Carlo Rubbia is an Italian particle physicist and inventor who shared the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1984 with Simon van der Meer for work leading to the discovery of the W and Z particles at CERN.

The charm quark, charmed quark, or c quark is an elementary particle found in composite subatomic particles called hadrons such as the J/psi meson and the charmed baryons created in particle accelerator collisions. Several bosons, including the W and Z bosons and the Higgs boson, can decay into charm quarks. All charm quarks carry charm, a quantum number. This second generation is the third-most-massive quark with a mass of 1.27±0.02 GeV/c2 as measured in 2022 and a charge of +2/3e.
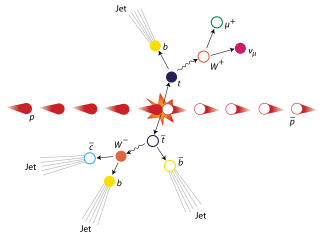
The top quark, sometimes also referred to as the truth quark, is the most massive of all observed elementary particles. It derives its mass from its coupling to the Higgs Boson. This coupling is very close to unity; in the Standard Model of particle physics, it is the largest (strongest) coupling at the scale of the weak interactions and above. The top quark was discovered in 1995 by the CDF and DØ experiments at Fermilab.

Gargamelle was a heavy liquid bubble chamber detector in operation at CERN between 1970 and 1979. It was designed to detect neutrinos and antineutrinos, which were produced with a beam from the Proton Synchrotron (PS) between 1970 and 1976, before the detector was moved to the Super Proton Synchrotron (SPS). In 1979 an irreparable crack was discovered in the bubble chamber, and the detector was decommissioned. It is currently part of the "Microcosm" exhibition at CERN, open to the public.
Vojteh Ravnikar was a Slovenian architect.
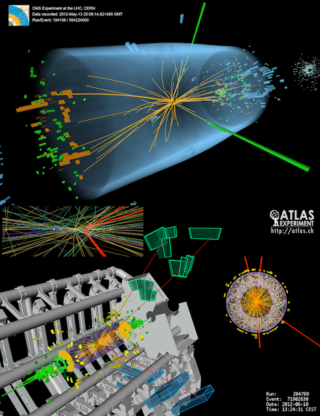
The Higgs boson, sometimes called the Higgs particle, is an elementary particle in the Standard Model of particle physics produced by the quantum excitation of the Higgs field, one of the fields in particle physics theory. In the Standard Model, the Higgs particle is a massive scalar boson with zero spin, even (positive) parity, no electric charge, and no colour charge that couples to mass. It is also very unstable, decaying into other particles almost immediately upon generation.

Ivan Aničin, was Yugoslav and Serbian nuclear physicist, particle physicist, astrophysicist, and cosmologist, university Full Professor and Distinguished (teaching/research) Professor of scientific institutes in Belgrade (Serbia), Bristol, Grenoble (France), and Munich (Germany).

Don Lincoln is an American physicist, author, host of the YouTube channel Fermilab, and science communicator. He conducts research in particle physics at Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory, and was an adjunct professor of physics at the University of Notre Dame, although he is no longer affiliated with the university. He received a Ph.D. in experimental particle physics from Rice University in 1994. In 1995, he was a co-discoverer of the top quark. He has co-authored hundreds of research papers, and more recently, was a member of the team that discovered the Higgs boson in 2012.

David George Charlton is Professor of Particle Physics in the School of Physics and Astronomy at the University of Birmingham, UK. From 2013 to 2017, he served as Spokesperson of the ATLAS experiment at the Large Hadron Collider at CERN. Prior to becoming Spokesperson, he was Deputy Spokesperson for four years, and before that Physics Coordinator of ATLAS in the run-up to the start of collision data-taking.

Sir Tejinder Singh Virdee,, is a Kenyan-born British experimental particle physicist and Professor of Physics at Imperial College London. He is best known for originating the concept of the Compact Muon Solenoid (CMS) with a few other colleagues and has been referred to as one of the 'founding fathers' of the project. CMS is a world-wide collaboration which started in 1991 and now has over 3500 participants from 45 countries.

Sau Lan Wu is a Chinese American particle physicist and the Enrico Fermi Distinguished Professor of Physics at the University of Wisconsin-Madison. She made important contributions towards the discovery of the J/psi particle, which provided experimental evidence for the existence of the charm quark, and the gluon, the vector boson of the strong force in the Standard Model of physics. Recently, her team located at the European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN), using data collected at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC), was part of the international effort in the discovery of a boson consistent with the Higgs boson.

