Related Research Articles
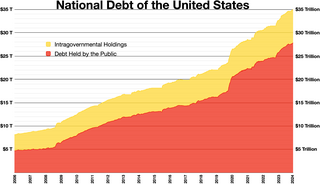
The national debt of the United States is the total national debt owed by the federal government of the United States to Treasury security holders. The national debt at any point in time is the face value of the then-outstanding Treasury securities that have been issued by the Treasury and other federal agencies. The terms "national deficit" and "national surplus" usually refer to the federal government budget balance from year to year, not the cumulative amount of debt. In a deficit year the national debt increases as the government needs to borrow funds to finance the deficit, while in a surplus year the debt decreases as more money is received than spent, enabling the government to reduce the debt by buying back some Treasury securities. In general, government debt increases as a result of government spending and decreases from tax or other receipts, both of which fluctuate during the course of a fiscal year. There are two components of gross national debt:
A balanced budget amendment is a constitutional rule requiring that a state cannot spend more than its income. It requires a balance between the projected receipts and expenditures of the government.
The Golden Rule is a guideline for the operation of fiscal policy. The Golden Rule states that over the economic cycle, the Government will borrow only to invest and not to fund current spending. In layman's terms this means that on average over the ups and downs of an economic cycle the government should only borrow to pay for investment that benefits future generations. Day-to-day spending that benefits today's taxpayers should be paid for with today's taxes, not with leveraged investment. Therefore, over the cycle the current budget must balance or be brought into surplus.

The United States budget comprises the spending and revenues of the U.S. federal government. The budget is the financial representation of the priorities of the government, reflecting historical debates and competing economic philosophies. The government primarily spends on healthcare, retirement, and defense programs. The non-partisan Congressional Budget Office provides extensive analysis of the budget and its economic effects. It has reported that large budget deficits over the next 30 years are projected to drive federal debt held by the public to unprecedented levels—from 98 percent of gross domestic product (GDP) in 2020 to 195 percent by 2050.

Olaf Scholz is a German politician who has been serving as the chancellor of Germany since 8 December 2021. A member of the Social Democratic Party (SPD), he previously served as Vice Chancellor in the fourth Merkel cabinet and as Federal Minister of Finance from 2018 to 2021. He was also First Mayor of Hamburg from 2011 to 2018, deputy leader of the SPD from 2009 to 2019, and Federal Minister of Labour and Social Affairs from 2007 to 2009.

Canadian public debt, or general government debt, is the liabilities of the government sector. Government gross debt consists of liabilities that are a financial claim that requires payment of interest and/or principal in future. They consist mainly of Treasury bonds, but also include public service employee pension liabilities. Changes in debt arise primarily from new borrowing, due to government expenditures exceeding revenues.

The history of Germany from 1990 to the present spans the period following the German reunification, when West Germany and East Germany were reunited after being divided during the Cold War. Germany after 1990 is referred to by historians as the Berlin Republic. This time period is also determined by the ongoing process of the "inner reunification" of the formerly divided country.

The Australian government debt is the amount owed by the Australian federal government. The Australian Office of Financial Management, which is part of the Treasury Portfolio, is the agency which manages the government debt and does all the borrowing on behalf of the Australian government. Australian government borrowings are subject to limits and regulation by the Loan Council, unless the borrowing is for defence purposes or is a 'temporary' borrowing. Government debt and borrowings have national macroeconomic implications, and are also used as one of the tools available to the national government in the macroeconomic management of the national economy, enabling the government to create or dampen liquidity in financial markets, with flow on effects on the wider economy.
In the United States, the debt ceiling or debt limit is a legislative limit on the amount of national debt that can be incurred by the U.S. Treasury, thus limiting how much money the federal government may pay by borrowing more money, on the debt it already borrowed. The debt ceiling is an aggregate figure that applies to gross debt, which includes debt in the hands of the public and intra-government accounts. About 0.5 percent of the debt is not covered by the ceiling. Because expenditures are authorized by separate legislation, the debt ceiling does not directly limit government deficits. In effect, it can only restrain the Treasury from paying for expenditures and other financial obligations after the limit has been reached, but which have already been approved and appropriated.
In 2011, ongoing political debate in the United States Congress about the appropriate level of government spending and its effect on the national debt and deficit reached a crisis centered on raising the debt ceiling, leading to the passage of the Budget Control Act of 2011.
A debt limit or debt ceiling is a legislative mechanism restricting the total amount that a country can borrow or how much debt it can be permitted to take on. Several countries have debt limitation restrictions.
The history of the United States debt ceiling deals with movements in the United States debt ceiling since it was created in 1917. Management of the United States public debt is an important part of the macroeconomics of the United States economy and finance system, and the debt ceiling is a limitation on the federal government's ability to manage the economy and finance system. The debt ceiling is also a limitation on the federal government's ability to finance government operations, and the failure of Congress to authorize an increase in the debt ceiling has resulted in crises, especially in recent years.

