Related Research Articles

A chordate is an animal of the phylum Chordata. All chordates possess 5 synapomorphies, or primary characteristics, at some point during their larval or adulthood stages that distinguish them from all other taxa. These 5 synapomorphies include a notochord, dorsal hollow nerve cord, endostyle or thyroid, pharyngeal slits, and a post-anal tail. The name “chordate” comes from the first of these synapomorphies, the notochord, which plays a significant role in chordate structure and movement. Chordates are also bilaterally symmetric, have a coelom, possess a circulatory system, and exhibit metameric segmentation.

Paleontology, also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch. It includes the study of fossils to classify organisms and study their interactions with each other and their environments. Paleontological observations have been documented as far back as the 5th century BCE. The science became established in the 18th century as a result of Georges Cuvier's work on comparative anatomy, and developed rapidly in the 19th century. The term itself originates from Greek παλα, ὄν, and λόγος.
The Treatise on Invertebrate Paleontology published by the Geological Society of America and the University of Kansas Press, is a definitive multi-authored work of some 50 volumes, written by more than 300 paleontologists, and covering every phylum, class, order, family, and genus of fossil and extant invertebrate animals. The prehistoric invertebrates are described as to their taxonomy, morphology, paleoecology, stratigraphic and paleogeographic range. However, taxa with no fossil record whatsoever have just a very brief listing.

The Society of Vertebrate Paleontology (SVP) is a professional organization that was founded in the United States in 1940 to advance the science of vertebrate paleontology around the world.
Neontology is a part of biology that, in contrast to paleontology, deals with living organisms. It is the study of extant taxa : taxa with members still alive, as opposed to (all) being extinct. For example:

Archaeoceti, or Zeuglodontes in older literature, is a paraphyletic group of primitive cetaceans that lived from the Early Eocene to the late Oligocene. Representing the earliest cetacean radiation, they include the initial amphibious stages in cetacean evolution, thus are the ancestors of both modern cetacean suborders, Mysticeti and Odontoceti. This initial diversification occurred in the shallow waters that separated India and Asia 53 to 45 mya, resulting in some 30 species adapted to a fully oceanic life. Echolocation and filter-feeding evolved during a second radiation 36 to 35 mya.
Mesadactylus is an extinct genus of pterosaur from the Kimmeridgian-Tithonian-age Upper Jurassic Morrison Formation of Colorado, United States. The genus was named in 1989 by James Jensen and Kevin Padian. The type species is Mesadactylus ornithosphyos.
The Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology is a bimonthly peer-reviewed scientific journal that was established in 1980 by Jiri Zidek. It covers all aspects of vertebrate paleontology, including vertebrate origins, evolution, functional morphology, taxonomy, biostratigraphy, paleoecology, paleobiogeography, and paleoanthropology. The journal is published by Taylor & Francis on behalf of the Society of Vertebrate Paleontology. According to Journal Citation Reports, the journal has a 2017 impact factor of 2.190.
The Journal of Paleontology is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering the field of paleontology. It is published by the Paleontological Society.

Berru is a commune in the Marne department in northeastern France.

Cernay-lès-Reims is a commune in the Marne department in north-eastern France.
Cosmochelys is an extinct genus of sea turtle from the Eocene of Africa. It was first named by Andrews in 1920, and contains one species, C. dolloi.
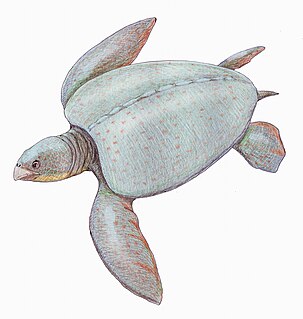
Protosphargis is an extinct genus of sea turtle from the Upper Cretaceous of Italy. It was first named by Capellini in 1884.
Protochelydra zangerli is an extinct species of chelydid in the extinct genus Protochelydra of Chelydridae.

Dinochelys is an extinct genus of paracryptodiran turtle from the Late Jurassic Morrison Formation.

Paleontology or palaeontology is the study of prehistoric life forms on Earth through the examination of plant and animal fossils. This includes the study of body fossils, tracks (ichnites), burrows, cast-off parts, fossilised feces (coprolites), palynomorphs and chemical residues. Because humans have encountered fossils for millennia, paleontology has a long history both before and after becoming formalized as a science. This article records significant discoveries and events related to paleontology that occurred or were published in the year 2010.
Cerrejonemys wayuunaiki is an extinct podocnemid turtle which existed in Colombia during the Paleogene period; the Middle to Late Paleocene epoch.
Selenemys is an extinct genus of pleurosternid turtle from the Late Jurassic of Central West of Portugal. It is known from several specimens recovered from the Lusitanian Basin, dating to the upper Kimmeridgian age. It was one of the earliest European pleurosternids, more closely related to the later Cretaceous pleurosternids of Europe than the contemporary pleurosternids of North America. This genus was named by Adán Pérez-García and Francisco Ortega in 2011, and the type species is Selenemys lusitanica.
Paleontology in Arkansas refers to paleontological research occurring within or conducted by people from the U.S. state of Arkansas. The fossil record of Arkansas spans from the Ordovician to the Eocene. Nearly all of the state's fossils have come from ancient invertebrate life. During the early Paleozoic, much of Arkansas was covered by seawater. This sea would come to be home to creatures including Archimedes, brachiopods, and conodonts. This sea would begin its withdrawal during the Carboniferous, and by the Permian the entire state was dry land. Terrestrial conditions continued into the Triassic, but during the Jurassic, another sea encroached into the state's southern half. During the Cretaceous the state was still covered by seawater and home to marine invertebrates such as Belemnitella. On land the state was home to long necked sauropod dinosaurs, who left behind footprints and ostrich dinosaurs such as Arkansaurus.
Cretaaviculus is an extinct genus of birds from the Upper Cretaceous Bostobe Formation of Kazakhstan. The type species, C. sarysuensis, is known only from an isolated of isolated, asymmetrical contour feather.
References
- 1 2 Sepkoski, Jack (2002). "A compendium of fossil marine animal genera (Trilobita entry)". Bulletins of American Paleontology. 364: 560. Archived from the original on 2006-09-05. Retrieved 2008-01-12.