Related Research Articles
Linear predictive coding (LPC) is a method used mostly in audio signal processing and speech processing for representing the spectral envelope of a digital signal of speech in compressed form, using the information of a linear predictive model.
Vector quantization (VQ) is a classical quantization technique from signal processing that allows the modeling of probability density functions by the distribution of prototype vectors. Developed in the early 1980s by Robert M. Gray, it was originally used for data compression. It works by dividing a large set of points (vectors) into groups having approximately the same number of points closest to them. Each group is represented by its centroid point, as in k-means and some other clustering algorithms. In simpler terms, vector quantization chooses a set of points to represent a larger set of points.
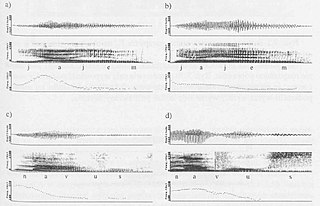
PSOLA is a digital signal processing technique used for speech processing and more specifically speech synthesis. It can be used to modify the pitch and duration of a speech signal. It was invented around 1986.

In signal processing, the chirplet transform is an inner product of an input signal with a family of analysis primitives called chirplets.
Keyword spotting is a problem that was historically first defined in the context of speech processing. In speech processing, keyword spotting deals with the identification of keywords in utterances.
Scale-space segmentation or multi-scale segmentation is a general framework for signal and image segmentation, based on the computation of image descriptors at multiple scales of smoothing.
Warped linear predictive coding is a variant of linear predictive coding in which the spectral representation of the system is modified, for example by replacing the unit delays used in an LPC implementation with first-order all-pass filters. This can have advantages in reducing the bitrate required for a given level of perceived audio quality/intelligibility, especially in wideband audio coding.
The IEEE Signal Processing Society is one of the nearly 40 technical societies of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) and the first one created. Its mission is to "advance and disseminate state-of-the-art scientific information and resources; educate the signal processing community; and provide a venue for people to interact and exchange ideas."
Speaker adaptation is an important technology to fine-tune either features or speech models for mis-match due to inter-speaker variation. In the last decade, eigenvoice (EV) speaker adaptation has been developed. It makes use of the prior knowledge of training speakers to provide a fast adaptation algorithm. Inspired by the kernel eigenface idea in face recognition, kernel eigenvoice (KEV) is proposed. KEV is a non-linear generalization to EV. This incorporates Kernel principal component analysis, a non-linear version of Principal Component Analysis, to capture higher order correlations in order to further explore the speaker space and enhance recognition performance.
Nelson Harold Morgan is an American computer scientist and professor in residence (emeritus) of electrical engineering and computer science at the University of California, Berkeley. Morgan is the co-inventor of the Relative Spectral (RASTA) approach to speech signal processing, first described in a technical report published in 1991.
Financial signal processing is a branch of signal processing technologies which applies to signals within financial markets. They are often used by quantitative analysts to make best estimation of the movement of financial markets, such as stock prices, options prices, or other types of derivatives.
In communications technology, the technique of compressed sensing (CS) may be applied to the processing of speech signals under certain conditions. In particular, CS can be used to reconstruct a sparse vector from a smaller number of measurements, provided the signal can be represented in sparse domain. "Sparse domain" refers to a domain in which only a few measurements have non-zero values.

An audio coding format is a content representation format for storage or transmission of digital audio. Examples of audio coding formats include MP3, AAC, Vorbis, FLAC, and Opus. A specific software or hardware implementation capable of audio compression and decompression to/from a specific audio coding format is called an audio codec; an example of an audio codec is LAME, which is one of several different codecs which implements encoding and decoding audio in the MP3 audio coding format in software.

In Western music, the term chroma feature or chromagram closely relates to twelve different pitch classes. Chroma-based features, which are also referred to as "pitch class profiles", are a powerful tool for analyzing music whose pitches can be meaningfully categorized and whose tuning approximates to the equal-tempered scale. One main property of chroma features is that they capture harmonic and melodic characteristics of music, while being robust to changes in timbre and instrumentation.
V John Mathews is an Indian-American engineer and educator who is currently a Professor of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science (EECS) at the Oregon State University, United States.
The IARPA Babel program developed speech recognition technology for noisy telephone conversations. The main goal of the program was to improve the performance of keyword search on languages with very little transcribed data, i.e. low-resource languages. Data from 26 languages was collected with certain languages being held-out as "surprise" languages to test the ability of the teams to rapidly build a system for a new language.
The IEEE Fourier Award for Signal Processing is a Technical Field Award that is given by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers. This award is presented for contributions in the field of signal processing.

Matti Antero Karjalainen was a Finnish speech processing researcher and inventor in the fields of speech synthesis, speech analysis, speech technology, audio signal processing and psychoacoustics. He was the head of Acoustics Laboratory at the Helsinki University of Technology from 1980 to 2006.
Namrata Vaswani is an Indian-American electrical engineer known for her research in compressed sensing, robust principal component analysis, signal processing, statistical learning theory, and computer vision. She is a Joseph and Elizabeth Anderlik Professor in Electrical and Computer Engineering at Iowa State University, and a professor of mathematics at Iowa State.

Athina Petropulu is a Greek electrical engineer, researcher and academic. She is Distinguished Professor in the Electrical and Computer Engineering (ECE) Department at Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey. She has made contributions in signal processing, wireless communications and networks, and radar systems. She received many awards for her work in these areas.
References
- ↑ Rabiner, L.R. (1984). "The Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing Society. A Historical Perspective" (PDF). IEEE ASSP Magazine. Retrieved 23 January 2018.
- ↑ SoC Conference Ranking Archived 2011-03-10 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ Conference Ranks
- ↑ "Conference Table of Contents - International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP)". IEEE Xplore.