The Treaty on Stability, Coordination and Governance in the Economic and Monetary Union; also referred to as TSCG, or more plainly the Fiscal Stability Treaty is an intergovernmental treaty introduced as a new stricter version of the Stability and Growth Pact, signed on 2 March 2012 by all member states of the European Union (EU), except the Czech Republic and the United Kingdom. The treaty entered into force on 1 January 2013 for the 16 states which completed ratification prior to this date. As of 3 April 2019, it had been ratified and entered into force for all 25 signatories plus Croatia, which acceded to the EU in July 2013, and the Czech Republic.

Robert Habeck is a German Green politician and writer who has been serving as Vice Chancellor of Germany, Federal Minister for Economic Affairs and Climate Action in the cabinet of Chancellor Olaf Scholz and as a Member of the German Bundestag for Flensburg – Schleswig since 2021. From 2018 to 2022, he also served as co-leader of Alliance 90/The Greens, alongside Annalena Baerbock. For the 2021 German federal election, he was a member of the leading duo, alongside Baerbock, who ran for chancellor of Germany.

Eckhardt Rehberg is a German politician of the Christian Democratic Union (CDU) who served as a member of the Bundestag from the state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern from 2005 until 2021.

The economic policy of the Joe Biden administration, dubbed Bidenomics, is characterized by relief measures and vaccination efforts to address the COVID-19 pandemic, investments in infrastructure, and strengthening the social safety net, funded by tax increases on higher-income individuals and corporations. Other goals include increasing the national minimum wage and expanding worker training, narrowing income inequality, expanding access to affordable healthcare, and forgiveness of student loan debt. The March 2021 enactment of the American Rescue Plan to provide relief from the economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic was the first major element of the policy. Biden's Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act was signed into law in November 2021 and contains about $550 billion in additional investment. His Inflation Reduction Act was enacted in August 2022.

The Scholz cabinet is the current cabinet of Germany, led by Federal Chancellor Olaf Scholz. The cabinet is composed of Scholz's Social Democratic Party, Alliance 90/The Greens and the Free Democratic Party, an arrangement known as a "traffic light coalition" in Germany after the parties' traditional colours, respectively red, green and yellow, matching the colours of a traffic light (Ampel). This traffic light coalition-government is the first of its kind at the federal level in the history of the German federal republic.
The Government of Quebec adopted the Balanced Budget Act (BBA) in 1996. The BBA prohibits a budget deficit, other than in special circumstances.
The inflation in Chile has been a significant issue in the economy of Chile in the 20th century. In the 2020s it surfaced as an economic problem again during the second presidency of Sebastián Piñera and continues beyond it. This inflation has been attributed to a series of private pension fund withdrawals allowed by the Congress of Chile in response to the economic hardships of the COVID-19 pandemic in Chile. Besides this, food prices are held by the Food and Agriculture Organization to have increased as consequence of the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine.
In German budget law, an off-budget fund is an independent additional budget that is intended exclusively to fulfill individual, limited tasks of the federal government in an emergency situation, is not part of the regular budget and thus is not subject to the debt brake. Management and financial responsibility for the off-budget entities is provided by the federal government, the funds are set up and managed in accordance with the provisions of the Federal Budget Code (BHO). In the 2020s the use of off-budget funds dramatically expanded, with the total (multi-year) potential deficits by the end of fiscal 2022 coming to 400 billion euro, about 10% of 2023 GDP. For comparison, the debt brake limit would only allow borrowing of 13 billion euro in 2023.
References
- ↑ The Economist: Germany’s debt brake – Tie your hands, please
- 1 2 Rinke, Andreas; Marsh, Sarah (2023-11-26). "Germany's budget crisis spurs calls to change its borrowing limits". Reuters . Retrieved 2023-11-26.
- ↑ "Germany's debt brake: surveillance by the Stability Council" (PDF). Bundesbank. April 2019. Retrieved 2022-06-18.
- ↑ "Schuldenbremse erhält Verfassungsrang". Frankfurter Allgemeine Zeitung (in German). 2009-06-12.
- 1 2 "The end of the German debt brake?" . Economist Intelligence Unit. 2021-03-01.
- ↑ "Olaf Scholz plots a way round Germany's debt rules" . Financial Times. 2021-12-06.
- 1 2 "Germany's cabinet agrees to lift debt brake again for 2023". Deutsche Welle . 2023-11-27. Retrieved 2023-11-27.
- ↑ "Germany's Greens clash with finance minister over return to debt brake". Reuters. 2021-05-12.
- ↑ "Germany approves €100bn fund to modernise its armed forces". Financial Times. 2022-06-03.
- ↑ Martinez, Maria; Kraemer, Christian (2023-11-15). "German court deals 60 billion euro budget blow to Scholz government". Reuters . Retrieved 2023-11-28.