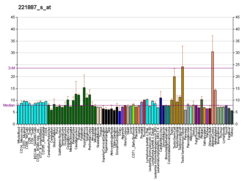
Harmonin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the USH1C gene. It is expressed in sensory cells of the inner ear and retina, where it plays a role in hearing, balance, and vision. Mutations at the USH1C locus cause Usher syndrome type 1c and nonsyndromic sensorineural deafness.
Cadherin-23 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CDH23 gene.

Transmembrane protease, serine 3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the TMPRSS3 gene.

24-Dehydrocholesterol reductase is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DHCR24 gene.

TRIO and F-actin-binding protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TRIOBP gene.

Claudin-14 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CLDN14 gene. It belongs to a related family of proteins called claudins.

Alpha-tectorin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TECTA gene.

Adenylate kinase 2 is an enzyme that is encoded in humans by the AK2 gene. The AK2 protein is found in the intermembrane space of the mitochondrion.

WW domain-binding protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the WBP2 gene.

Elongation factor G 1, mitochondrial is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GFM1 gene. It is an EF-G homolog.

Putative Polycomb group protein ASXL1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ASXL1 gene.

SET and MYND domain-containing protein 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SMYD4 gene.

Transmembrane channel-like protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TMC1 gene. TMC1 contains six transmembrane domains with both the C and N termini on the endoplasmic side of the membrane, as well as a large loop between domains 4 and 5. This topology is similar to that of transient receptor potential channels (TRPs), a family of proteins involved in the perception of senses such as temperature, taste, pressure, and vision. TMC1 has been located in the post-natal mouse cochlea, and knockouts for TMC1 and TMC2 result in both auditory and vestibular deficits indicating TMC1 is a molecular part of auditory transduction.

Stereocilin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the STRC gene.

Myosin-XV is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MYO15A gene.

Meckel syndrome, type 1 also known as MKS1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MKS1 gene.

Espin, also known as autosomal recessive deafness type 36 protein or ectoplasmic specialization protein, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ESPN gene. Espin is a microfilament binding protein.

Ubiquinone biosynthesis protein COQ9, mitochondrial, also known as coenzyme Q9 homolog (COQ9), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the COQ9 gene.

Coiled-coil domain-containing protein 57 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCDC57 gene.

caprin family member 2, also known as CAPRIN2, is a human gene.