Bitcoin (₿) is a cryptocurrency invented in 2008 by an unknown person or group of people using the name Satoshi Nakamoto and started in 2009 when its implementation was released as open-source software.

A cryptocurrency is a digital asset designed to work as a medium of exchange wherein individual coin ownership records are stored in a ledger existing in a form of computerized database using strong cryptography to secure transaction records, to control the creation of additional coins, and to verify the transfer of coin ownership. It typically does not exist in physical form and is typically not issued by a central authority. Cryptocurrencies typically use decentralized control as opposed to centralized digital currency and central banking systems. When a cryptocurrency is minted or created prior to issuance or issued by a single issuer, it is generally considered centralized. When implemented with decentralized control, each cryptocurrency works through distributed ledger technology, typically a blockchain, that serves as a public financial transaction database.

Ethereum is the second-largest cryptocurrency platform by market capitalization, behind Bitcoin. It is a decentralized open source blockchain featuring smart contract functionality. Ether (ETH) is the cryptocurrency generated by Ethereum miners as a reward for computations performed to secure and add blocks to the blockchain. Ethereum serves as the platform for over 1,900 different cryptocurrencies and tokens, including 47 of the top 100 cryptocurrencies by market capitalization.
A decentralized autonomous organization (DAO), sometimes labeled a decentralized autonomous corporation (DAC), is an organization represented by rules encoded as a computer program that is transparent, controlled by the organization members and not influenced by a central government. A DAO's financial transaction record and program rules are maintained on a blockchain. The precise legal status of this type of business organization is unclear.

Nxt is an open source cryptocurrency and payment network launched in 2013 by anonymous software developer BCNext. It uses proof-of-stake to reach consensus for transactions—as such there is a static money supply and, unlike bitcoin, no mining. Nxt was specifically conceived as a flexible platform around which to build applications and financial services.
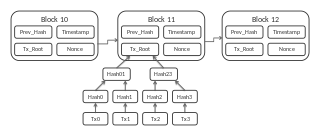
A blockchain, originally block chain, is a growing list of records, called blocks, that are linked using cryptography. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data.
A decentralized application is a computer application that runs on a distributed computing system. DApps have been popularized by distributed ledger technologies (DLT) such as the Ethereum Blockchain, where DApps are often referred to as smart contracts.

Ethereum Classic is an open source, blockchain-based distributed computing platform featuring smart contract (scripting) functionality. It supports a modified version of Nakamoto consensus via transaction-based state transitions executed on a public Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM).
Steemit is a blockchain-based blogging and social media website, which rewards its users with the cryptocurrency STEEM for publishing and curating content, and is owned by Steemit Inc., a privately held company based in New York City and a headquarters in Virginia.
Everipedia is a wiki-based online encyclopedia. Founded in December 2014, the site was launched in January 2015 as a fork of Wikipedia. It is owned by Everipedia, Inc., a for-profit company headquartered in Westwood, Los Angeles, California. As of October 2017, the majority of Everipedia pages are copies of Wikipedia articles.

STEEM is a cryptocurrency based on the social media and content-focused Steem blockchain, which was created on March 24, 2016 by Ned Scott and the blockchain developer Dan Larimer. In terms of total market capitalization, STEEM is currently ranked at place 40. with a market capitalization of more than 159 million USD..
EOS.IO is a blockchain protocol based on the cryptocurrency EOS. The smart contract platform claims to eliminate transaction fees and also conduct millions of transactions per second.
Hashgraph is a distributed ledger technology developed by Leemon Baird, the co-founder and CTO of Swirlds, in 2016. It is an asynchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerance (aBFT) consensus algorithm that they consider capable of securing the platform against attacks. It does not use miners to validate transactions, and uses directed acyclic graphs for time-sequencing transactions without bundling them into blocks.

DAV Foundation is a blockchain-based open source global transportation company.

Brendan Blumer is an American entrepreneur, executive, and investor. He is the CEO of Block.one, the tech company producing the EOS.IO distributed ledger software. He is based in Hong Kong.
TRON is a Blockchain-based decentralized operating system based on a cryptocurrency native to the system, known as TRX.
Crypto art is a category of art related to blockchain technology.
Bancor Protocol is a standard for decentralized exchange networks used to allow for the automated conversion of cryptocurrency tokens into other tokens, including across blockchains, without the need for an order book or counterparty to facilitate the exchange. Bancor invented the world’s first blockchain-based automated liquidity pool, or automated market maker (AMM) called a Smart Token, a digital currency with an embedded converter that allows it to be issued or exchanged automatically for any token in its network. Bancor Network consists of all the different tokens utilizing the Bancor Protocol and connected through BNT, the Bancor Network Token, which serves as the hub token for the network through which any token can be converted into any other token.







