
The British Columbia Electric Railway (BCER) was an historic railway which operated in southwestern British Columbia, Canada. Originally the parent company for, and later a division of, BC Electric Company, the BCER assumed control of existing streetcar and interurban lines in southwestern British Columbia in 1897, and operated the electric railway systems in the region until the last interurban service was discontinued in 1958. During and after the streetcar era, BC Electric also ran bus and trolleybus systems in Greater Vancouver and bus service in Greater Victoria; these systems subsequently became part of BC Transit, and the routes in Greater Vancouver eventually came under the control of TransLink. Trolley buses still run in the City of Vancouver with one line extending into Burnaby.
Highway 1 is a provincial highway in British Columbia, Canada, that carries the main route of the Trans-Canada Highway (TCH). The highway is 1,047 kilometres (651 mi) long and connects Vancouver Island, the Greater Vancouver region in the Lower Mainland, and the Interior. It is the westernmost portion of the main TCH to be numbered "Highway 1", which continues through Western Canada and extends to the Manitoba–Ontario boundary. The section of Highway 1 in the Lower Mainland is the second-busiest freeway in Canada, after Ontario Highway 401 in Toronto.

The Ironworkers Memorial Second Narrows Crossing, also called the Ironworkers Memorial Bridge and Second Narrows Bridge, is the second bridge constructed at the Second (east) Narrows of Burrard Inlet in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada. Originally named the Second Narrows Bridge, it connects Vancouver to the North Shore of Burrard Inlet, which includes the District of North Vancouver, the City of North Vancouver, and West Vancouver. It was constructed adjacent to the older Second Narrows Bridge, which is now exclusively a rail bridge. Its construction, from 1956 to 1960, was marred by a multi-death collapse on June 17, 1958. The First Narrows Bridge, better known as Lions Gate Bridge, crosses Burrard Inlet about 8 kilometres (5.0 mi) west of the Second Narrows.
Highway 99 is a provincial highway in British Columbia that runs 377 kilometres (234 mi) from the U.S. border to near Cache Creek, serving Greater Vancouver and the Squamish–Lillooet corridor. It is a major north–south artery within Vancouver and connects the city to several suburbs as well as the U.S. border, where it continues south as Interstate 5. The central section of the route, also known as the Sea to Sky Highway, serves the communities of Squamish, Whistler, and Pemberton. Highway 99 continues through Lillooet and ends at a junction with Highway 97 near Cache Creek.
Highway 7, known for most of its length as the Lougheed Highway and Broadway, is an alternative route to Highway 1 through the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia. Whereas the controlled-access Highway 1 follows the southern bank of the Fraser River, Highway 7 follows the northern bank.
Highway 99A is a series of former highways in the southwestern part of British Columbia, Canada. It was the designation of the former 1942 alignment of Highway 99 as well a various alternate routes which existed in the 1950s and 1960s. The last official use of '99A' was decommissioned in 2006, although some present-day, commercially published road maps still show it and some remnant signage still remains. Some brand new 99A signs can be seen as well as of 2023.
Highway 91 is an alternative freeway route to Highway 99 through Delta, New Westminster and Richmond, British Columbia. The highway was built in two sections, the first section from Delta to East Richmond in 1986, and the second section across Richmond in 1989.
Highway 91A, or the Queensborough Connector, is a 3 km (2 mi) long spur off Highway 91. Highway 91A crosses the Queensborough Bridge and terminates at Marine Way, allowing traffic into New Westminster. Residents of New Westminster can use Highway 91A as a convenient route towards the Canada/U.S. border. Although the Queensborough Bridge has existed since 1960, the highway spur section was opened only in 1986, at the same time the first section of Highway 91 was completed.
There are many roads in the southwestern part of British Columbia and Vancouver Island that were designated as Highway 1A. These roads were sections of the original 1941 route of Highway 1 before its various re-alignments, and are used today as service routes and frontage roads. The "B.C. Highway 1A" designations were removed from these sections by the province between 2005 and 2010, although signage remains along some of the route and the designation on some maps.

