Related Research Articles
Janaki may refer to:

Sita, also known as Siya, Janaki and Maithili, is a Hindu goddess and the female protagonist of the Hindu epic Ramayana. Sita is the consort of Rama, the avatar of god Vishnu, and is regarded as an avatar of goddess Lakshmi. She is the chief goddess of the Ramanandi Sampradaya and is the goddess of beauty and devotion. Sita's birthday is celebrated every year on the occasion of Sita Navami.
Janakpur Road is a town and a notified area in Sitamarhi district in the Indian state of Bihar.

Janaki Mandir is a Hindu temple in Janakpurdham, Nepal, dedicated to the Hindu goddess Sita. It is an example of Koiri Hindu architecture. Fully built in bright white and constructed in an area of 1,480 square metres, it is a three-storied structure made entirely of stone and marble.

The Gandarbha caste or Gaine are a tribal community which belongs to the Indo-Aryan ethnic group from the central, hilly region of Nepal. They have also been called a "caste of professional musicians" and "itinerant bards." By tradition they make their living by singing Gandarbha Geet or Gaine Geet, a type of folk song. The Gandarbhas traditionally work as travelling musicians and play traditional folk and historical songs. They improvise songs too, incorporating news into them as a service, in return for which they receive donations of food or other things. They use the Nepali sarangi, a type of violin, as their main musical instrument. The sarangi has been an iconic musical instrument identified with the Gandarbha people. The instrument has replaced another instrument they played, the aarbajo, which was larger and "more cumbersome." They speak their own language which is called Parse kura.

Janakpurdham or Janakpur, is the capital city of Madhesh Province. This sub-metropolitan city is a central hub for the Maithili language, as well as for religious and cultural tourism in Nepal.
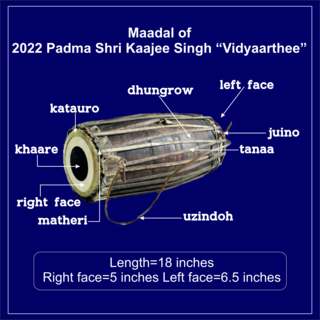
The madal or maadal is a Nepalese folk musical instrument. The madal is used mainly for rhythm-keeping in Nepalese folk music. It is very popular and widely used as a hand drum in Nepal. The madal has a cylindrical body with a slight bulge at its center and heads at both ends, one head larger than the other. It is usually played horizontally in a seated position, with both heads played simultaneously.

Duhabi is a Village Development Committee in Dhanusa District in the Janakpur Zone of south-eastern Nepal. At the time of the 1991 Nepal census it had a population of 5,762 persons residing in 990 individual households.
Sita Kund is a Hindu pilgrimage site that honours the birthplace of the goddess, Sita. The Punaura Dham Janki Mandir is a Hindu pilgrimage site in Sitamarhi district, Bihar, which has an ancient Hindu temple. It is situated 5 km west of Sitamarhi City and a popular visitor's attraction.

The arbajo is a Nepali four-string lute used as a rhythm instrument. It is the traditional instrument of the Gandarbha caste of musical performers, and is considered a companion to the Nepali sarangi. The Gandarbhas consider the aarbajo to be the "male instrument", the sarangi the "female." The aarbajo is used less than in the past, and been replaced by the sarangi, which was considered in 1999 to have superseded the aarbajo in common use.
Dharharwa is a village in Parihar Tehsil in Sitamarhi District in Bihar State, India. In Hindi: धरहरवा

Chhireshwarnath is a municipality in the Dhanusa District of Madhesh Province of Nepal. The municipality was established on 18 May 2014, as a result of the merger between Village Development Committees Ramdaiya, Kumhraul, Sakhuwa Mahendranagar, Hariharpur, Gopalpur, Baninya, and Digambarpur.
Janakpur is a sub-metropolitan in Dhanusa District of Nepal.

Shrikhandi Bhittha or Bhitthamore is an Indian village in the Mithila region of Bihar, situated near the Indo-Nepal border, on the banks of the perennial Ratnawati (Raato) river.

Kapileshwar Temple is a temple of Lord Shiva situated at Janakpur, Nepal. According to the legend, in Treta Yuga, King Janak had constructed Shiva temples at the four corners of his capital Janakpur. Kaplileshowar is one of the temples. It is believed that the temple was used by Kapil, a Hindu sage, as an Aashram as well, hence the name.
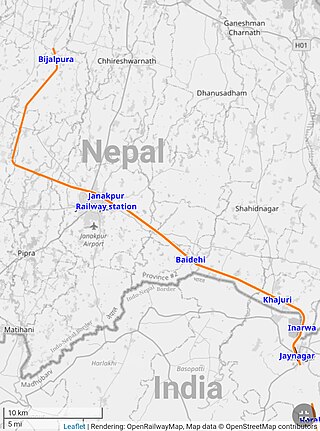
The Jaynagar–Janakpur–Bardibas railway line is a cross-border railway line between India and Nepal. The railway links Bijalpura with Jaynagar, crossing the India–Nepal border near Inarwa. An extension to Bardibas is being constructed. The line began as a 2 ft 6 in freight railway in 1937, and subsequently became a passenger railway. It closed in 2014 to allow it to be converted to 5 ft 6 in broad gauge, and reopened in 2022. At that time it was the only operational passenger railway line in Nepal.
Mithila Madhya Parikrama is an annual periodic journey of the central part of the ancient Mithila in Nepal and Bihar (India). It is held every year between the months of Kartik (October–November), Falgun (February–March) and Baishakh (April–May). But nowadays only Falgun (February–March) journey is famous. It is a circular journey of the central part of the Ancient Mithila. It covers a distance of 128 km circular path. It is mentioned in the epic Mithila Mahatmya which was composed in the 18th century.
Municipal election for Janakpur took place on 13 May 2022, with all 127 positions up for election across 25 wards. The electorate elected a mayor, a deputy mayor, 25 ward chairs and 100 ward members. An indirect election will also be held to elect five female members and an additional three female members from the Dalit and minority community to the municipal executive.

Janaki Sthan is a historical place related to the temple of Goddess Sita in the city of Sitamarhi. According to some scholars and Saints, Janaki Sthan is claimed to be the manifestation place of Goddess Sita in Ramayana. This is a temple dedicated to the Goddess Sita called Janaki Sthan Mandir. This temple is about 2 kilometers away from Sitamarhi Railway Station. The temple comes under Ramanuja tradition in Hinduism.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 Kadel, Ram Prasad (2007). Musical Instruments of Nepal. Katmandu, Nepal: Nepali Folk Instrument Museum. p. 239. ISBN 978-9994688302.
- ↑ "Nepali Musical Instruments - We All Nepali". Archived from the original on 2018-04-09. Retrieved 2021-11-05.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ↑ kandel, Ramprasad. बालबोध-हाम्रा लोक बाजाहरु (51 ed.). Sanothimi, Bhaktapur: Nepal government.