
The DSDP 367 was an area that was drilled as part of the Deep Sea Drilling Project that took place below the Cape Verde Basin.

The DSDP 367 was an area that was drilled as part of the Deep Sea Drilling Project that took place below the Cape Verde Basin.
The area was drilled from February 22 to March 1, 1975 by the ship Glomar Challenger before DSDP 368 was drilled. Its location was at 12°29.2'N and, 20°02.8'W and is located 370 km southwest of Dakar and 460 km southeast of Praia, Cape Verde and south of the Cape Verde Rise. The seabed is 4,768 meters deep. The drilling carried a total of 984.5 meters of sediment.
At the ocean floor and below consists of several layers including nanomarls (1), clays (2), multicolored silty clay (3), that level located 5,000 meters deep, below are black shales (4a and 4b) and nano-limestones (5a and 5b). Below is the oceanic crust composing basalt (7) just below around 5,800 metres deep.
The top part were formed during the Pleistocene and Miocene age, the second unit were formed during the Late Eocene age, the b subunit were also formed during the Late Paleocene age. The lower units were formed during the Valangian, Oxfordian and Kimmeridgian ages.
Not including benthic and planktonic (or planctonic) materials. There are types of nanoplanktons (or nanoplanktons) as well as sponge needles.
Planktonic foraminifers are found at around 200 meters below the ocean floor, they include:
Coccoliths are founded up to 250 meters below the ocean floor, the drilling area, they include:
Several radiolaria were made during the Late Pleistocene, Early Miocene and Early Eocene periods:
Unlike DSDP 368 which is located 550 km north in the Cape Verde Basin, the Upper Jurassic and the Lower Cretaceous sediments below the black shale of the oceanic crust are founded. [1]

The Cretaceous is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of the entire Phanerozoic. The name is derived from the Latin creta, "chalk", which is abundant in the latter half of the period. It is usually abbreviated K, for its German translation Kreide.

Podocnemididae is a family of pleurodire (side-necked) turtles, once widely distributed. Most of its 41 genera and 57 species are now extinct. Seven of its eight surviving species are native to South America: the genus Peltocephalus, with two species, only one of which is extant ; and the genus Podocnemis, with six living species of South American side-necked river turtles and four extinct. There is also one genus native to Madagascar: Erymnochelys, the Madagascan big-headed turtle, whose single species E. madagascariensis.

Nothofagus, also known as the southern beeches, is a genus of 43 species of trees and shrubs native to the Southern Hemisphere in southern South America and east and southeast Australia, New Zealand, New Guinea, and New Caledonia. The species are ecological dominants in many temperate forests in these regions. Some species are reportedly naturalised in Germany and Great Britain. The genus has a rich fossil record of leaves, cupules, and pollen, with fossils extending into the late Cretaceous period and occurring in Australia, New Zealand, Antarctica, and South America.

The Deep Sea Drilling Project (DSDP) was an ocean drilling project operated from 1968 to 1983. The program was a success, as evidenced by the data and publications that have resulted from it. The data are now hosted by Texas A&M University, although the program was coordinated by the Scripps Institution of Oceanography at the University of California, San Diego. DSDP provided crucial data to support the seafloor spreading hypothesis and helped to prove the theory of plate tectonics. DSDP was the first of three international scientific ocean drilling programs that have operated over more than 40 years. It was followed by the Ocean Drilling Program (ODP) in 1985, the Integrated Ocean Drilling Program in 2004 and the present International Ocean Discovery Program in 2013.
The Hatton Basin is a ca. 600 km long SW–NE trending sedimentary basin, located off the west coast of Ireland. It lies between the Hatton and Edoras Banks to the west and the Rockall Bank to the east. The basin contains about 4,000 m of sediments of probable Cretaceous to Cenozoic age. Its relationship to the Rockall Basin remains uncertain.

The Geology of Bangladesh is affected by the country's location, as Bangladesh is mainly a riverine country. It is the eastern two-thirds of the Ganges and Brahmaputra river delta plain stretching to the north from the Bay of Bengal. There are two small areas of slightly higher land in the north-centre and north-west composed of old alluvium called the Madhupur Tract and the Barind Tract, and steep, folded, hill ranges of older (Tertiary) rocks along the eastern border.
The Magallanes Basin or Austral Basin is a major sedimentary basin in southern Patagonia. The basin covers a surface of about 170,000 to 200,000 square kilometres and has a NNW-SSE oriented shape. The basin is bounded to the west by the Andes mountains and is separated from the Malvinas Basin to the east by the Río Chico-Dungeness High. The basin evolved from being an extensional back-arc basin in the Mesozoic to being a compressional foreland basin in the Cenozoic. Rocks within the basin are Jurassic in age and include the Cerro Toro Formation. Three ages of the SALMA classification are defined in the basin; the Early Miocene Santacrucian from the Santa Cruz Formation and Friasian from the Río Frías Formation and the Pleistocene Ensenadan from the La Ensenada Formation.

Neuquén Basin is a sedimentary basin covering most of Neuquén Province in Argentina. The basin originated in the Jurassic and developed through alternating continental and marine conditions well into the Tertiary. The basin bounds to the west with the Andean Volcanic Belt, to the southeast with the North Patagonian Massif and to the northeast with the San Rafael Block and to the east with the Sierra Pintada System. The basin covers an area of approximately 120,000 square kilometres (46,000 sq mi). One age of the SALMA classification, the Colloncuran, is defined in the basin, based on the Collón Curá Formation, named after the Collón Curá River, a tributary of the Limay River.

