Related Research Articles
The Internet protocol suite, commonly known as TCP/IP, is a framework for organizing the set of communication protocols used in the Internet and similar computer networks according to functional criteria. The foundational protocols in the suite are the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP), the User Datagram Protocol (UDP), and the Internet Protocol (IP). Early versions of this networking model were known as the Department of Defense (DoD) model because the research and development were funded by the United States Department of Defense through DARPA.
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is a routing technique in telecommunications networks that directs data from one node to the next based on labels rather than network addresses. Whereas network addresses identify endpoints, the labels identify established paths between endpoints. MPLS can encapsulate packets of various network protocols, hence the multiprotocol component of the name. MPLS supports a range of access technologies, including T1/E1, ATM, Frame Relay, and DSL.

A router is a computer and networking device that forwards data packets between computer networks, including internetworks such as the global Internet.
Routing is the process of selecting a path for traffic in a network or between or across multiple networks. Broadly, routing is performed in many types of networks, including circuit-switched networks, such as the public switched telephone network (PSTN), and computer networks, such as the Internet.
A network switch is networking hardware that connects devices on a computer network by using packet switching to receive and forward data to the destination device.

Network topology is the arrangement of the elements of a communication network. Network topology can be used to define or describe the arrangement of various types of telecommunication networks, including command and control radio networks, industrial fieldbusses and computer networks.

In computer networking, a routing table, or routing information base (RIB), is a data table stored in a router or a network host that lists the routes to particular network destinations, and in some cases, metrics (distances) associated with those routes. The routing table contains information about the topology of the network immediately around it.
In the seven-layer OSI model of computer networking, the network layer is layer 3. The network layer is responsible for packet forwarding including routing through intermediate routers.
In telecommunications, message switching involves messages routed in their entirety, one hop at a time. It evolved from circuit switching and was the precursor of packet switching.
A broadcast address is a network address used to transmit to all devices connected to a multiple-access communications network. A message sent to a broadcast address may be received by all network-attached hosts.

A wireless mesh network (WMN) is a communications network made up of radio nodes organized in a mesh topology. It can also be a form of wireless ad hoc network.
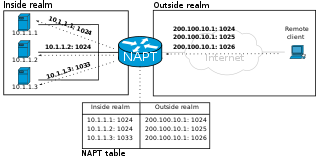
In computer networking, port forwarding or port mapping is an application of network address translation (NAT) that redirects a communication request from one address and port number combination to another while the packets are traversing a network gateway, such as a router or firewall. This technique is most commonly used to make services on a host residing on a protected or masqueraded (internal) network available to hosts on the opposite side of the gateway, by remapping the destination IP address and port number of the communication to an internal host.
Packet forwarding is the relaying of packets from one network segment to another by nodes in a computer network.
In computer networking, linear network coding is a program in which intermediate nodes transmit data from source nodes to sink nodes by means of linear combinations.

A computer network is a set of computers sharing resources located on or provided by network nodes. Computers use common communication protocols over digital interconnections to communicate with each other. These interconnections are made up of telecommunication network technologies based on physically wired, optical, and wireless radio-frequency methods that may be arranged in a variety of network topologies.
WAN optimization is a collection of techniques for improving data transfer across wide area networks (WANs). In 2008, the WAN optimization market was estimated to be $1 billion, and was to grow to $4.4 billion by 2014 according to Gartner, a technology research firm. In 2015 Gartner estimated the WAN optimization market to be a $1.1 billion market.
A wireless ad hoc network (WANET) or mobile ad hoc network (MANET) is a decentralized type of wireless network. The network is ad hoc because it does not rely on a pre-existing infrastructure, such as routers or wireless access points. Instead, each node participates in routing by forwarding data for other nodes. The determination of which nodes forward data is made dynamically on the basis of network connectivity and the routing algorithm in use.
Named Data Networking (NDN) is a proposed Future Internet architecture that seeks to address problems in contemporary internet architectures like IP. NDN has its roots in an earlier project, Content-Centric Networking (CCN), which Van Jacobson first publicly presented in 2006. The NDN project is investigating Jacobson's proposed evolution from today's host-centric network architecture IP to a data-centric network architecture (NDN). The stated goal of this project is that with a conceptually simple shift, far-reaching implications for how people design, develop, deploy, and use networks and applications could be realized.

In routing, the data plane, sometimes called the forwarding plane or user plane, defines the part of the router architecture that decides what to do with packets arriving on an inbound interface. Most commonly, it refers to a table in which the router looks up the destination address of the incoming packet and retrieves the information necessary to determine the path from the receiving element, through the internal forwarding fabric of the router, and to the proper outgoing interface(s).
Data center bridging (DCB) is a set of enhancements to the Ethernet local area network communication protocol for use in data center environments, in particular for use with clustering and storage area networks.
References
- ↑ Naugle, Matthew G. (1994). The illustrated network book: a graphic guide to understanding computer networks. VNR communications library. New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold. p. 285. ISBN 978-0-442-01826-9 – via Internet Archive (hourly borrow).
- ↑ Naugle, Matthew G. (1996). Local area networking. McGraw-Hill series on computer communications (2nd ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Companies. p. 291. ISBN 978-0-07-912256-8.
- ↑ Craft, Melissa (2003). Faster smarter Network+ certification: take charge of the Network+ exam-- faster, smarter, better!. Redmond, Wash: Microsoft Press. p. 88. ISBN 978-0-7356-1932-6 – via Internet Archive (hourly borrow).
Most of the content arises from: ![]() This article incorporates public domain material from Federal Standard 1037C. General Services Administration. Archived from the original on 2022-01-22.
This article incorporates public domain material from Federal Standard 1037C. General Services Administration. Archived from the original on 2022-01-22.