
The papaya, papaw, or pawpaw is the plant species Carica papaya, one of the 21 accepted species in the genus Carica of the family Caricaceae. It was first domesticated in Mesoamerica, within modern-day southern Mexico and Central America. It is grown in several countries in regions with a tropical climate. In 2020, India produced 42% of the world's supply of papayas.

Pollination of fruit trees is required to produce seeds with surrounding fruit. It is the process of moving pollen from the anther to the stigma, either in the same flower or in another flower. Some tree species, including many fruit trees, do not produce fruit from self-pollination, so pollinizer trees are planted in orchards.

Cytochromes P450 are a superfamily of enzymes containing heme as a cofactor that mostly, but not exclusively, function as monooxygenases. In mammals, these proteins oxidize steroids, fatty acids, and xenobiotics, and are important for the clearance of various compounds, as well as for hormone synthesis and breakdown. In 1963, Estabrook, Cooper, and Rosenthal described the role of CYP as a catalyst in steroid hormone synthesis and drug metabolism. In plants, these proteins are important for the biosynthesis of defensive compounds, fatty acids, and hormones.

Phytoalexins are antimicrobial substances, some of which are antioxidative as well. They are defined, not by their having any particular chemical structure or character, but by the fact that they are defensively synthesized de novo by plants that produce the compounds rapidly at sites of pathogen infection. In general phytoalexins are broad spectrum inhibitors; they are chemically diverse, and different chemical classes of compounds are characteristic of particular plant taxa. Phytoalexins tend to fall into several chemical classes, including terpenoids, glycosteroids, and alkaloids; however the term applies to any phytochemicals that are induced by microbial infection.

The mountain papaya also known as mountain pawpaw, papayuelo, chamburo, or simply "papaya" is a species of the genus Vasconcellea, native to the Andes of northwestern South America from Colombia south to central Chile, typically growing at altitudes of 1,500–3,000 metres (4,900–9,800 ft).

Cauliflory is a botanical term referring to plants that flower and fruit from their main stems or woody trunks, rather than from new growth and shoots. It is rare in temperate regions but common in tropical forests.
The Shapiro reaction or tosylhydrazone decomposition is an organic reaction in which a ketone or aldehyde is converted to an alkene through an intermediate hydrazone in the presence of 2 equivalents of organolithium reagent. The reaction was discovered by Robert H. Shapiro in 1967. The Shapiro reaction was used in the Nicolaou Taxol total synthesis. This reaction is very similar to the Bamford–Stevens reaction, which also involves the basic decomposition of tosyl hydrazones.
The Julia olefination (also known as the Julia–Lythgoe olefination) is the chemical reaction used in organic chemistry of phenyl sulfones (1) with aldehydes (or ketones) to give alkenes (olefins)(3) after alcohol functionalization and reductive elimination using sodium amalgam or SmI2. The reaction is named after the French chemist Marc Julia.

Phytophthora palmivora is an oomycete that causes bud-rot of palms, fruit-rot or kole-roga of coconut and areca nut. These are among the most serious diseases caused by fungi and moulds in South India. It occurs almost every year in Malnad, Mysore, North & South Kanara, Malabar and other areas. Similar diseases of palms are also known to occur in Sri Lanka, Mauritius, and Sumatra. The causative organism was first identified as P. palmivora by Edwin John Butler in 1917.

Papaya ringspot virus (PRSV) is a pathogenic plant virus in the genus Potyvirus and the virus family Potyviridae which primarily infects the papaya tree.

The 3-Deoxyanthocyanidins and their glycosides are molecules with an anthocyanidins backbone lacking an hydroxyl group at position 3 on the C-ring. This nomenclature is the inverse of that which is commonly used in flavonoids, where the hydroxy-group is assumed absent if it is not specified, e. g. flavan-3-ol, flavan-4-ol, flavan-3,4-ol and flavonol.
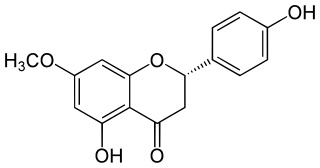
Sakuranetin is a flavan-on, the 7-methoxy derivative of naringenin, found in Polymnia fruticosa and rice, where it acts as a phytoalexin against spore germination of Pyricularia oryzae.

