
The Indo-Pacific, sometimes known as the Indo-West Pacific or Indo-Pacific Asia, is a biogeographic region of Earth's seas, comprising the tropical waters of the Indian Ocean, the western and central Pacific Ocean, and the seas connecting the two in the general area of Indonesia. It does not include the temperate and polar regions of the Indian and Pacific oceans, nor the Tropical Eastern Pacific, along the Pacific coast of the Americas, which is also a distinct marine realm.

The red lionfish is a venomous coral reef fish in the family Scorpaenidae, order Scorpaeniformes. P. volitans is natively found in the Indo-Pacific region, but has become an invasive problem in the Caribbean Sea, as well as along the East Coast of the United States. This and a similar species, Pterois miles, have both been deemed invasive species. Red lionfish are clad in white stripes alternated with red/maroon/brown stripes. Adults in this species can grow as large as 47 cm (18.5 in) in length, making it one of the largest species of lionfish in the ocean, while juveniles are typically shorter than 1 inch (2.5 cm). The average red lionfish lives around 10 years. As with many species within the family Scopaenidae, it has large, venomous spines that protrude from the body, similar to a mane, giving it the common name lionfish. The venomous spines make the fish inedible or deter most potential predators. Lionfish reproduce monthly and are able to quickly disperse during their larval stage for expansion of their invasive region. No definitive predators of the lionfish are known, and many organizations are promoting the harvest and consumption of lionfish in efforts to prevent further increases in the already high population densities.

The common sunstar or Crossaster papposus is a species of sea star belonging to the family Solasteridae. It is found in the northern parts of both the Atlantic and the Pacific Oceans.

Glaucus is a genus of small blue pelagic sea slugs. They are aeolid nudibranchs, ranging in size from 20 to 40 mm. They feed on colonial cnidarians such as Portuguese man o' wars, blue buttons, and purple sails. They can produce painful and potentially dangerous stings when handled, as they store the venomous nematocysts of their prey. Glaucus is the only genus in the family Glaucidae. It includes five species.
Antiplanes diomedea is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Pseudomelatomidae.
Boreotrophon pedroanus is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Muricidae, the murex snails or rock snails.
Hemioniscus balani, a species of isopod crustacean, is a widespread parasitic castrator of barnacle in the northern Atlantic Ocean. Its range extends from Norway to the Atlantic coast of France, and as far west as Massachusetts. It is also commonly found on the Pacific coast of North America; it is not known if the Pacific and Atlantic populations are the same species, or if the Pacific population exists following human-assisted introduction.

Leptogorgia is a genus of soft coral in the family Gorgoniidae. The genus has a widespread distribution with members being found in the eastern Atlantic Ocean from Western Europe to South Africa, the Mediterranean Sea, the Atlantic coasts of North and South America, the Antilles and the Pacific coast of America. Species are found in both shallow and deep waters.

Skenea californica, common name the California skenea, is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Skeneidae.
Skenea carmelensis, common name the Carmel skenea, is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Skeneidae.
Solariella rhyssa is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Solariellidae.
Macrarene cookeana, common name Miss Cooke's liotia, is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Liotiidae.

Calliostoma turbinum is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Calliostomatidae.
Asterophila japonica is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Eulimidae. The species is one of three known species within the genus Asterophila, the other congeneric species being Asterophila perknasteri and Asterophila rathbunasteri.
Cythnia albida is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Eulimidae. The species is one of two known species to exist within the genus, Cythnia, with the other one being Cythnia asteriaphila.
Seguenzia certoma is a species of extremely small deep water sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Seguenziidae.
Seguenzia cervola is a species of extremely small deep water sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Seguenziidae.
Doris fontainii is a species of sea slug, a dorid nudibranch, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Dorididae.
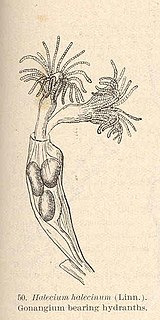
Halecium halecinum, commonly known as the herring-bone hydroid, is a species of hydrozoan in the family Haleciidae. It is native to the eastern Atlantic Ocean, the western Atlantic Ocean and the eastern Pacific Ocean.