Highway 7B, known as the Mary Hill Bypass, is a 7.27 km (4.52 mi) long riverside east-west link between the cities of Coquitlam to the west and Port Coquitlam to the east. The Mary Hill Bypass gained its numbered designation in 1996, when it was widened from two to four lanes north of Broadway. Highway 7B meets Highway 7 at both of its ends, and also links to Highway 1 within Coquitlam at the Cape Horn Interchange.
Highway 5 is a 543 km (337 mi) north–south route in southern British Columbia, Canada. Highway 5 connects the southern Trans-Canada route with the northern Trans-Canada/Yellowhead route, providing the shortest land connection between Vancouver and Edmonton. Despite the entire route being signed as part of the Yellowhead Highway, the portion of Highway 5 south of Kamloops is also known as the Coquihalla Highway while the northern portion is known as the Southern Yellowhead Highway. The Coquihalla section was a toll road until 2008.
Highway 3B is an alternate loop to the Crowsnest Highway between Nancy Greene Lake and an area called Meadows, just west of Erie on the Crowsnest. Originally, Highway 3B went between Nancy Greene Lake to Trail, where the Crowsnest picked up the route to the Meadows area. One of its original component sections, the Rossland and Nancy Greene Lake was opened on the 1st of October 1965 at a cost of $3.5 million

The Alex Fraser Bridge is a cable-stayed bridge over the Fraser River that connects Richmond and New Westminster with North Delta in Greater Vancouver, British Columbia. The bridge is named for Alex Fraser, a former British Columbia Minister of Transportation. The bridge was the longest cable-stayed bridge in the world when it opened on September 22, 1986, and was the longest in North America until the Arthur Ravenel Jr. Bridge, in the U.S. state of South Carolina opened in 2005.

The George Massey Tunnel is a highway traffic tunnel in the Metro Vancouver region of southwestern British Columbia. It is located approximately 20 km (12.4 mi) south of the city centre of Vancouver, British Columbia, and approximately 30 km (18.6 mi) north of the Canada–United States border at Blaine, Washington.

The Oak Street Bridge is a crossing over the north arm of the Fraser River, the Canada Line, and several roads, in Metro Vancouver.

The Port Mann Bridge is a 10-lane cable-stayed bridge, 100 km/h speed limit, in British Columbia, Canada, that opened to traffic in 2012. It carries 10 lanes of traffic with space reserved for a light rail line.

The Pitt River Bridge is a cable-stayed bridge that spans the Pitt River between Port Coquitlam and Pitt Meadows in British Columbia, Canada. The bridge is part of Highway 7, carrying Lougheed Highway across the river. The current bridge opened on October 4, 2009. The bridge includes a 380 m cable stay bridge structure, 126 m of multi-span approaches, a 50 m interchange structure and approximately 2 km of grade construction. Total project cost for the bridge was $200 million

The Pattullo Bridge is a through arch bridge that crosses the Fraser River and links the city of New Westminster to the city of Surrey in British Columbia. It was named in honour of Thomas Dufferin Pattullo, the 22nd Premier of British Columbia. A key link between Surrey and the rest of Greater Vancouver, the Pattullo Bridge handles an average of 75,700 cars and 3840 trucks daily, or roughly 20% of vehicle traffic across the Fraser River as of 2013.
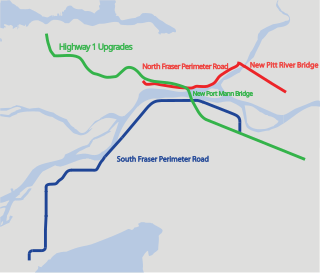
The Gateway Program is a C$3.0 billion regional transportation project for Metro Vancouver and surrounding areas that is being managed by the British Columbia Ministry of Transportation. The ministry introduced the Gateway Program on January 31, 2006, as a means to address growing congestion and reduce travel times. The bulk of the construction took place from 2006 to 2014 and saw the completion of the Golden Ears Bridge, the Pitt River Bridge, the Port Mann Bridge, improvements on the Sea-to-Sky highway, and finally the construction of the South Fraser Perimeter Road. The Greater Gateway Program is expected to finish by 2030.












