In physical chemistry, the Arrhenius equation is a formula for the temperature dependence of reaction rates. The equation was proposed by Svante Arrhenius in 1889, based on the work of Dutch chemist Jacobus Henricus van 't Hoff who had noted in 1884 that the van 't Hoff equation for the temperature dependence of equilibrium constants suggests such a formula for the rates of both forward and reverse reactions. This equation has a vast and important application in determining the rate of chemical reactions and for calculation of energy of activation. Arrhenius provided a physical justification and interpretation for the formula. Currently, it is best seen as an empirical relationship. It can be used to model the temperature variation of diffusion coefficients, population of crystal vacancies, creep rates, and many other thermally induced processes and reactions. The Eyring equation, developed in 1935, also expresses the relationship between rate and energy.
Thermal conduction is the diffusion of thermal energy (heat) within one material or between materials in contact. The higher temperature object has molecules with more kinetic energy; collisions between molecules distributes this kinetic energy until an object has the same kinetic energy throughout. Thermal conductivity, frequently represented by k, is a property that relates the rate of heat loss per unit area of a material to its rate of change of temperature. Essentially, it is a value that accounts for any property of the material that could change the way it conducts heat. Heat spontaneously flows along a temperature gradient. For example, heat is conducted from the hotplate of an electric stove to the bottom of a saucepan in contact with it. In the absence of an opposing external driving energy source, within a body or between bodies, temperature differences decay over time, and thermal equilibrium is approached, temperature becoming more uniform.
Fitness is a quantitative representation of individual reproductive success. It is also equal to the average contribution to the gene pool of the next generation, made by the same individuals of the specified genotype or phenotype. Fitness can be defined either with respect to a genotype or to a phenotype in a given environment or time. The fitness of a genotype is manifested through its phenotype, which is also affected by the developmental environment. The fitness of a given phenotype can also be different in different selective environments.
In physical chemistry, Henry's law is a gas law that states that the amount of dissolved gas in a liquid is directly proportional at equilibrium to its partial pressure above the liquid. The proportionality factor is called Henry's law constant. It was formulated by the English chemist William Henry, who studied the topic in the early 19th century. In simple words, we can say that the partial pressure of a gas in vapour phase is directly proportional to the mole fraction of a gas in solution.
The Lotka–Volterra equations, also known as the Lotka–Volterra predator–prey model, are a pair of first-order nonlinear differential equations, frequently used to describe the dynamics of biological systems in which two species interact, one as a predator and the other as prey. The populations change through time according to the pair of equations:
In physics, chemistry and biology, a potential gradient is the local rate of change of the potential with respect to displacement, i.e. spatial derivative, or gradient. This quantity frequently occurs in equations of physical processes because it leads to some form of flux.

The classical rocket equation, or ideal rocket equation is a mathematical equation that describes the motion of vehicles that follow the basic principle of a rocket: a device that can apply acceleration to itself using thrust by expelling part of its mass with high velocity and can thereby move due to the conservation of momentum. It is credited to Konstantin Tsiolkovsky, who independently derived it and published it in 1903, although it had been independently derived and published by William Moore in 1810, and later published in a separate book in 1813. Robert Goddard also developed it independently in 1912, and Hermann Oberth derived it independently about 1920.
In the theory of evolution and natural selection, the Price equation describes how a trait or allele changes in frequency over time. The equation uses a covariance between a trait and fitness, to give a mathematical description of evolution and natural selection. It provides a way to understand the effects that gene transmission and natural selection have on the frequency of alleles within each new generation of a population. The Price equation was derived by George R. Price, working in London to re-derive W.D. Hamilton's work on kin selection. Examples of the Price equation have been constructed for various evolutionary cases. The Price equation also has applications in economics.
In physical systems, damping is the loss of energy of an oscillating system by dissipation. Damping is an influence within or upon an oscillatory system that has the effect of reducing or preventing its oscillation. Examples of damping include viscous damping in a fluid, surface friction, radiation, resistance in electronic oscillators, and absorption and scattering of light in optical oscillators. Damping not based on energy loss can be important in other oscillating systems such as those that occur in biological systems and bikes. Damping is not to be confused with friction, which is a type of dissipative force acting on a system. Friction can cause or be a factor of damping.
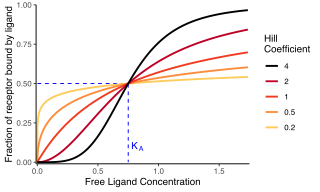
In biochemistry and pharmacology, the Hill equation refers to two closely related equations that reflect the binding of ligands to macromolecules, as a function of the ligand concentration. A ligand is "a substance that forms a complex with a biomolecule to serve a biological purpose", and a macromolecule is a very large molecule, such as a protein, with a complex structure of components. Protein-ligand binding typically changes the structure of the target protein, thereby changing its function in a cell.

