Cyclin-O is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCNO gene. [5]
Cyclin-O is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCNO gene. [5]
Cyclin O has been shown to interact with RPA2 [6] and PCNA. [6] [7]
DNA glycosylases are a family of enzymes involved in base excision repair, classified under EC number EC 3.2.2. Base excision repair is the mechanism by which damaged bases in DNA are removed and replaced. DNA glycosylases catalyze the first step of this process. They remove the damaged nitrogenous base while leaving the sugar-phosphate backbone intact, creating an apurinic/apyrimidinic site, commonly referred to as an AP site. This is accomplished by flipping the damaged base out of the double helix followed by cleavage of the N-glycosidic bond.
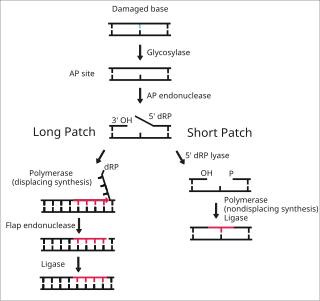
Base excision repair (BER) is a cellular mechanism, studied in the fields of biochemistry and genetics, that repairs damaged DNA throughout the cell cycle. It is responsible primarily for removing small, non-helix-distorting base lesions from the genome. The related nucleotide excision repair pathway repairs bulky helix-distorting lesions. BER is important for removing damaged bases that could otherwise cause mutations by mispairing or lead to breaks in DNA during replication. BER is initiated by DNA glycosylases, which recognize and remove specific damaged or inappropriate bases, forming AP sites. These are then cleaved by an AP endonuclease. The resulting single-strand break can then be processed by either short-patch or long-patch BER.

MUTYH is a human gene that encodes a DNA glycosylase, MUTYH glycosylase. It is involved in oxidative DNA damage repair and is part of the base excision repair pathway. The enzyme excises adenine bases from the DNA backbone at sites where adenine is inappropriately paired with guanine, cytosine, or 8-oxo-7,8-dihydroguanine, a common form of oxidative DNA damage.
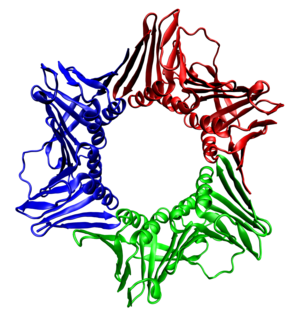
Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) is a DNA clamp that acts as a processivity factor for DNA polymerase δ in eukaryotic cells and is essential for replication. PCNA is a homotrimer and achieves its processivity by encircling the DNA, where it acts as a scaffold to recruit proteins involved in DNA replication, DNA repair, chromatin remodeling and epigenetics.

p21Cip1, also known as cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1 or CDK-interacting protein 1, is a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor (CKI) that is capable of inhibiting all cyclin/CDK complexes, though is primarily associated with inhibition of CDK2. p21 represents a major target of p53 activity and thus is associated with linking DNA damage to cell cycle arrest. This protein is encoded by the CDKN1A gene located on chromosome 6 (6p21.2) in humans.

Cullin-4A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CUL4A gene. CUL4A belongs to the cullin family of ubiquitin ligase proteins and is highly homologous to the CUL4B protein. CUL4A regulates numerous key processes such as DNA repair, chromatin remodeling, spermatogenesis, haematopoiesis and the mitotic cell cycle. As a result, CUL4A has been implicated in several cancers and the pathogenesis of certain viruses including HIV. A component of a CUL4A complex, Cereblon, was discovered to be a major target of the teratogenic agent thalidomide.

DNA ligase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the LIG1 gene. DNA ligase I is the only known eukaryotic DNA ligase involved in both DNA replication and repair, making it the most studied of the ligases.

Flap endonuclease 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the FEN1 gene.
Uracil-DNA glycosylase, also known as UNG or UDG. Its most important function is to prevent mutagenesis by eliminating uracil from DNA molecules by cleaving the N-glycosidic bond and initiating the base-excision repair (BER) pathway.
DNA polymerase lambda, also known as Pol λ, is an enzyme found in all eukaryotes. In humans, it is encoded by the POLL gene.

G/T mismatch-specific thymine DNA glycosylase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the TDG gene. Several bacterial proteins have strong sequence homology with this protein.

DNA-3-methyladenine glycosylase also known as 3-alkyladenine DNA glycosylase (AAG) or N-methylpurine DNA glycosylase (MPG) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MPG gene.
DUTP pyrophosphatase, also known as DUT, is an enzyme which in humans is encoded by the DUT gene on chromosome 15.
Endonuclease VIII-like 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the NEIL2 gene.

Single-strand selective monofunctional uracil DNA glycosylase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SMUG1 gene. SMUG1 is a glycosylase that removes uracil from single- and double-stranded DNA in nuclear chromatin, thus contributing to base excision repair.
DNA polymerase delta subunit 3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the POLD3 gene. It is a component of the DNA polymerase delta complex.

DNA polymerase epsilon catalytic subunit is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the POLE gene. It is the central catalytic subunit of DNA polymerase epsilon.
DNA polymerase epsilon is a member of the DNA polymerase family of enzymes found in eukaryotes. It is composed of the following four subunits: POLE, POLE2, POLE3, and POLE4. Recent evidence suggests that it plays a major role in leading strand DNA synthesis and nucleotide and base excision repair.

Replication protein A 32 kDa subunit is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RPA2 gene.

AlkB homolog 1, histone H2A dioxygenase is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ALKBH1 gene.