Eaton Corporation Inc is an Irish-domiciled multinational power management company with 2018 sales of $21.6 billion, founded in the United States with corporate headquarters in Dublin, Ireland, and operational headquarters in Beachwood, Ohio. Eaton has approximately 99,000 employees and sells products to customers in more than 175 countries.

An automatic transmission, also called auto, self-shifting transmission, n-speed automatic, or AT, is a type of motor vehicle transmission that automatically changes the gear ratio as the vehicle moves, meaning that the driver does not have to shift the gears manually. Like other transmission systems on vehicles, it allows an internal combustion engine, best suited to run at a relatively high rotational speed, to provide a range of speed and torque outputs necessary for vehicular travel. The number of forward gear ratios is often expressed for manual transmissions as well.

Fluid power is the use of fluids under pressure to generate, control, and transmit power. Fluid power is subdivided into hydraulics using a liquid such as mineral oil or water, and pneumatics using a gas such as air or other gases. Compressed-air and water-pressure systems were once used to transmit power from a central source to industrial users over extended geographic areas; fluid power systems today are usually within a single building or mobile machine.

A transmission is a machine in a power transmission system, which provides controlled application of the power. Often the term 5 speed transmission refers simply to the gearbox that uses gears and gear trains to provide speed and torque conversions from a rotating power source to another device.
A continuously variable transmission (CVT), also known as a shiftless transmission, stepless transmission, pulley transmission, or, in case of motorcycles, a "twist-and-go", is an automatic transmission that can change seamlessly through a continuous range of effective gear ratios. This contrasts with other mechanical transmissions that offer a fixed number of gear ratios. The flexibility of a CVT with suitable control may allow the input shaft to maintain a constant angular velocity even as the output speed varies.

Hydraulic machines use liquid fluid power to perform work. Heavy construction vehicles are a common example. In this type of machine, hydraulic fluid is pumped to various hydraulic motors and hydraulic cylinders throughout the machine and becomes pressurised according to the resistance present. The fluid is controlled directly or automatically by control valves and distributed through hoses, tubes, and/or pipes.
Ultramatic was the trademarked name of the Packard Motor Car Company's automatic transmission introduced in 1949 and produced until 1954, at Packard's Detroit, Michigan East Grand Boulevard factory. It was produced thereafter from late 1954, thru 1956 at the new Packard "Utica" Utica, Michigan facility.

Adjustable speed drive (ASD), also known as variable-speed drive (VSD), describes equipment used to control the speed of machinery. Many industrial processes such as assembly lines must operate at different speeds for different products. Where process conditions demand adjustment of flow from a pump or fan, varying the speed of the drive may save energy compared with other techniques for flow control.
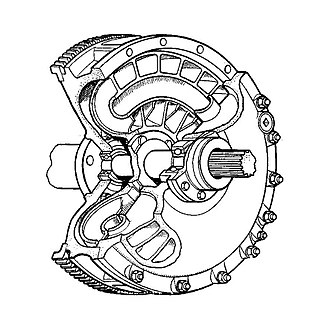
A fluid coupling or hydraulic coupling is a hydrodynamic or 'hydrokinetic' device used to transmit rotating mechanical power. It has been used in automobile transmissions as an alternative to a mechanical clutch. It also has widespread application in marine and industrial machine drives, where variable speed operation and controlled start-up without shock loading of the power transmission system is essential.

Tsubakimoto Chain Co. is a Japanese manufacturer of power transmission and roller chain products. It was founded in Osaka in 1917 as a bicycle chain manufacturer. Later it became the first roller chain manufacturer in Japan approved by Japanese Industrial Standards. Tsubakimoto Chain has the world's largest market share for steel chains for general industrial applications and enjoys the world's top market share for timing drive systems for automobiles. The company is headquartered in Osaka, with its main manufacturing base in Kyotanabe, Kyoto.
Artificial lift refers to the use of artificial means to increase the flow of liquids, such as crude oil or water, from a production well. Generally this is achieved by the use of a mechanical device inside the well or by decreasing the weight of the hydrostatic column by injecting gas into the liquid some distance down the well. A newer method called Continuous Belt Transportation (CBT) uses an oil absorbing belt to extract from marginal and idle wells. Artificial lift is needed in wells when there is insufficient pressure in the reservoir to lift the produced fluids to the surface, but often used in naturally flowing wells to increase the flow rate above what would flow naturally. The produced fluid can be oil, water or a mix of oil and water, typically mixed with some amount of gas.
A hydraulic drive system is a quasi-hydrostatic drive or transmission system that uses pressurized hydraulic fluid to power hydraulic machinery. The term hydrostatic refers to the transfer of energy from pressure differences, not from the kinetic energy of the flow.
Hydraulic transmission or Hydraulic drive systems are various transmission methods for transferring engine power to drive wheels, using hydraulic fluid. It may refer to:

A cross-drive steering transmission is a transmission which is used in tracked vehicles to allow precise and energy efficient steering.
Edwards Rail Car Company (1997–2008) was located in Montgomery, Alabama, specializing in the manufacture of self-propelled rail cars patterned after original Edwards designs dating from the mid-1920s. Edward's also restored and manufactured other types of rail cars, including streetcars.

Sundyne is the company’s common name and the brand name for its products and services.
Nexteer Automotive is an automotive parts supplier owned by Pacific Century Motors and headquartered in Auburn Hills, Michigan, United States. Nexteer, a global leader in intuitive motion control, is a multi-billion dollar global steering and driveline business delivering electric and hydraulic power steering systems, steering columns, driveline systems, as well as advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and automated driving enabling technologies for original equipment manufacturers (OEMs). The company has 28 manufacturing plants, three technical centers, one software center and 13 customer service centers strategically located in North and South America, Europe, Asia and Africa. The company serves more than 60 customers in every major region of the world including BMW, Fiat Chrysler, Ford, GM, PSA Groupe, Toyota and VW, as well as automakers in India and China.
Sullair is a major manufacturer of portable and stationary rotary screw air compressors designed for commercial and industrial use. Founded in 1965 in the town of Michigan City, Indiana U.S.A., Sullair has manufacturing facilities in Michigan City that distribute and service air compressor packages and systems worldwide. Sullair also has manufacturing facilities in Suzhou, Jiangsu and Shenzhen, Guangdong China that service the Asian and Australasian markets. Sullair also has offices in Dandenong South, Australia near Melbourne, and in Sunderland, United Kingdom that services markets in the EMEA and Russia.
LHD loaders are similar to conventional front end loaders but developed for the toughest of hard rock mining applications, with overall production economy, safety and reliability in mind. They are extremely rugged, highly maneuverable and exceptionally productive. More than 75% of world's underground metal mines use LHD for handling the muck of their excavations.

Linde Hydraulics is a manufacturer of heavy duty drive systems consisting of hydraulics, power transmissions, and electronics. The company’s product offerings include hydraulic pumps and motors, directional control valves, power transmissions as well as peripheral electronics and software. Its products are used in agricultural, construction, forestry, landscaping, marine, material handling, mining, municipal, and stationary segments, as well as mobile lifting platforms.










