| DPY19L2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | DPY19L2 , SPATA34, SPGF9, dpy-19 like 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 613893 MGI: 2444662 HomoloGene: 77569 GeneCards: DPY19L2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dpy-19-like 2 (C. elegans) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DPY19L2 gene. [5]
| DPY19L2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | DPY19L2 , SPATA34, SPGF9, dpy-19 like 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 613893 MGI: 2444662 HomoloGene: 77569 GeneCards: DPY19L2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dpy-19-like 2 (C. elegans) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DPY19L2 gene. [5]
The C. elegans gene dpy-19 belongs to the dpy ("dumpy" phenotype) [6] gene class and encodes DPY-19, transmembrane protein with C-linked mannosyltransferase activity. [7] [8] In humans, it is highly expressed in testis, and is required for sperm head elongation and acrosome formation during spermatogenesis. Mutations in this gene are associated with an infertility disorder, spermatogenic failure type 9 (SPGF9).

Keratin 14 is a member of the type I keratin family of intermediate filament proteins. Keratin 14 was the first type I keratin sequence determined. Keratin 14 is also known as cytokeratin-14 (CK-14) or keratin-14 (KRT14). In humans it is encoded by the KRT14 gene.

Recombination activating gene 1 also known as RAG-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RAG1 gene.

Emodepside is an anthelmintic drug that is effective against a number of gastrointestinal nematodes, is licensed for use in cats and belongs to the class of drugs known as the octadepsipeptides, a relatively new class of anthelmintic, which are suspected to achieve their anti-parasitic effect by a novel mechanism of action due to their ability to kill nematodes resistant to other anthelmintics.

Carnitine O-palmitoyltransferase 2, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CPT2 gene.

Spo11 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SPO11 gene. Spo11, in a complex with mTopVIB, creates double strand breaks to initiate meiotic recombination. Its active site contains a tyrosine which ligates and dissociates with DNA to promote break formation. One Spo11 protein is involved per strand of DNA, thus two Spo11 proteins are involved in each double stranded break event.

The short transient receptor potential channel 4 (TrpC4), also known as Trp-related protein 4, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TRPC4 gene.

Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MAP2K1 gene.

DNA polymerase subunit gamma is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the POLG gene. Mitochondrial DNA polymerase is heterotrimeric, consisting of a homodimer of accessory subunits plus a catalytic subunit. The protein encoded by this gene is the catalytic subunit of mitochondrial DNA polymerase. Defects in this gene are a cause of progressive external ophthalmoplegia with mitochondrial DNA deletions 1 (PEOA1), sensory ataxic neuropathy dysarthria and ophthalmoparesis (SANDO), Alpers-Huttenlocher syndrome (AHS), and mitochondrial neurogastrointestinal encephalopathy syndrome (MNGIE).

Blood group Rh(CE) polypeptide is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RHCE gene. RHCE has also recently been designated CD240CE.
DNA topoisomerase 3-alpha is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the TOP3A gene.

DNA polymerase theta is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the POLQ gene. This polymerase plays a key role in one of the three major double strand break repair pathways: theta-mediated end joining (TMEJ). Most double-strand breaks are repaired by non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) or homology directed repair (HDR). However, in some contexts, NHEJ and HR are insufficient and TMEJ is the only solution to repair the break. TMEJ is often described as alternative NHEJ, but differs in that it lacks a requirement for the Ku heterodimer, and it can only act on resected DNA ends. Following annealing of short regions on the DNA overhangs, DNA polymerase theta catalyzes template-dependent DNA synthesis across the broken ends, stabilizing the paired structure.

SH3 and multiple ankyrin repeat domains protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SHANK1 gene.

Aurora kinase C, also Serine/threonine-protein kinase 13 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the AURKC gene.

Angiopoietin-4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ANGPT4 gene.
SH3 and multiple ankyrin repeat domains 3 (Shank3), also known as proline-rich synapse-associated protein 2 (ProSAP2), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SHANK3 gene on chromosome 22. Additional isoforms have been described for this gene but they have not yet been experimentally verified.

Teashirt homolog 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TSHZ3 gene. In mice, it is a necessary part of the neural circuitry that controls breathing. The gene is also a homolog of the Drosophila melanogaster teashirt gene, which encodes a zinc finger transcription factor important for development of the trunk.

Hemoglobin, alpha 2 also known as HBA2 is a gene that in humans codes for the alpha globin chain of hemoglobin.

Cell lineage denotes the developmental history of a tissue or organ from the fertilized embryo. This is based on the tracking of an organism's cellular ancestry due to the cell divisions and relocation as time progresses, this starts with the originator cells and finishing with a mature cell that can no longer divide.
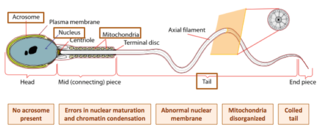
Globozoospermia is a rare and severe form of monomorphic teratozoospermia. This means that the spermatozoa show the same abnormality, and over 85% of spermatozoa in sperm have this abnormality. Globozoospermia is responsible for less than 0.1% of male infertility. It is characterised by round-headed spermatozoa without acrosomes, an abnormal nuclear membrane and midpiece defects. Affected males therefore suffer from either reduced fertility or infertility. Studies suggest that globozoospermia can be either total or partial, however it is unclear whether these two forms are variations on the same syndrome, or actually different syndromes.

Dynein axonemal heavy chain 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DNAH1 gene.
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.