
The GNU Image Manipulation Program, commonly known by its acronym GIMP, is a free and open-source raster graphics editor used for image manipulation (retouching) and image editing, free-form drawing, transcoding between different image file formats, and more specialized tasks. It is extensible by means of plugins, and scriptable. It is not designed to be used for drawing, though some artists and creators have used it in this way.

Adobe Photoshop is a raster graphics editor developed and published by Adobe for Windows and macOS. It was created in 1987 by Thomas and John Knoll. It is the most used tool for professional digital art, especially in raster graphics editing, and its name has become genericised as a verb although Adobe disapproves of such use.
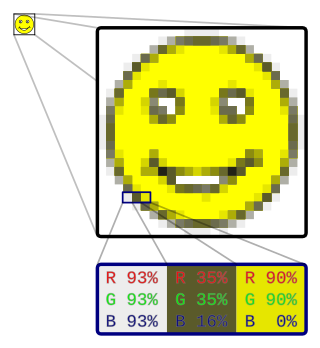
In computer graphics and digital photography, a raster graphic represents a two-dimensional picture as a rectangular matrix or grid of pixels, viewable via a computer display, paper, or other display medium. A raster image is technically characterized by the width and height of the image in pixels and by the number of bits per pixel. Raster images are stored in image files with varying dissemination, production, generation, and acquisition formats.
Gamma correction or gamma is a nonlinear operation used to encode and decode luminance or tristimulus values in video or still image systems. Gamma correction is, in the simplest cases, defined by the following power-law expression:

Color grading is a post-production process common to filmmaking and video editing of altering the appearance of an image for presentation in different environments on different devices. Various attributes of an image such as contrast, color, saturation, detail, black level, and white balance may be enhanced whether for motion pictures, videos, or still images. Color grading and color correction are often used synonymously as terms for this process and can include the generation of artistic color effects through creative blending and compositing of different layer masks of the source image. Color grading is generally now performed in a digital process either in a controlled environment such as a color suite, and is usually done in a dim or dark environment.

The CIELAB color space, also referred to as L*a*b*, is a color space defined by the International Commission on Illumination in 1976. It expresses color as three values: L* for perceptual lightness and a* and b* for the four unique colors of human vision: red, green, blue and yellow. CIELAB was intended as a perceptually uniform space, where a given numerical change corresponds to a similar perceived change in color. While the LAB space is not truly perceptually uniform, it nevertheless is useful in industry for detecting small differences in color.

Unsharp masking (USM) is an image sharpening technique, first implemented in darkroom photography, but now commonly used in digital image processing software. Its name derives from the fact that the technique uses a blurred, or "unsharp", negative image to create a mask of the original image. The unsharp mask is then combined with the original positive image, creating an image that is less blurry than the original. The resulting image, although clearer, may be a less accurate representation of the image's subject.

Photograph manipulation involves the transformation or alteration of a photograph. Some photograph manipulations are considered to be skillful artwork, while others are considered to be unethical practices, especially when used to deceive. Motives for manipulating photographs include political propaganda, altering the appearance of a subject, entertainment and humor.

Corel Photo-Paint is a raster graphics editor developed and marketed by Corel since 1992. Corel markets the software for Windows and Mac OS operating systems, previously having marketed versions for Linux. Its primary market competitor is Adobe Photoshop.

Krita is a free and open-source raster graphics editor designed primarily for digital art and 2D animation. Originally created for Linux, the software also runs on Windows, macOS, Haiku, Android, and ChromeOS, and features an OpenGL-accelerated canvas, colour management support, an advanced brush engine, non-destructive layers and masks, group-based layer management, vector artwork support, and switchable customisation profiles.
Digital "darkroom" is the hardware, software and techniques used in digital photography that replace the darkroom equivalents, such as enlarging, cropping, dodging and burning, as well as processes that do not have a film equivalent.
A camera raw image file contains unprocessed or minimally processed data from the image sensor of either a digital camera, a motion picture film scanner, or other image scanner. Raw files are so named because they are not yet processed, and contain large amounts of potentially redundant data. Normally, the image is processed by a raw converter, in a wide-gamut internal color space where precise adjustments can be made before conversion to a viewable file format such as JPEG or PNG for storage, printing, or further manipulation. There are dozens of raw formats in use by different manufacturers of digital image capture equipment.

Adobe Photoshop Lightroom, usually called Lightroom, is an image organization and processing application developed by Adobe. It is licensed as a standalone subscription or as part of Creative Cloud. It is supported on Windows, macOS, iOS, Android, and tvOS. Its primary uses include importing, saving, viewing, organizing, tagging, editing, and sharing large numbers of digital images. Lightroom's editing functions include white balance, presence, tone, tone curve, HSL, color grading, detail, lens corrections, and calibration manipulation, as well as transformation, spot removal, red eye correction, graduated filters, radial filters, and adjustment brushing. The name Lightroom is a play on the darkrooms used for processing film.
Dan Margulis is an expert on color correction and reproduction of photographs, using Adobe Photoshop or similar software.

Layers are used in digital image editing to separate different elements of an image. A layer can be compared to a transparency on which imaging effects or images are applied and placed over or under an image. Today they are an integral feature of image editor.

Helicon Filter, also referred to as Helicon, Filter, or as HF, was a proprietary commercial and shareware photo editing software program for Microsoft Windows, similar to such programs as Adobe Photoshop and GIMP, developed and published by Helicon Soft Ltd. Unlike these other programs, Helicon Filter is designed primarily to edit and improve existing photos and not for graphics creation. Helicon Filter's interface also differs from other programs in that compact toolbars and menus containing editing tools are replaced with labeled "filter" tabs, each tab containing labeled edit options specific to a single aspect of the picture. Although some editors used to Photoshop-style programs may initially find this layout unfamiliar and unlike the standard toolbar layout, beginners and those who don't recognize the standard icons generally find this very helpful for getting through the editing process.
Photoshop plugins are add-on programs aimed at providing additional image effects or performing tasks that are impossible or hard to fulfill using Adobe Photoshop alone. Plugins can be opened from within Photoshop and several other image editing programs and act like mini editors that modify the image.

Blend modes in digital image editing and computer graphics are used to determine how two layers are blended with each other. The default blend mode in most applications is simply to obscure the lower layer by covering it with whatever is present in the top layer ; because each pixel has numerical values, there also are many other ways to blend two layers.

Image editing encompasses the processes of altering images, whether they are digital photographs, traditional photo-chemical photographs, or illustrations. Traditional analog image editing is known as photo retouching, using tools such as an airbrush to modify photographs or edit illustrations with any traditional art medium. Graphic software programs, which can be broadly grouped into vector graphics editors, raster graphics editors, and 3D modelers, are the primary tools with which a user may manipulate, enhance, and transform images. Many image editing programs are also used to render or create computer art from scratch. The term "image editing" usually refers only to the editing of 2D images, not 3D ones.

Darktable is a free and open-source photography application and raw developer. Rather than being a raster graphics editor like Adobe Photoshop or GIMP, it comprises a subset of image editing operations specifically aimed at non-destructive raw image post-production. It is primarily focused on improving a photographer's workflow by facilitating the handling of large numbers of images. It is freely available in versions tailored for most major Linux distributions, macOS, Solaris and Windows and is released under the GPL-3.0-or-later.













