Cyprus is a member of the United Nations along with most of its agencies as well as the Commonwealth of Nations, World Bank, International Monetary Fund and Council of Europe. In addition, the country has signed the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) and the Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency Agreement (MIGA). Cyprus has been a member of the European Union since 2004 and in the second half of 2012 it held the Presidency of the Council of the European Union.
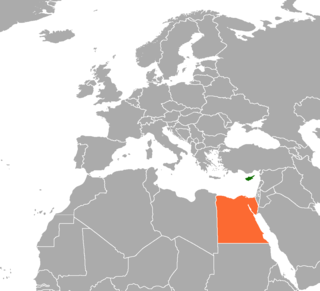
Cyprus–Egypt relations refer to bilateral relations between Cyprus and Egypt. Due to the strong cultural and historical ties between the two nations, Cyprus and Egypt today enjoy friendly, and strategic relations. Modern diplomatic relations between the two countries were established soon after Cyprus gained its independence in 1960, and are regarded as cordial. Cyprus has an embassy in Cairo and Egypt has an embassy in Nicosia.

Cypriot–Georgian relations are foreign relations between Cyprus and Georgia. After the dissolution of the Soviet Union, Cyprus recognized the independence of Georgia in December 1991. The formal Protocol on the Establishment of Diplomatic Relations between the two countries was signed in 1992 and the relations were established on July 9, 1993. Cyprus is represented in Georgia through its embassy in Athens (Greece). Georgia opened an embassy in 2005 in Nicosia and the current ambassador, Vladimir Konstindinidi, presented his credentials in 2009.
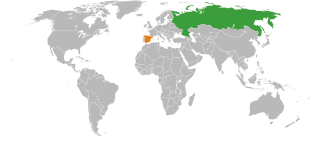
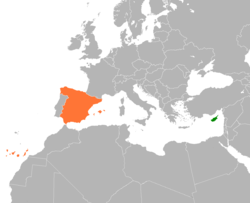
The Russian Federation and the Kingdom of Spain, a member state of the European Union, have bilateral foreign relations. Spain and the Grand Duchy of Moscow first exchanged envoys in 1520s; regular embassies were established in 1722. The two countries share a long history of relations, characterized at times by close cooperation and at other times by deep hostility. Soviet-Spanish relations, once terminated after the Spanish Civil War, were gradually reestablished starting in 1963 and were fully established by 1977. Trade between the two countries amounted to two billion euros in 2008. In March 2009, the two countries signed an energy agreement providing national energy companies access to other party's domestic markets.

Cyprus–Denmark relations refers to the bilateral relations between Cyprus and Denmark. Cyprus has an embassy in Copenhagen. Denmark has an embassy in Nicosia. Diplomatic relations were established on 2 November 1960. Both countries are members of the European Union.

The Kingdom of Spain and the Republic of Turkey maintain diplomatic relations. Spain has an embassy in Ankara and a consulate general in Istanbul. Turkey has an embassy in Madrid and a consulate general in Barcelona.

Malta–Spain relations are the foreign relations between Malta and Spain. Both countries established mutual diplomatic relations in 1977. Malta has an embassy in Madrid and 5 honorary consulates. Spain has an embassy in Ta' Xbiex and Cultural Centre in Balzan. Both countries are full members of the European Union and of the Union for the Mediterranean. In 2019, both countries celebrated 50 years of relations, highlighting "the strong cultural and historical ties" of both countries and their contribution to the European Union and the Mediterranean.
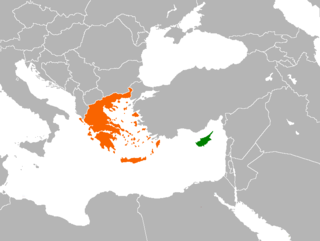
Cyprus–Greece relations are the bilateral relations between Cyprus and Greece. Cyprus has an embassy in Athens and a consulate-general in Thessaloniki. Greece has an embassy in Nicosia. Both countries are full members of the United Nations, European Union, Council of Europe and the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE). Relations between the two countries have been exceptionally close since the Republic of Cyprus was formed in 1960. The Greek populations in Cyprus and Greece share a common ethnicity, heritage, language, and religion. Greece has given full support to Cyprus' membership in the European Union.

Cyprus–Germany relations are the bilateral relations between Cyprus and Germany. Germany is represented in Cyprus through its embassy in Nicosia, Cyprus. Cyprus is represented in Germany through its embassy in Berlin, Germany. Both countries are members of the European Union, Council of Europe and Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe.

Formal relations between Albania and Spain were established in 1986. Albania has an embassy in Madrid, and Spain has an embassy in Tirana.

Formal diplomatic relations between Angola and Spain were established in 1977. Angola has an embassy in Madrid. Spain has an embassy in Luanda.

Slovenia–Spain relations are the bilateral relations between Slovenia and Spain. Slovenia has an embassy in Madrid and three consulates in Barcelona, San Sebastián and Seville. Spain has an embassy in Ljubljana. The Spanish representation in Slovenia is exercised through the Embassy, which has the support of two Aggregators: Defense and Interior; two departments: Tourism and Economy and Commerce, all of them with residence in surrounding countries, although the Economic and Commercial Office has an Antenna in Ljubljana. There is a Cervantes Classroom under the Instituto Cervantes of Vienna. The relations of these two countries are mainly defined by their membership in both the European Union and the NATO.

Latvia–Spain relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between Latvia and Spain. Both countries are full members of the Council of Europe, the European Union and NATO.

Czech Republic–Spain relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Relationships are mainly defined by the membership of both countries to the European Union and NATO. The Czech Republic has an embassy in Madrid and consulates in Barcelona, Benidorm, Bilbao, Oviedo, Palma de Mallorca and Santa Cruz de Tenerife. Spain has an embassy in Prague, as well as an Education Attaché, a Commercial Office and an Instituto Cervantes; the Delegation of Spanish Tourism for this country operates from Vienna.
Spain–Sweden relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Sweden has an embassy in Madrid, a consulate general in Barcelona. Spain has an embassy in Stockholm, as well as an Economic and Social Department and another Tourism Department in the same city. Both countries are full members of Council of Europe, NATO, and of the European Union. Spain strongly supported Sweden's NATO membership during the latter's accession process.

Marshall Islands–Spain relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. The Spanish embassy in Manila, Philippines, is accredited for the Marshall Islands, plus Spain has an honorary consulate in Majuro. The Marshall Islands have an embassy in Madrid and a consulate in Barcelona.

South Korea–Spain relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Spain has an embassy in Seoul. South Korea has an embassy in Madrid and a consulate general in Barcelona and Las Palmas de Gran Canaria. The bilateral relations are good and friendly.
Ghana–Spain relations are the bilateral relations between Ghana and Spain. Ghana has an embassy in Madrid since March 2024 and a consulate in Barcelona. Spain has an embassy in Accra.

The nations of Cyprus and Mexico established diplomatic relations in 1974. Both nations are members of the United Nations.