Peter Jenni, is an experimental particle physicist working at CERN. He is best known as one of the "founding fathers" of the ATLAS experiment at the CERN Large Hadron Collider together with a few other colleagues. He acted as spokesperson of the ATLAS Collaboration until 2009. ATLAS is a world-wide collaboration which started in 1992 involving roughly 3,000 physicists at 183 institutions in 38 countries. Jenni was directly involved in the experimental work leading to the discoveries of the W and Z bosons in the 1980s and the Higgs boson in 2012. He is (co-)author of about 1000 publications in scientific journals.
Philip Michael Tuts is an American high-energy experimental particle physicist, and Professor and Chair of the Columbia University Physics Department. Tuts is a Fellow of the American Physical Society. He holds a seat on the executive committees of the United States LHC Users' Association and the American Physics Society Forum on Physics and Society, and is Divisional Councilor of the Division of Particles and Fields of APS. Tuts earned his Bachelor's in Physics from MIT in 1974, and his MA and PhD from the State University of New York at Stony Brook in 1976 and 1979, respectively. He joined the physics department at Columbia University in the City of New York in 1983 and was appointed Chair in 2014. Tuts is currently a member of the ATLAS experiment team at CERN and formerly served as US ATLAS Operations Program Manager.

James E. Brau is an American physicist at the University of Oregon (UO) who conducts research on elementary particles and fields. He founded the Oregon experimental high energy physics group in 1988 and served as director of the UO Center for High Energy Physics from 1997 to 2016. Prior to joining the Oregon faculty, he served in the Air Force and held positions at the Stanford Linear Accelerator Center and the University of Tennessee. He is a fellow of both the American Physical Society and also the American Association for the Advancement of Science. In 2006 he was appointed the Philip H. Knight Professor of Natural Science, an endowed professorship.
Mayda Velasco is a physicist and professor in the Department of Physics and Astronomy at Northwestern University. She works in experimental particle physics and is a leading member of the CMS Collaboration at the CERN LHC. She founded COFI and is its first director. She is a pioneer in the physics potential of photon colliders.

]
Laura Baudis (1969) is a Romanian-born Swiss particle astrophysicist. She is employed as a full professor by the University of Zurich, Switzerland. Her research focuses on dark matter and neutrino physics. She is a member of the science strategy team for XENON as well as the CERN Scientific Policy Committee (2016–18) and the PSI Research Committee for Particle Physics.
George H. Trilling was a Polish-born American particle physicist. He was co-discoverer of the J/ψ meson which evinced the existence of the charm quark. Trilling joined the Physics Department faculty at the University of California, Berkeley, in 1960, where he was Department Chair from 1968 through 1972. Trilling was on sabbatical leave to CERN in 1973–74, where he worked on the study of the properties of charm particles, their decay modes and excited states. He was also Director of the Physics Division at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory from 1984 until 1987. Trilling was a principal proponent of the Superconducting Super Collider project and spokesperson for the Solenoidal Detector Collaboration. After the SSC was cancelled in 1993, Trilling transitioned most of the SDC team to collaborate on the ATLAS experiment at the LHC, which led to the discovery of the Higgs boson in 2012. Trilling was elected Vice-President of the American Physical Society, beginning his term on 1 January 1999, and was President of the society in 2001.

Bradley Cox is an American physicist, academic and researcher. He is a Professor of Physics and the founder of the High Energy Physics Group at the University of Virginia.
Oliver Buchmueller is a scientist and professor of physics at the Faculty of Natural Science, Imperial College London. Buchmueller is presently serving as one of the lead scientists on the Compact Muon Solenoid experiment at CERN’s Large Hadron Collider, the principal investigator of the Atom Interferometer Observatory and Network and also one of the lead authors at Atomic Experiment for Dark Matter and Gravity Exploration in Space (AEDGE). Previously he has been associated with the ALEPH experiment at CERN’s LEP collider and the BaBar experiment at SLAC. Buchmueller was among the group of scientists responsible for the discovery of Higgs Boson particle at the LHC, CERN and later in the scientific exploration to find the traces of dark matter through the LHC.