Greenland is located between the Arctic Ocean and the North Atlantic Ocean, northeast of Canada and northwest of Iceland. The territory comprises the island of Greenland—the largest island in the world—and more than a hundred other smaller islands. Greenland has a 1.2-kilometer-long (0.75 mi) border with Canada on Hans Island. A sparse population is confined to small settlements along certain sectors of the coast. Greenland possesses the world's second-largest ice sheet.

The Last Glacial Period (LGP), also known as the Last glacial cycle, occurred from the end of the Last Interglacial to the beginning of the Holocene, c. 115,000 – c. 11,700 years ago, and thus corresponds to most of the timespan of the Late Pleistocene.

The Greenland Ice Core Project (GRIP) was a research project organized through the European Science Foundation (ESF). The project ran from 1989 to 1995, with drilling seasons from 1990 to 1992. In 1988, the project was accepted as an ESF-associated program, and the fieldwork was started in Greenland in the summer of 1989.

Jakobshavn Glacier, also known as Ilulissat Glacier, is a large outlet glacier in West Greenland. It is located near the Greenlandic town of Ilulissat and ends at the sea in the Ilulissat Icefjord.

Glacier morphology, or the form a glacier takes, is influenced by temperature, precipitation, topography, and other factors. The goal of glacial morphology is to gain a better understanding of glaciated landscapes and the way they are shaped. Types of glaciers can range from massive ice sheets, such as the Greenland ice sheet, to small cirque glaciers found perched on mountain tops. Glaciers can be grouped into two main categories:

Helheim Glacier is a glacier in the Sermersooq municipality, Eastern Greenland.

Charcot Land is a peninsula of Eastern Greenland, part of the Scoresby Sound system. It lies in the Northeast Greenland National Park zone.

Petermann Glacier is a large glacier located in North-West Greenland to the east of Nares Strait. It connects the Greenland ice sheet to the Arctic Ocean at 81°10' north latitude, near Hans Island.

Zachariae Isstrom is a large glacier located in King Frederick VIII Land, northeast Greenland.

Nioghalvfjerdsbrae, sometimes referred to as "79 N Glacier", is a large glacier located in King Frederick VIII Land, northeastern Greenland. It drains an area of 103,314 km2 (39,890 sq mi) of the Greenland Ice Sheet with a flux of 14.3 km3 (3.4 cu mi) per year, as measured for 1996. The glacier has two calving fronts where the glacier meets the ocean, separated by Hovgaard Island. In July 2020, the northern offshoot, the Spalte Glacier broke away from Nioghalvfjerdsbrae and completely disintegrated.

Rink Glacier is a glacier in Avannaata, Greenland.

Lindhard Island is an uninhabited island of NE Greenland.

King Christian X Land is an area of northeastern Greenland.
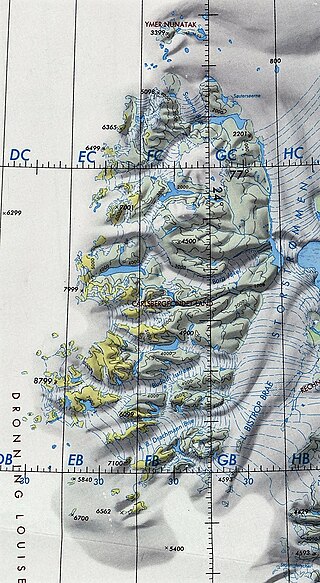
Storstrommen, is one of the major glaciers in northeastern Greenland. The North-East Greenland Ice Stream (NEGIS) discharges into 3 main marine-terminating outlets: 79N Glacier, Zachariae Isstrøm and Storstrommen - as arranged North to South.
Akuliarutsip Sermerssua, also known as Nordenskiöld Glacier,, is a large glacier located on the east coast of Greenland.

Daugaard-Jensen Land,, is a peninsula in northwestern Greenland. It is a part of the Avannaata municipality.

Petermann Fjord is a fjord in northwestern Greenland. Administratively it marks the boundary between the Avannaata municipality and the Northeast Greenland National Park.

Nordvestfjord, meaning 'Northwest Fjord', is a fjord in King Christian X Land, eastern Greenland.