related to receptor tyrosine kinase (RYK) gene encodes the protein Ryk.
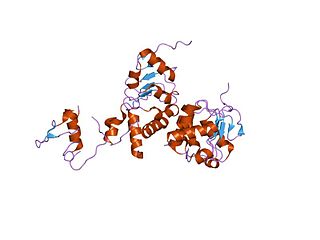
Nuclear RNA export factor 1, also known as NXF1 or TAP, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the NXF1 gene.

Splicing factor U2AF 65 kDa subunit is a protein that in humans is encoded by the U2AF2 gene.

ELAV-like protein 1 or HuR is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ELAVL1 gene.

CUG triplet repeat, RNA binding protein 1, also known as CUGBP1, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the CUGBP1 gene.
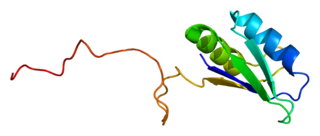
Serine/arginine-rich splicing factor 7 (SRSF7) also known as splicing factor, arginine/serine-rich 7 (SFRS7) or splicing factor 9G8 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SRSF7 gene.

CUGBP, Elav-like family member 2, also known as Etr-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CELF2 gene.

FUS-interacting serine-arginine-rich protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SFRS13A gene.
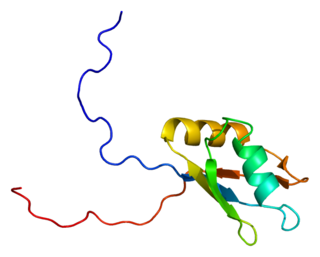
APOBEC1 complementation factor is a protein that in humans is encoded by the A1CF gene.

RNA-binding protein with multiple splicing is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RBPMS gene.

Muscleblind Like Splicing Regulator 1 (MBNL1) is an RNA splicing protein that in humans is encoded by the MBNL1 gene. It has a well characterized role in Myotonic dystrophy where impaired splicing disrupts muscle development and function. In addition to regulating mRNA maturation of hundreds of genes MBNL1 autoregulate alternative splicing of the MBNL1 pre-mRNA transcript. The founding member of the human MBNL family of proteins was the Drosophila Muscleblind protein.

Putative RNA-binding protein 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RBM3 gene.

Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein D-like, also known as HNRPDL, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the HNRPDL gene.
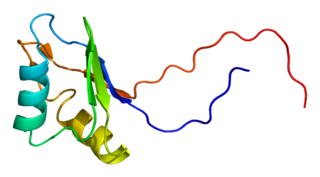
Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IGF2BP2 gene.
ELAV-like protein 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ELAVL3 gene.
CUGBP Elav-like family member 4 (CELF4) also known as bruno-like protein 4 (BRUNOL4) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CELF4 gene.

Serine/arginine-rich splicing factor 1 (SRSF1) also known as alternative splicing factor 1 (ASF1), pre-mRNA-splicing factor SF2 (SF2) or ASF1/SF2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SRSF1 gene. ASF/SF2 is an essential sequence specific splicing factor involved in pre-mRNA splicing. SRSF1 is the gene that codes for ASF/SF2 and is found on chromosome 17. The resulting splicing factor is a protein of approximately 33 kDa. ASF/SF2 is necessary for all splicing reactions to occur, and influences splice site selection in a concentration-dependent manner, resulting in alternative splicing. In addition to being involved in the splicing process, ASF/SF2 also mediates post-splicing activities, such as mRNA nuclear export and translation.

Sex-lethal (Sxl) is a gene found in Dipteran insects, named for its mutation phenotype in Drosophila melanogaster. It is most closely related to the ELAV/HUD subfamily of splicing factors.
References
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: CUGBP Elav-like family member 6" . Retrieved 2018-04-18.