
The Strait of Georgia or the Georgia Strait is an arm of the Pacific Ocean between Vancouver Island and the extreme southwestern mainland coast of British Columbia, Canada and the extreme northwestern mainland coast of Washington, United States. It is approximately 240 kilometres (150 mi) long and varies in width from 20 to 58 kilometres. Along with the Strait of Juan de Fuca and Puget Sound, it is a constituent part of the Salish Sea. Archipelagos and narrow channels mark each end of the Strait of Georgia, the Gulf Islands and San Juan Islands in the south, and the Discovery Islands in the north. The main channels to the south are Boundary Pass, Haro Strait and Rosario Strait, which connect the Strait of Georgia to the Strait of Juan de Fuca. In the north, Discovery Passage is the main channel connecting the Strait of Georgia to Johnstone Strait. The strait is a major navigation channel on the west coast of North America, owing to the presence of the port of Vancouver, and also due to its role as the southern entrance to the infracoastal route known as the Inside Passage.

HVDC Vancouver Island is a high-voltage direct current interconnection between the Vancouver Island Terminal (VIT) in North Cowichan, British Columbia on Vancouver Island at 48°49′39″N 123°42′55″W and the Arnott Substation (ARN) in Delta, British Columbia at 49°5′31″N 123°2′31″W on the Canadian mainland. It went into operation in 1968 and was extended in 1977. HVDC Vancouver Island consists of three overhead line sections with a total length of 42 kilometres and two submarine cable sections with a length of 33 kilometres.
The North Shore is a term commonly used to refer to several areas adjacent to Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada:

The Lynn Canyon Suspension Bridge is a pedestrian bridge located within Lynn Canyon Park, in the District of North Vancouver, British Columbia. It is 50 metres (160 ft) high from the bottom of the canyon. The bridge was built as a private venture in 1912.

Lulu Island is the name of the largest island in the estuary of the Fraser River, located south of Vancouver, British Columbia. The island is made up of the city of City of Richmond, while a small section at the eastern tip, known as Queensborough, is part of the City of New Westminster.

Deas Island is an island in the south arm of the Fraser River between Delta, British Columbia and Richmond, British Columbia, Canada. The island is home to a regional park approximately 300 acres (120 ha) in size. It is home to three historic buildings; Burrvilla, a stately Victorian home, Inverholme, a one-room schoolhouse, and the Delta Agricultural Hall.
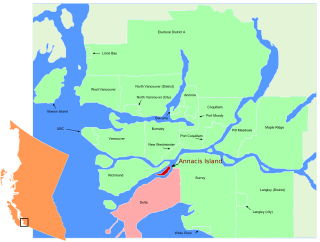
Annacis Island is an island located in the south arm of the Fraser River, in Delta, British Columbia. The island is now mostly industrial, and it contains one of Metro Vancouver's secondary wastewater treatment plants.

Mitchell Island is an island in the North Arm of the Fraser River in British Columbia, Canada, located between the cities of Vancouver and Richmond and is incorporated as part of the latter city. It is crossed by, and has on and off ramps for, the Knight Street Bridge, which is one of the main bridges between the City of Vancouver and Richmond.

Westham Island is an island located near Ladner, British Columbia, Canada within the municipality of Delta, which in turn is part of Greater Vancouver. The George C. Reifel Refuge for migratory birds is located at the northern end of the island. The Alaksen National Wildlife Area is also located on the island. The island is accessible via the Westham Island Bridge

Capilano River Regional Park is located in the District of North Vancouver in British Columbia, Canada. It is one of twenty-one regional parks operated by the Metro Vancouver. The park encompasses most of the upstream areas of the Capilano River below the Cleveland Dam. The area north of the dam surrounding Capilano Lake is closed to the public as it is a GVRD watershed. The privately operated Capilano Suspension Bridge crosses the river, but it is not within park boundaries and does not access the park.
The Marpole Bridge is a swing span railway bridge that crosses the north arm of the Fraser River and connects Vancouver with Richmond, British Columbia.

The Middle Arm Bridge is one of three transit-only bridges in Metro Vancouver. It spans the middle arm of the Fraser River, linking Lulu Island with the Vancouver International Airport on Sea Island. It is used by the airport branch of the Canada Line, which opened in August 2009.
The Squamish Nation, Sḵwx̱wú7mesh Úxwumixw in Sḵwx̱wú7mesh Sníchim, is an Indian Act government originally imposed on the Squamish (Sḵwx̱wú7mesh) by the Federal Government of Canada in the late 19th century. The Squamish are Indigenous to British Columbia, Canada. Their band government comprises 16 elected councillors, serving four-year terms, with an elected band manager. Their main reserves are near the town of Squamish, British Columbia and around the mouths of the Capilano River, Mosquito Creek, and Seymour River on the north shore of Burrard Inlet in North Vancouver, British Columbia.
The Lonsdale Tunnel is a freight railway tunnel in North Vancouver, British Columbia, running under Lonsdale Avenue, and running parallel to Esplanade Ave between St. Georges and Chesterfield Ave.
Little Deer Isle is an island in Penobscot Bay, lying just north of the town of Deer Isle, of which it is a part. The island is served by Maine State Route 15 via the Deer Isle Bridge. The north end of the island is called Eggemoggin and there is a small island with a lighthouse on it at the tip called Pumpkin Island. Little Deer is about 4 miles long and connects to Deer Isle by way of a causeway. There are only about 300 year-round residents of Little Deer, but many more summer residents.
Mudge Island is one of the Southern Gulf Islands in the Strait of Georgia, in British Columbia (BC), Canada. It lies between Gabriola Island and Vancouver Island, and is considered part of the De Courcy group of islands. It is about 0.8 km (0.50 mi) wide and 4 km (2.5 mi) long.

Anvil Island, is the third-largest of the islands in Howe Sound, British Columbia, Canada, and the northernmost of the major islands in that sound. It is located northeast of Gambier Island and southwest of Britannia Beach and west of Porteau Cove. The Defence Islands are to its northeast and are Indian Reserves of the Squamish Nation. A summer camp, Daybreak Point Bible Camp, operates on the south of the island, and some summer homes are located there.
The Thornton Tunnel is a freight railway tunnel in Burnaby, British Columbia, running under the Willingdon Heights and Vancouver Heights neighbourhoods. It was built in 1969 by Canadian National to connect Second Narrows Bridge to the main line in Willingdon, and is 3.4 km long.

Deer Island is a small island with only 1-2 residences, located in the Merrimack River in Amesbury, Massachusetts. The island connects to mainland Amesbury by way of the Derek S. Hines Memorial Bridge, and to neighboring Newburyport via Chain Bridge.














