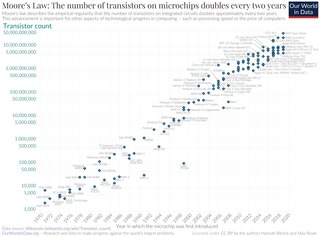
Moore's law is the observation that the number of transistors in an integrated circuit (IC) doubles about every two years. Moore's law is an observation and projection of a historical trend. Rather than a law of physics, it is an empirical relationship linked to gains from experience in production.
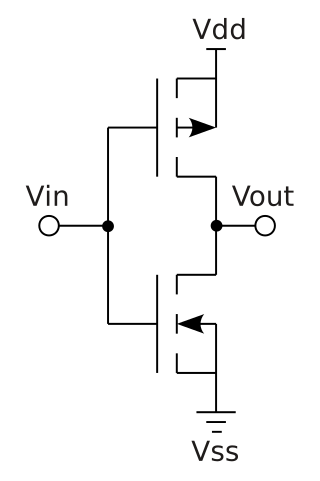
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor is a type of metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) fabrication process that uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type MOSFETs for logic functions. CMOS technology is used for constructing integrated circuit (IC) chips, including microprocessors, microcontrollers, memory chips, and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for analog circuits such as image sensors, data converters, RF circuits, and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication.

The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) is an American 501(c)(3) professional association for electronics engineering, electrical engineering, and other related disciplines.
A bandgap voltage reference is a voltage reference circuit widely used in integrated circuits. It produces an almost constant voltage corresponding to the particular semiconductor's theoretical band gap, with very little fluctuations from variations of power supply, electrical load, time, temperature.
International Solid-State Circuits Conference is a global forum for presentation of advances in solid-state circuits and Systems-on-a-Chip. The conference is held every year in February at the San Francisco Marriott Marquis in downtown San Francisco. ISSCC is sponsored by IEEE Solid-State Circuits Society.
The J. J. Ebers Award was established in 1971 to foster progress in electron devices. It commemorates Jewell James Ebers, whose contributions, particularly to transistors, shaped the understanding and technology of electron devices. It is presented annually to one or more individuals who have made either a single or a series of contributions of recognized scientific, economic, or social significance in the broad field of electron devices. The recipient is awarded a certificate and check for $5,000, presented at the International Electron Devices Meeting.

Technology computer-aided design is a branch of electronic design automation (EDA) that models semiconductor fabrication and semiconductor device operation. The modeling of the fabrication is termed process TCAD, while the modeling of the device operation is termed device TCAD. Included are the modelling of process steps, and modelling of the behavior of the electrical devices based on fundamental physics, such as the doping profiles of the devices. TCAD may also include the creation of "compact models", which try to capture the electrical behavior of such devices but do not generally derive them from the underlying physics. SPICE simulator itself is usually considered as part of EDA rather than TCAD.

Semiconductor device modeling creates models for the behavior of the electrical devices based on fundamental physics, such as the doping profiles of the devices. It may also include the creation of compact models, which try to capture the electrical behavior of such devices but do not generally derive them from the underlying physics. Normally it starts from the output of a semiconductor process simulation.
The International Conference on Computer-Aided Design (ICCAD) is a yearly conference about electronic design automation. From the start in 1982 until 2014 the conference was held in San Jose, California. It is sponsored by the IEEE Circuits and Systems Society, Computer-Aided Design Technical Committee (CANDE), the IEEE Council on Electronic Design Automation (CEDA), and SIGDA, and in cooperation with the IEEE Electron Devices Society and the IEEE Solid State Circuits Society.

Asad Ali Abidi is a Pakistani-American electrical engineer. He serves as a tenured professor at University of California, Los Angeles, and is the inaugural holder of the Abdus Salam Chair at the Lahore University of Management Sciences (LUMS). He is best known for pioneering RF CMOS technology during the late 1980s to early 1990s. As of 2008, the radio transceivers in all wireless networking devices and modern mobile phones are mass-produced as RF CMOS devices.

Dr.Vladimír Székely was a Hungarian electrical engineer, professor emeritus at the Budapest University of Technology and Economics and a corresponding member of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences. He was Head of Department of Electron Devices at the Budapest University of Technology and Economics between 1990 and 2005. He published research results in 360 peer-reviewed papers listed in Web of Science, the most cited being referenced over 200 times, along with 12 books or book-chapters based on his theoretical and practical results.
Adrian Mihai Ionescu is a Romanian and Swiss physicist and academic. He is full Professor at the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology in Lausanne (EPFL), where he is founder and director of the Nanoelectronic Devices Laboratory.

Ian A. Young is an Intel engineer. Young is a co-author of 50 research papers, and has 71 patents in switched capacitor circuits, DRAM, SRAM, BiCMOS, x86 clocking, Photonics and spintronics.
The IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM) is an annual micro- and nanoelectronics conference held each December that serves as a forum for reporting technological breakthroughs in the areas of semiconductor and related device technologies, design, manufacturing, physics, modeling and circuit-device interaction.

The Task Force on Rebooting Computing (TFRC), housed within IEEE Computer Society, is the new home for the IEEE Rebooting Computing Initiative. Founded in 2013 by the IEEE Future Directions Committee, Rebooting Computing has provided an international, interdisciplinary environment where experts from a wide variety of computer-related fields can come together to explore novel approaches to future computing. IEEE Rebooting Computing began as a global initiative launched by IEEE that proposes to rethink the concept of computing through a holistic look at all aspects of computing, from the device itself to the user interface. As part of its work, IEEE Rebooting Computing provides access to various resources like conferences and educational events, feature and scholarly articles, reports, and videos.
Bruno Murari is an Italian inventor. During his career he has patented about 200 inventions in the field of circuit design, power technologies and MEMS devices. He is the only Italian to have received the Elmer A. Sperry Award, which is awarded to those who have distinguished themselves with proven engineering contributions to advance the field of transport. He was defined "legendary analog engineer" and "father" of the BCD technology.
Ehsan Afshari is an Iranian-American electrical engineer, researcher and academic. He is Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering at University of Michigan.

Edoardo Charbon is a Swiss electrical engineer. He is a professor of quantum engineering at EPFL and the head of the Laboratory of Advanced Quantum Architecture (AQUA) at the School of Engineering.