In biochemistry, naturally occurring phenols are natural products containing at least one phenol functional group. Phenolic compounds are produced by plants and microorganisms. Organisms sometimes synthesize phenolic compounds in response to ecological pressures such as pathogen and insect attack, UV radiation and wounding. As they are present in food consumed in human diets and in plants used in traditional medicine of several cultures, their role in human health and disease is a subject of research. Some phenols are germicidal and are used in formulating disinfectants.

Allixin is a phytoalexin found in garlic bulbs. It was first isolated and characterized in 1989. When garlic is stored for long periods of time, it can form visible accumulations of crystalline allixin on its surface, particularly in areas where tissue has become necrotic. After 2 years of storage, the amount of allixin accumulated can approach 1% of the dry weight of the cloves. Since allixin has weak antimicrobial activity, these high concentrations are thought to be produced by the garlic bulb to protect itself from further damage from microorganisms.
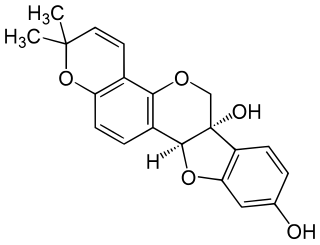
Glyceollin I is a glyceollin, a type of prenylated pterocarpan. It is a phytoalexin found in the soybean.
In molecular biology, the cerato-platanin family of proteins includes the phytotoxin cerato-platanin (CP) produced by the Ascomycete Ceratocystis platani. CP homologs are also found in both the Ascomycota and the Basidiomycota branches of Dikarya. This toxin causes the severe plant disease: canker stain. This protein occurs in the cell wall of the fungus and is involved in the host-pathogen interaction and induces both cell necrosis and phytoalexin synthesis which is one of the first plant defense-related events. CP, like other fungal surface proteins, is able to self-assemble in vitro. CP is a 120 amino acid protein, containing 40% hydrophobic residues. It is one of the rare examples of protein in which contains a Hopf link. The link is formed by covalent loops - the pieces of protein backbone closed by two disulphide bonds. The N-terminal region of CP is very similar to cerato-ulmin, a phytotoxic protein produced by the Ophiostoma species belonging to the hydrophobin family, which also self-assembles.

Pisatin (3-hydroxy-7-methoxy-4′,5′-methylenedioxy-chromanocoumarane) is the major phytoalexin made by the pea plant Pisum sativum. It was the first phytoalexin to be purified and chemically identified. The molecular formula is C17H14O6.
Papaya Bunchy Top Disease was first discovered in 1931 in Puerto Rico. Early on, the identity of the pathogen was highly contested due to the inability of isolating it; thus Koch’s postulates could not be fulfilled. Scientists have previously believed that Papaya Bunchy Top Disease was caused by a virus, a mycoplasma-like organism (MLO), or a phytoplasma, but these possible pathogens have since been disproven. Since the identity of the pathogen was unknown, all diagnoses were given solely based on a list of commonly associated symptoms. Through sequencing and microscopy, scientists identified the pathogen to be a part of the genus Rickettsia in 1996. The bacterium is described as being rod-shaped, small, gram-negative, and laticifer-inhibiting. Rickettsia causes diseases in animals, such as typhus and spotted fever, as well as in other plants, such as phony disease of peach and almond leaf scorch. Papaya Bunchy Top is found throughout the American tropics and has been economically important due to its major impact on fruit production. There is little information about the current economic impact.

Rishitin is a terpenoid compound, produced by some plants belonging to the Solanum family, including the potato and tomato. Rishitin belongs to a heterogeneous group of anti-microbial plant defense compounds termed phytoalexins and is produced upon pathogen attack. Same as the phytoalexin capsidiol, it belongs to the group of sesquiterpenes and is as such an FPP derivative. Rishitin was named after the potato cultivar Rishiri, where it was first discovered in 1968.
Elizabeth S. Sattely is an American scientist and biotechnology engineer. She is an Associate Professor of Chemical Engineering in the Department of Chemical Engineering, an HHMI investigator, and a ChEM-H Faculty Fellow at Stanford University.