Flory–Huggins solution theory is a lattice model of the thermodynamics of polymer solutions which takes account of the great dissimilarity in molecular sizes in adapting the usual expression for the entropy of mixing. The result is an equation for the Gibbs free energy change for mixing a polymer with a solvent. Although it makes simplifying assumptions, it generates useful results for interpreting experiments.
The Van 't Hoff equation relates the change in the equilibrium constant, Keq, of a chemical reaction to the change in temperature, T, given the standard enthalpy change, ΔrH⊖, for the process. The subscript means "reaction" and the superscript means "standard". It was proposed by Dutch chemist Jacobus Henricus van 't Hoff in 1884 in his book Études de Dynamique chimique.
The Kelvin equation describes the change in vapour pressure due to a curved liquid–vapor interface, such as the surface of a droplet. The vapor pressure at a convex curved surface is higher than that at a flat surface. The Kelvin equation is dependent upon thermodynamic principles and does not allude to special properties of materials. It is also used for determination of pore size distribution of a porous medium using adsorption porosimetry. The equation is named in honor of William Thomson, also known as Lord Kelvin.

In thermodynamics, entropy is a numerical quantity that shows that many physical processes can go in only one direction in time. For example, cream and coffee can be mixed together, but cannot be "unmixed"; a piece of wood can be burned, but cannot be "unburned". The word 'entropy' has entered popular usage to refer to a lack of order or predictability, or of a gradual decline into disorder. A more physical interpretation of thermodynamic entropy refers to spread of energy or matter, or to extent and diversity of microscopic motion.
In laser physics, gain or amplification is a process where the medium transfers part of its energy to the emitted electromagnetic radiation, resulting in an increase in optical power. This is the basic principle of all lasers. Quantitatively, gain is a measure of the ability of a laser medium to increase optical power. However, overall a laser consumes energy.
In electrochemistry, the Butler–Volmer equation, also known as Erdey-Grúz–Volmer equation, is one of the most fundamental relationships in electrochemical kinetics. It describes how the electrical current through an electrode depends on the voltage difference between the electrode and the bulk electrolyte for a simple, unimolecular redox reaction, considering that both a cathodic and an anodic reaction occur on the same electrode:

Diffusion is the net movement of anything generally from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion is driven by a gradient in Gibbs free energy or chemical potential. It is possible to diffuse "uphill" from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration, as in spinodal decomposition. Diffusion is a stochastic process due to the inherent randomness of the diffusing entity and can be used to model many real-life stochastic scenarios. Therefore, diffusion and the corresponding mathematical models are used in several fields beyond physics, such as statistics, probability theory, information theory, neural networks, finance, and marketing.
In astrophysics, the virial mass is the mass of a gravitationally bound astrophysical system, assuming the virial theorem applies. In the context of galaxy formation and dark matter halos, the virial mass is defined as the mass enclosed within the virial radius of a gravitationally bound system, a radius within which the system obeys the virial theorem. The virial radius is determined using a "top-hat" model. A spherical "top hat" density perturbation destined to become a galaxy begins to expand, but the expansion is halted and reversed due to the mass collapsing under gravity until the sphere reaches equilibrium – it is said to be virialized. Within this radius, the sphere obeys the virial theorem which says that the average kinetic energy is equal to minus one half times the average potential energy, , and this radius defines the virial radius.
Laser linewidth is the spectral linewidth of a laser beam.
Plant growth analysis refers to a set of concepts and equations by which changes in size of plants over time can be summarised and dissected in component variables. It is often applied in the analysis of growth of individual plants, but can also be used in a situation where crop growth is followed over time.