The Lhasa terrane is a terrane, or fragment of crustal material, sutured to the Eurasian Plate during the Cretaceous that forms present-day southern Tibet. It takes its name from the city of Lhasa in the Tibet Autonomous Region, China. The northern part may have originated in the East African Orogeny, while the southern part appears to have once been part of Australia. The two parts joined, were later attached to Asia, and then were impacted by the collision of the Indian Plate that formed the Himalayas.
The Tarfaya Basin is a structural basin located in southern Morocco that extends westward into the Moroccan territorial waters in the Atlantic Ocean. The basin is named for the city of Tarfaya located near the border of Western Sahara, a region governed by the Kingdom of Morocco. The Canary Islands form the western edge of the basin and lie approximately 100 km to the west.
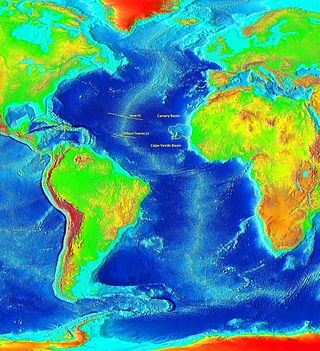
The Cape Verde Rise is an oceanic feature that includes the Cape Verde Islands and the areas north and east of the islands and west of the African Continental Shelf as well as Mauritania and Senegal.

The DSDP 368 was an area that was drilled as part of the Deep Sea Drilling Project that took place below the Cape Verde Rise.

The geology of Senegal formed beginning more than two billion years ago. The Archean greenschist Birimian rocks common throughout West Africa are the oldest in the country, intruded by Proterozoic granites. Basins formed in the interior during the Paleozoic and filled with sedimentary rocks, including tillite from a glaciation. With the rifting apart of the supercontinent Pangaea in the Mesozoic, the large Senegal Basin filled with thick sequences of marine and terrestrial sediments. Sea levels declined in the Eocene forming large phosphate deposits. Senegal is blanketed in thick layers of terrestrial sediments formed in the Quaternary. The country has extensive natural resources, including gold, diamonds, and iron.

Wōdejebato is a Cretaceous guyot or tablemount in the northern Marshall Islands, Pacific Ocean. Wōdejebato is probably a shield volcano and is connected through a submarine ridge to the smaller Pikinni Atoll 74 kilometres (46 mi) southeast of the guyot; unlike Wōdejebato, Pikinni rises above sea level. The seamount rises for 4,420 metres (14,500 ft) to 1,335 metres (4,380 ft) depth and is formed by basaltic rocks. The name Wōdejebato refers to a sea god of Pikinni.

Ita Mai Tai is a Cretaceous-early Cenozoic seamount northwest of the Marshall Islands and north of Micronesia. One among a number of seamounts in the Pacific Ocean, it is part of the Magellan Seamounts which may have a hotspot origin although Ita Mai Tai itself may not have formed on a hotspot.

Resolution Guyot is a guyot (tablemount) in the underwater Mid-Pacific Mountains in the Pacific Ocean. It is a circular flat mountain, rising 500 metres (1,600 ft) above the seafloor to a depth of about 1,320 metres (4,330 ft), with a 35-kilometre-wide (22 mi) summit platform. The Mid-Pacific Mountains lie west of Hawaii and northeast of the Marshall Islands, but at the time of its formation, the guyot was located in the Southern Hemisphere.

Horizon Guyot is a presumably Cretaceous guyot (tablemount) in the Mid-Pacific Mountains, Pacific Ocean. It is an elongated ridge, over 300 kilometres (190 mi) long and 4.3 kilometres (2.7 mi) high, that stretches in a northeast–southwest direction and has two flat tops; it rises to a minimum depth of 1,443 metres (4,730 ft). The Mid-Pacific Mountains lie west of Hawaii and northeast of the Line Islands.
Darwin Guyot is a volcanic underwater mountain top, or guyot, in the Mid-Pacific Mountains between the Marshall Islands and Hawaii. Named after Charles Darwin, it rose above sea level more than 118 million years ago during the early Cretaceous period to become an atoll, developed rudist reefs, and then drowned, perhaps as a consequence of sea level rise. The flat top of Darwin Guyot now rests 1,266 metres (4,154 ft) below sea level.
Cape Johnson Guyot is a guyot in the Pacific Ocean, more precisely in the Mid-Pacific Mountains, and the type locality of guyots. It is of middle Cretaceous age and a number of fossils have been dredged from it.

Calcareous nannofossils are a class of tiny microfossils that are similar to coccoliths deposited by the modern-day coccolithophores. The nannofossils are a convenient source of geochronological data due to the abundance and rapid evolution of the single-cell organisms forming them (nannoplankton) and ease of handling of the sediment samples. The practical applications of calcareous nannofossils in the areas of biostratigraphy and paleoecology became clear once the deepwater drilling took off in 1968 with the Deep Sea Drilling Project, and they have been extensively studied ever since. Nannofossils provide one of the most important paleontological records with the contiguous length of 220 million years.